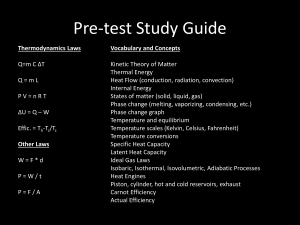
Day 15, Physics 131
advertisement

Day 15, Physics 131 HW Problem 16-9 • A world record for the greatest change in temperature was set in Spearfish, SD, on January 22, 1943. At 7:30 a.m. the temperature was -4.00oF; two minutes later the temperature was 45oF. • ? Find the average rate of temperature change during those two minutes in Kelvins per second. ?? HW Problem 16-19 • It is desired to slip an aluminum ring over a steel bar. At 10.00oC the inside diameter of the ring is 4.000 cm and the diameter of the rod is 4.040 cm. • ? (a) In order for the ring to slip over the bar, should the ring be heated or cooled?? • ? (b) Find the temperature of the ring at which it fits over the bar. The bar remains at 10.0oC ? HW Problem 16-25 • An aluminum saucepan with a diameter of 23 cm and a height of 6.0 cm is filled to the brim with water. The initial temperature of the pan and water is 19oC. The pan is now placed on a stove burner and heated to 88oC. • Aaluminum = 24x10-6 K-1 bwater = 0.21x10-3 K-1 • ? (a) Will the water overflow from the pan ? • ? (b) Calculate the volume of water that overflows ?? HW Problem 16-27 • An exercise machine indicates that you have worked off 2.5 Calories in a minute-and-a-half of running in place. • ? What was your power output during this time ?? • Give you answer both in Watts and hp. HW Problem 16-37 • Silver pellets with a mass of 1.0 g and a temperature of 85oC are added to 220 g of water at 14oC. • ? (a) How many pellets must be added to increase the equilibrium temperature of the system to 25oC ? • ? (b) If copper pellets are used instead, does the required number of pellets increase, decrease, or stay the same ? • ? (c) Find the number of copper pellets that are required. ?? HW Problem 6-40 • A 97.6-g lead ball is dropped from rest from a height of 4.57 m. The collision between the ball and the ground is totally inelastic. • ? Assuming all the ball’s kinetic energy goes into heating the ball, find its change in temperature. ?? HW Problem 6-51 • Assume: your skin temperature is 37.2 oC and the temperature of your surroundings is 21.8 oC. • ? Determine the length of time for you to radiate away the energy gained by eating a 306-Calorie ice cream cone. ?? • Let the emissivity of your skin be 0.915 and its area to be 1.22 m3. HW Problem 16-76 • If heat is transferred to 150 g of water at a constant rate for 2.5 minutes, its temperature increases by 13 oC. When heat is transferred at the same rate for the same amount of time to a 150-g object of unknown material, its temperature increases by 61 oC. • ? (a) From what material is the object made. ? • ? (b) What is the heating rate ?? HW Problem 16-92 • When the Blackbird lands, it is 8.0 inches longer than it was at takeoff. • Its coefficient of linear expansion is 22 x 10-6 K-1, and its temperature at takeoff is 23oC. • ? How hot is the Blackbird when it lands ?? Ideal Gas • An Ideal Gas is a collection of atoms or molecules that move randomly and exert no long-range forces on each other. Each particle of the ideal gas individually point-like, occupying a negligible volume. • A “mole” is a convenient measure. • NA = 6.02 x 1023 particles/mole; • NA = Avagadro’s number Ideal Gas Law • • • • • • • Ideal Gas Law, PV = nRT N = number of moles T in Kelvin (K) P in Pa V in m3 R = 8.31 J/mole K So – if one pumps up footballs in a sauna and then takes then out to a cold, cold football game, what happens to the pressure of the gas inside the balls? Ideal Gas Example • • • • • • • 4.50 L of ideal gas = 4.5 x 10-3 m3 Ti = 375 K Tf = 275 K V = constant Pi = atmospheric pressure = 1.01 x 105 Pa ? (a) Pf = ? ? (b) n = ? Sealed Container • A sealed cubical container 20.0 cm on a side contains three time Avagadro’s number of molecules at a temperature of 20oC. • ? Find the