Heating and cooling curves
advertisement

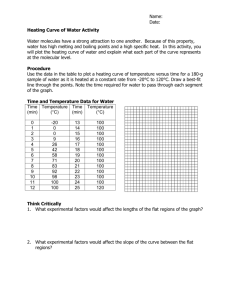
Name ______________________________________ Date ___________________ Period _____________ Heating and Cooling Curves Heating Curves A heating curve shows how the _____________ (y-axis) changes as a substance is heated up at a constant rate over _____________ (x-axis). Heating Point A - substance exists at a _____________ state. As time passes, _____________ is added to the substance. This causes the molecules of the substance to _____________ more rapidly which we detect by an increase in _____________ in the substance. Point B - the temperature of the substance is _______°C which is the “_____________ point” (Tm) of water. The solid begins to _____________ . Both _____________ and _____________ are present. ● The energy put in the substance between minutes 5-9 (between B&C) was used to convert the substance from a ____________ to a ____________ . This heat energy is called the “latent heat of fusion.” Point C - the substance is completely ____________ and in the ____________ state. ● Between 9 & 13 minutes (between C&D) the added energy increases the ____________ of the substance. Point D - the temperature of the substance is _______°C which is the “_____________ point” (Tb) of water. The liquid begins to _____________ .Both _____________ and _____________ are present. ● Between 13 and 18 minutes (between D&E) the energy added to convert the _____________ to the _____________ state is called the “latent heat of vaporization.” Point E - the substance is completely ____________ and in the ____________ state. ● Beyond point E the substance is still in the _____________ phase but molecules are moving _____________ as indicated by the increasing temperature. What element is this heat diagram diagram for? Compare Tm and Tb of the heating curve above with the values below. This is the heating curve of the element ________________ which has a melting point of ____________ and boiling point of ____________. Cooling Curve A cooling curve shows how the temperature (y-axis) changes as a substance is cooled down a constant rate over time (x-axis). Kinetic energy is (lost / gained) during a cooling curve therefore the temperature goes (up / down). ● The substance starts in the ________________ phase. ● At the first plateau where temperature is (changing / constant), the substance changes from a ________________ to a ________________. The temperature at this region is also called the ________________ point (Tc) and is the same temperature as Tb in the substance’s heating curve. ● ● When temperature continues to decrease after Tc, the substance is completely in the ________________ state and continues to (lose / gain) ________________ . At the second plateau the ________________ begins to ________________ - the temperature in this region is called the ________________ point (Tf). Both ________________ and ________________ states exist. ● When the temperature continues to drop after the plateau, the substance is completely in the ________________ state. Cooling Curve Practice Given the data table below, draw a cooling curve for water. Draw the heating curve of water given the following data and label the graph with when it’s SOLID, LIQUID, and GAS and label the condensation (Tc) and freezing points (Tf). Temperature (C) 0 140 5 120 10 100 15 100 20 80 25 60 30 40 14 0 12 0 Temperatur Time (min) 10 0 80 60 40 20 0 40 5 10 15 20 25 30 45 50 55 35