Explain
advertisement
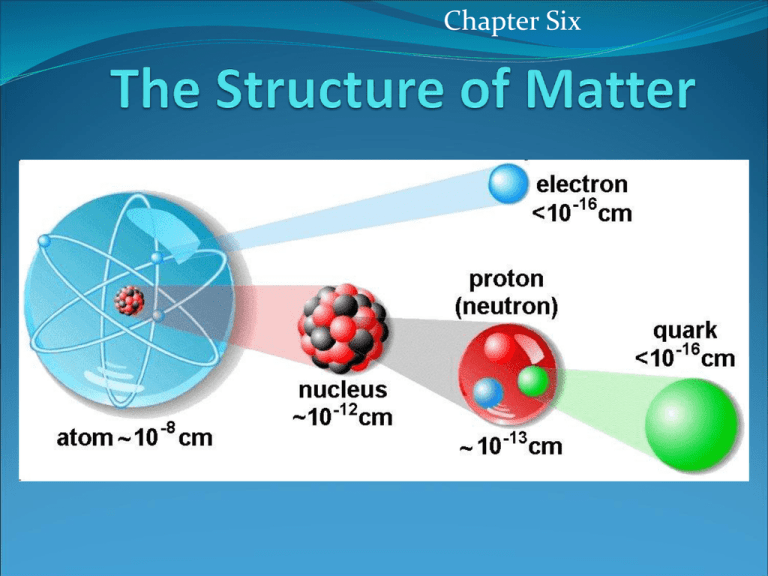
Chapter Six The Structure of Matter PA Standards 3.1.12.A Unifying Themes 3.4.10.A Physical Science, Chemistry and Physics 3.4.12.A Physical Science, Chemistry and Physics Apply concepts of models as a method to predict and understand science and technology. Explain concepts about the properties and structure of matter. Explain the formation of compounds and their resulting properties using bonding theories (ionic and covalent). Objectives: Compounds and Molecules Distinguish between compounds and mixtures. Relate the chemical formula of a compound to the relative numbers of atoms or ions present in the compound. Use models to visualize a compound’s chemical structure. Describe how the chemical structure of a compound affects its properties. Chemical Bonds H2 O2 Chemical Reaction H 2O Chemical Structure Structure and Properties Structure and Properties Compound State (at 25°C) Melting Point (°C) Boiling Point (°C) Silicon dioxide, SO2 (quartz) Solid 1,700 2,230 Magnesium fluoride, MgF2 Solid 1,261 2,239 Sodium Chloride, NaCl (table salt) Solid 801 1,413 Sugar, C12H22,O11 Solid 185-186 - Liquid 0 100 Gas -86 -61 Water, H2O Dihydrogen sulfide, H2S Structure and Properties Ionic and Covalent Bonding Explain why atoms sometimes join to form bonds. Explain why some atoms transfer their valence electrons to form ionic bonds, while other atoms share valence electrons to form different bonds. Differentiate between ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds. Compare the properties of substances with different types of bonds. Objectives: Compound Names and Formulas Name simple ionic and covalent compounds. Predict the charge of a transition metal cation in an ionic compound. Write chemical formulas for simple ionic compounds. Distinguish a covalent compound’s empirical formula from its molecular formula. Objectives: Organic and Biochemical Compounds Describe how carbon atoms bond covalently to form organic compounds. Identify the names and structures of groups of simple organic compounds and polymers. Identify what makes up the polymers that are essential to life. Organic Compound Organic Compound Covalently bounded compound that contains carbon Hydrocarbons Alkanes, Alkenes, Alcohols Polymers Polymer Molecule that is a long chain made of smaller molecules Monomer Smaller molecule that makes up the polymer Examples Plastic Wood Cotton Starch Protein DNA Examples Biochemical Compounds Biochemical Compounds Biochemical Compounds