force exerted by the gas on one of the walls of the container. ?? Internal Energy of Helium • Helium has the special property that its internal energy is directly proportional to its absolute temperature. Consider a flask of helium with a temperature of 2oC. • ? If it is heated until it has twice the internal energy, what will its temperature be ?? Deformation of Solids • Stress = force per unit area causing deformation • Strain = increase in the amount of deformation • For small stress, stress = (elastic modulus)*(strain) • Recall: F = k Dx , Hooke’s Law for springs Stress/Strain • • • • • • Tensile Stress defined as F/A Units of stress are N/m2 = Pascal (Pa) Tensile Strain defined as DL/Lo Tensile Strain is unitless F/A = Y * (DL/Lo) Young’s Modulus, Y, table on page 585 Bulk Modulus – Volume Elasticity • Volume Stress DP • DP = -B DV/V Steel Wire • Given: the elastic limit of steel is 5.0 x 108 Pa. • Given: circus performer has mass 70 kg. • ? What is the minimum diameter of a steel wire used to support the performer ?? Latent Heats • Latent Heat = L = Q / m (notice no DT) • Latent Heat of Fusion, Lf, the latent heat to melt (or fuse) a substance. • Latent Heat of vaporization, Lv is the latent heat required to convent a liquid to a gas. • … and, recalling the recent winter snow, … • Latent Heat of Sublimation is the latent heat needed to convent a solid directly to a gas. Heat and Phase Transfers • The most important information for today is the figure on the top of page 596. • It shows • A. Heating ice, for which you need cice • B. Melting ice, for which you need Lf of ice • C. Heating water, for which you need cwater • D. Converting water to steam, for which you need Lv of water • E. Heating steam, for which you need csteam. Temperature vs heat added or removed A Lead Bullet • Suppose a lead bullet with a mass of 5.00 g and initial temperature of 65oC hits a wall and completely liquifies. • ? What minimum speed did it have before impact ?? • Assume lead melting temp is 327.3oC • Assume specific heat of lead is 128 J/kg*K • Assume latent heat of fusion of lead is 2.45 x 104 J/kg. Party Time • At a party, 6.00 kg of ice at -5.00oC is added to a cooler holding 30 liters of water at 20.0oC. • ? What is the temperature of the water when it comes to equilibrium ? The Laws of Thermodynamics • Zeroth: If object A is in thermal equilibrium with object C, and object B is separately in thermal equilibrium with object C, and objects A and B will be in thermal equilibrium if they are placed in thermal contact. • First: The change in a system’s internal energy, DU, is related to the heat Q and the work W as follows: DU = Q - W Laws of Thermodynamics • Second: When object of different temperatures are brought into thermal contact, the spontaneous flow of heat that results is always from the high-temperature object to the low-temperature object. Spontaneous heat flow never proceeds in the reverse direction. Carnot Engine • The efficiency of a Carnot engine, ec = 1 – (Tc/Th) T in K in Kelvin !!! • *****No real engine operating between two energy reservoirs can be more efficient than a Carnot engine operating between the same two reservoirs.****** Heat Engine example • A Carnot engine is operating between a hot temperature, Thot of 100oC and a cold temperature , Tcold of 20oC. • ? What is the maximum possible efficiency of this engine ?? • ? If Thot = 500oC, what is the maximum possible efficiency ?? Power Plant • A power plant has been proposed that would make use of the temperature gradient in the ocean. The system is to operated between 20.0oC (surface water temperature) and 5.00oC (water temperature at a depth of about 1 km). • ? (a) What is the maximum efficiency of such a system. ?? • ? (b) If the useful power output of the plant is 75.0 MW, how much energy is absorbed per hour?