chemistry PowerPoint
advertisement

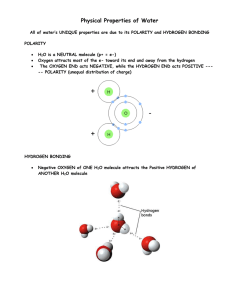
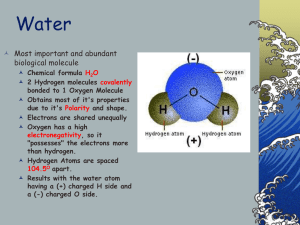
+ Basic Chemistry Honors Bio Ms. Napolitano + Water is everywhere! The Earth is ~71% water The human body is made up of about 5578% water Water is a polar molecule Molecules of water are held together by hydrogen bonds + Properties of Water 1. Cohesion –the attraction of H2O molecules to other H2O molecules due to hydrogen bonding Adhesion – attraction of H2O to other substances Capillary Action - ability of H2O to move within narrow spaces against gravity Surface Tension – cohesive forces at the surface of H2O + Properties of Water 2. Expansion upon freezing Solid state is less dense than liquid state Begins to expand at 4°C Floating ice creates insulation for underneath, allows for life in aquatic ecosystems + Properties of Water 3. Universal solvent Solute – substance being dissolved Solvent – dissolving agent Solution – homogenous mixture of 2 or more substances Aqueous solution – water is the solvent Water forms a hydration shell around ionic compounds Water dissolves polar compounds Hydrophilic – “water loving”, affinity for H2O Hydrophobic – “water fearing”, repels H2O + Properties of Water 4. Moderate Temperature Specific Heat – amount of heat that must be absorbed or lost for 1g of substance to change 1°C Calorie – amount of heat to raise 1g of water by 1°C Water has high specific heat: 1 cal/g/°C Water has high heat of vaporization Due to hydrogen bonding Moderates climate Evaporative cooling prevents organisms from overheating + 10/21 - Do Now Please take out your homework and a piece of notebook paper. Grab your clickers! + Properties of Water 4. Moderate Temperature Specific Heat – amount of heat that must be absorbed or lost for 1g of substance to change 1°C Calorie – amount of heat to raise 1g of water by 1°C Water has high specific heat: 1 cal/g/°C Water has high heat of vaporization Due to hydrogen bonding Moderates climate Evaporative cooling prevents organisms from overheating + Hydration Sphere + Hydration Sphere + pH Dissociation: the In breaking apart of 2+ molecules Usually capable of recombining water, one H+ ion shifts from one molecule to the other + pH Acid – increases H+ concentration of a solution HCl H+ + ClH2CO3 HCO3- + H+ Base – reduces H+ concentration of a solution NH3 + H+ NH4+ NaOH Na+ + OH- Acids and bases that dissociate completely in water are called strong acids and strong bases, respectively. + The pH Scale Measure of H+ concentration pH is lower as H+ concentration increases pH is higher as H+ concentration decreases pH 7 = neutral + Buffers Many Most bodily processes are pH specific living cells have pH of ~7 Buffers – substances that minimize change in H+ and OH- concentrations in a solution Accept or donate H+ ions Usually contain a weak acid and corresponding base