Forms of Energy and Calculations
advertisement

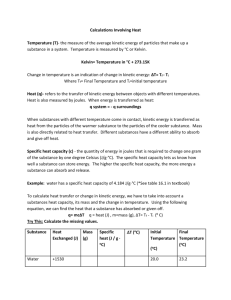
Revision Remember energy is the ability to do work. It is measured in Nm or Joules. We know that to do more work we require more energy, but we can use various types of energy to do this work for us. Other forms of energy Energy comes in several different forms, but the ones we shall deal with in this course are: Kinetic Energy Kinetic Energy is the energy of movement. It is the name given to the energy a body possesses due to its motion. Calculating Kinetic Energy The kinetic energy of a moving object is dependent on two factors: the mass, m, of the object (in kg) and its velocity, v (in m/s). Ek = ½ mv2 Potential Energy Potential Energy can be best thought of as energy stored in a static object. It can be due to how high the object is above a datum (starting point), or due to the fact that work has already been done on the object and energy is stored in it (for example a spring). Calculating Potential Energy Ep = mgh Where m is the mass of the object, g is the acceleration of gravity acting on the object and h is the height the object is above the ground or datum. Electrical Energy Electrical Energy is the energy provided by electricity It is one of the most convenient and commonly used forms of energy since it can be transported easily from place to place and can be easily changed into other forms of energy. Calculating Electrical Energy Ee = ItV Where V is the voltage of the circuit, I is the current flowing through the circuit and t is the time (in seconds) that the circuit has been operating. Heat Energy Heat Energy is the energy transferred to a body that results in a change in the body’s temperature. Calculating Heat Energy Eh = mcΔT Where m is the mass of the material, in kg, ΔT, is the change in temperature, in degrees (Celsius or Kelvin) and c is the specific heat capacity of the material being heated. The specific heat capacity of a substance is the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of the material by 1K. Other Forms of Energy – copy this into your notes Summary Kinetic Energy is the energy of movement. It is the name given to the energy a body possesses due to its motion. Ek (Joules)= ½ m(kg) x v2 (velocity) Potential Energy can be best thought of as energy stored in a static object. It can be due to how high the object is above a datum (starting point), or due to the fact that work has already been done on the object and energy is stored in it (for example a spring). Ep(Joules) = m(kg) x g (9.81m/s2) x h (height) Other Forms of Energy – copy this into your notes Summary Electrical Energy is the energy provided by electricity. It is one of the most convenient and commonly used forms of energy since it can be transported easily from place to place and can be easily changed into other forms of energy. Ee (Joules) = I (current in Amps) x t (secs) x V (voltage) Heat Energy is the energy transferred to a body that results in a change in the body’s temperature. Eh (Joules) = m (kg) x c xΔT (°C or K) Kelvin & Celsius The Kelvin is the SI (International System of Units) unit of temperature. The Kelvin scale is defined by a specific relationship between the pressure of gas and the temperature. This says that “the pressure of the gas is directly proportional to the temperature in Kelvin”. This means that Kelvin is an absolute temperature scale, and scientists use this scale more than any other. To convert a temperature originally expressed in degrees Celsius into Kelvins you must add 273.15 units. E.g. O°C is 273.15 K. Gravity Objects that have mass pull on each other. We call this ‘pull’ gravity. The strength of the pull between two objects depends on two things. The first is the mass of both of the objects. The larger the masses the stronger the pull of gravity. The second is the distance between the two objects. The larger the distance the weaker the pull of gravity. Both of the objects will feel this pull of gravity equally.




![Temperature Notes [9/22/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006907012_1-3fc2d93efdacd086a05519765259a482-300x300.png)