ERYTHROCYTES [RBCs]
advertisement
![ERYTHROCYTES [RBCs]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/010022214_1-beb1d7e17b6a0f039ee3618cfafe0436-768x994.png)
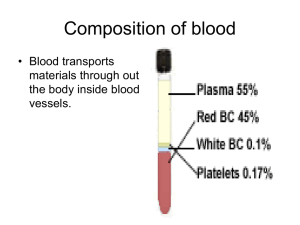
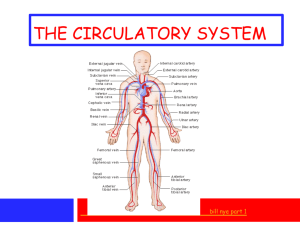
1 ERYTHROCYTES [RBCs] Lecture – 2 Dr. Zahoor Ali Shaikh 2 ERYTHROCYTES • Normal RBC count - 5 million per cubic millimeter (mm3) of blood. • RBC contain hemoglobin which carries O2. • Main function of RBC – O2 transport, also CO2 transport. 3 STRUCTURE OF RBC • RBC are biconcave discs 7.5 - 8 micrometer (µm) in diameter and 2µm thick at outer edge and 1µm thick at the center. • RBC membrane is flexible and can change as RBC pass through capillary with a narrow diameter of 5µm. 4 HEMOGLOBIN • Hemoglobin is found only in RBC. • Normal Hemoglobin – 15 gram / dl . Structure of Hemoglobin • It has two parts 1. Globin – protein has 4 polypeptide chain 2 α chain [141 amino acid in each chain] 2 β chain [146 amino acid in each chain] 2. Heme – 4 iron containing groups, each is bound to one polypeptide chain. 5 6 HEMOGLOBIN[cont] • Each iron atom present in Heme [iron is in ferrous state] can combine reversibly with one molecule of O2, therefore, each hemoglobin molecule can take four O2 molecules in the lungs. • 98.5% of O2 is carried in the blood bound to hemoglobin. • Hemoglobin is a pigment naturally colored because of iron content. 7 HEMOGLOBIN[cont] • It appears reddish when combine with O2, e.g. Arterial blood. • It appears bluish when deoxygenated, e.g. venous blood. HEMOGLOBIN FUNTIONS • Transports O2. • Also transports CO2. 8 HEMOGLOBIN FUNTIONS (cont) • Combines with H+ ion, therefore, plays part as buffer. • Combines with carbon monoxide (CO), therefore, can cause CO poisoning. • Nitric Oxide (NO) gas combines with hemoglobin and this NO is released at the tissues and causes vasodilation. 9 IMPORTANT NOTE • RBC is mainly a plasma membrane having hemoglobin. • RBC has no nucleus and organelle. • Enzyme in RBC - Glycolytic enzyme, it generates energy ATP for active transport at membrane. - Carbon anhydrase enzyme for CO2 transport. 10 ERYTHROPOIESIS [RBC FORMATION] • In adult RBC are formed in bone marrow. [Bone marrow is cellular tissue that fills the internal cavities of bones]. • Bone marrow normally generates new RBC to replace old ruptured cells. • In the fetus – RBC formation takes place in yolk sac during first 03 months of life then liver and spleen up to 7th month of intrauterine life. • Bone marrow starts from 4th month till birth of baby. 11 ERYTHROPOIESIS [RBC FORMATION] • In children, most bones produce RBC by red bone marrow then red bone marrow is replaced by fatty yellow bone marrow that does not produce RBC. • In adults, red bone marrow remains in sternum, ribs, vertebrae, pelvis, upper end of long bones e.g. femur, humerus. 12 13 IMPORTANT • If we need bone marrow sample for examination, we usually take from iliac crest or sternum. 14 MAJOR STEPS IN ERYTHROPOIESIS 15 ERYTHROPOIESIS • As RBC matures, it involves - reduction in size - disappearance of nucleus - acquiring of hemoglobin 16 NUTRIONAL REQUIREMENT OF RBC PRODUCTION • 1. Amino Acids – for synthesis of globin of hemoglobin. • 2. Iron – If iron deficiency, it causes microcytic hypochromic anemia [small RBC with less Hb]. • 3. Vitamins – Vitamin B12 and folic acid for synthesis of nucleo protein. If less DNA metabolism affected and results in megloblastic anemia [mega means large]. • 4. Trace elements – e.g. copper, zinc, cobalt • 5. Hormones – Cortisol, growth hormone. 17 CONTROL OF ERYTHROPOIESIS • It is done by Erythropoietin hormone. • Source of Erythropoietin – mainly kidney. • Erythropoietin is produced by the kidneys due to reduced O2 delivery to kidney. 18 CONTROL OF ERYTHROPOIESIS (cont) • Main stimulus for production of erythropoietin is hypoxia e.g. high altitude, anemia. • Hormone erythropoietin is secreted in blood and stimulates erythropoiesis in the bone marrow by acting on committed RBC. 19 20 IMPORTANT • Normal RBC count 5 millions / mm3. • In every person, 25 trillion – 30 trillion RBC are moving through our blood vessels. • Average life of RBC is 120 days. • RBC are replaced at average rate of 2 millions to 3 millions / sec. 21 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE Q . In case of hemorrhage [blood loss], what will happen to rate of Erythropoiesis ? Answer: Rate of Erythropoiesis can be increased more than 6 times. 22 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE Q. When you donate blood, your circulating RBC supply is replaced in how much time? Answer • During blood donation about 450ml of blood is donated. • Donated Plasma is replaced in 2-3 days. • RBC are replaced in 36 days [range 20–59 days], therefore, repeat donation of blood is recommended after 3 months. 23 RETICULOCYTES • It is immature erythrocyte. • Normal reticulocyte count 0.5 – 1.5% in blood. • Increased reticulocyte count in blood indicates high rate of erythropoietic activity. 24 SYNTHETIC ERYTHROPOIETIN • Synthetic erythropoietin is given to kidney failure patients or those patients under going chemotherapy for cancer as chemotherapy affects bone marrow and developing RBC. 25 RBC BREAKDOWN • Average life of RBC is 120 days then it is destroyed. • When RBC breakdown, they release hemoglobin. • Hemoglobin is taken by macrophages. • Hemoglobin is broken into heme + globin. • Globin is degraded into amino acids which are used. 26 RBC BREAKDOWN (cont) • From Heme, iron is released and passes back to blood. Porphyrin portion of heme molecule is converted into bilirubin. • Bilirubin is carried to liver [bound with albumin] and secreted in bile by liver. 27 WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW FROM THIS LECTURE ? • • • • • • • • Normal RBC count, Size, Shape and Function Life Span of RBC Erythropoiesis in Adults & Children Nutritional Requirement for Erythropoiesis Erythropoietin Functions of Hemoglobin Importance of Reticulocyte count in blood Hemoglobin Breakdown 28 THANK YOU