Includes
advertisement
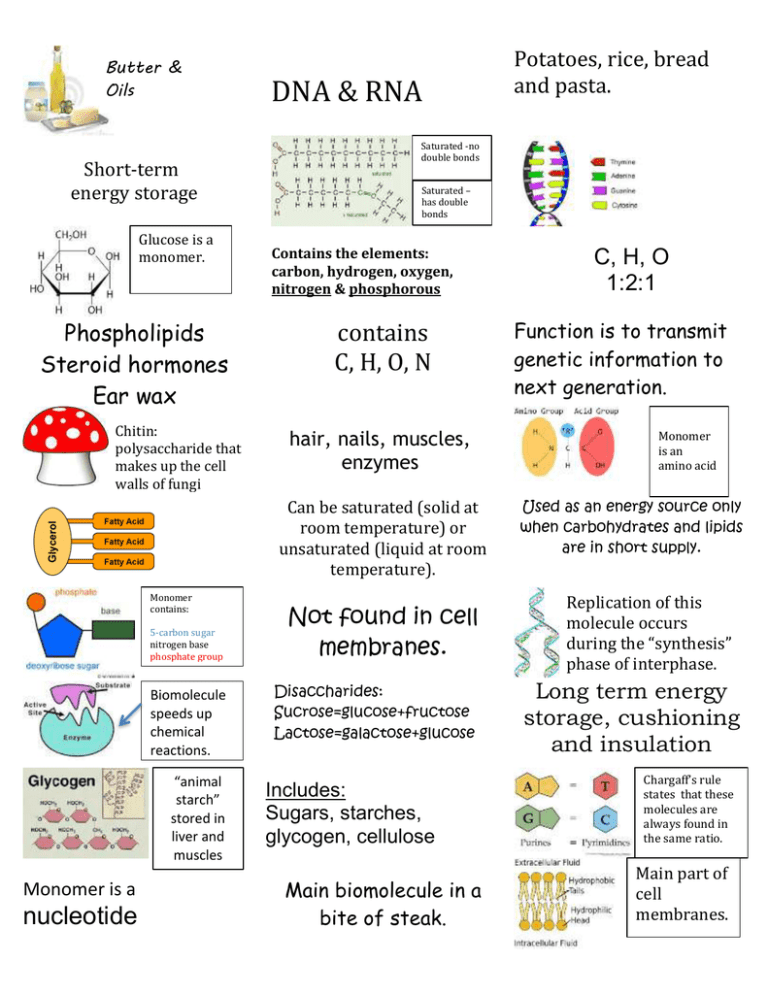
Butter & Oils Short-term energy storage Glucose is a monomer. Phospholipids Steroid hormones Ear wax Chitin: polysaccharide that makes up the cell walls of fungi DNA & RNA Saturated -no double bonds Saturated – has double bonds Contains the elements: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen & phosphorous contains C, H, O, N hair, nails, muscles, enzymes Can be saturated (solid at room temperature) or unsaturated (liquid at room temperature). Monomer contains: 5-carbon sugar nitrogen base phosphate group Biomolecule speeds up chemical reactions. “animal starch” stored in liver and muscles Monomer is a nucleotide Potatoes, rice, bread and pasta. Not found in cell membranes. Disaccharides: Sucrose=glucose+fructose Lactose=galactose+glucose Includes: Sugars, starches, glycogen, cellulose Main biomolecule in a bite of steak. C, H, O 1:2:1 Function is to transmit genetic information to next generation. Monomer is an amino acid Used as an energy source only when carbohydrates and lipids are in short supply. Replication of this molecule occurs during the “synthesis” phase of interphase. Long term energy storage, cushioning and insulation Chargaff’s rule states that these molecules are always found in the same ratio. Main part of cell membranes.