Livestock Digestive Systems
advertisement

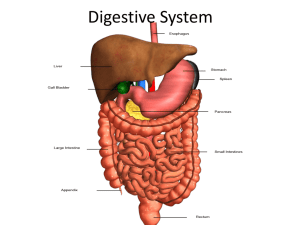
Identify herbivores, carnivores and omnivores Discuss the pathway which food travels through the digestive system. Construct a monogastric tract. Different species of animals have different digestive systems due to the food they eat These differences allow the animal to gain the most energy from its digested food The 3 types discussed today are: Omnivores Carnivores Herbivores Depend on plant material to survive, such as grass and leaves Some examples of herbivores are: Rabbits Cattle Deer Sheep Goats Horses Have a long and complex digestive system to break down plant matter. Depends on other animals as a food source Digestive tract is short and simple due to only consuming meat Some carnivores are: Cats Eagles Mountain Lion Snakes Spiders Depend on both plant matter and other animals for food sources Some examples of omnivores are: Chickens Pigs Dogs Bears Humans The path that most food travels (monogastric animals): Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small Intestine Large Intestine Rectum When eating the mouth works with your teeth and tongue to crush food while pushing it down the throat While in the mouth the salivary glands excrete salivary amylase to chemically break down starch The food travels down the esophagus to the stomach Once in the stomach the food will start to churn while adding hydrochloric acid and pepsin When fully mixed and the food has now become a chyme mixture then it leaves the stomach and heads to the small intestine When entering the small intestine the pancreas excretes digestive enzymes and stomach acid-neutralizing bicarbonate The liver also aids the small intestine in digestion by producing bile that is stored in the gall bladder Villi are little finger like folds that help absorb the nutrients The small intestine will due the most digestion in 3 different areas: Duodenum (upper) Jejunum (middle) Ileum (lower) After leaving the small intestine the remaining food enters the large intestine The large intestine is made of the colon, cecum, and rectum The colon is broken down into four sections Ascending Transverse Descending Sigmoid The cecum is connected by the entrance from the small intestine to the ascending colon The cecum helps with the fermentation of the food The ascending and transverse colon remove the remaining water The descending and sigmoid colon store food until it is removed This video explains how a horse digest food Take notes on what is shown http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8lqk7igz9 L4&feature=related (7:13) Using the craft supplies that I have provided, you will create a monogastric digestive tract. (you choose) You also need to write a description of the pathway and what is happening at each step. Label each section when complete: Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine http://ibdcrohns.about.com/od/ucbasics/g/di gestivesystem.htm http://www.qrg.northwestern.edu/projects/m arssim/simhtml/info/whats-a-herbivore.html http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8lqk7igz9 L4&feature=related http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabe e/biobk/biobookdigest.html Pictures: IMSonline.tamu.edu