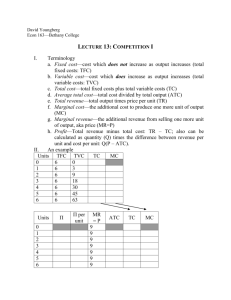
Chapter 8
The Costs of
Production
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2009 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Chapter Objectives
•
•
•
•
Explicit and implicit costs
Law of diminishing returns
Fixed and variable costs
Total, average, and marginal
costs
• The firm’s size in the long run
8-2
Economic Costs
• Equal to opportunity costs
• Explicit + implicit costs
• Explicit costs
–Monetary payments
• Implicit costs
–Value of next best use
–Self-owned resources (rent)
–Self-employed resources (labor)
8-3
Profit
• Accounting profit
–Total revenue less explicit cost
• Normal profit
–Equal to implicit cost
• Economic or pure profit
–Total revenue less economic cost
8-4
Profits Compared
Economic
Implicit Costs
(Including a
Normal Profit)
Explicit
Costs
Total Revenue
Economic
(Opportunity)
Costs
Economic
Profit
Accounting
Accounting
Profit
Accounting
Costs (Explicit
Costs Only)
8-5
Short and Long Run
• The short run
–Fixed plant capacity
–Variable intensity of plant use
–Variable output
• The long run
–Variable plant capacity
–Firms enter and exit
8-6
Production Relationships
• Total product (TP)
• Marginal product (MP)
Change in Total Product
Marginal Product =
Change in Labor Input
• Average product (AP)
Average Product
=
Total Product
Units of Labor
**AP = Productivity
8-7
Law of Diminishing Returns
• Fixed technology
• Add variable resource to fixed
resource
• Marginal product will decline
–Beyond some point
• Rationale
- farming, factory examples
8-8
Law of Diminishing Returns
(1)
Units of the
(2)
Variable Resource Total Product
(Labor)
(TP)
0
0
]
10
1
]
25
2
]
45
3
]
60
4
]
70
5
]
75
6
]
75
7
]
70
8
(3)
Marginal Product
(MP),
Change in (2)/
Change in (1)
10
15
20
15
10
5
0
-5
(3)
Average
Product
(AP),
(2)/(1)
Increasing
10.00
Marginal
12.50
Returns
15.00
Diminishing
15.00
Marginal
14.00
Returns
12.50
Negative
10.71
Marginal
Returns
8.75
8-9
Total Product, TP
Law of Diminishing Returns
30
20
10
0
Marginal Product, MP
TP
1
2
3
Increasing
Marginal
20 Returns
4
5
6
7
8
9
Negative
Marginal
Returns
Diminishing
Marginal
Returns
10
AP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8 9
MP
8-10
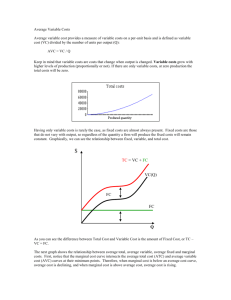
Short-Run Production Costs
• Fixed Costs
–Do not vary with output
–What are some fixed costs of
production?
• Variable Costs
–Materials, most labor
• Total Cost
–TC = TFC + TVC
8-11
Per-Unit Production Costs
• Why are per-unit costs important?
• Important when comparing to price
• Average fixed cost
AFC = TFC/Q
• Average variable cost
AVC = TVC/Q
• Average total cost
ATC = TC/Q = TFC/Q + TVC/Q
ATC = AFC+AVC
• Marginal cost
MC = change in TC/change in Q
8-12
Individual Firm in Short Run – Pg. 161
Short-Run Production Costs
$1100
TC
1000
900
TVC
800
Costs
700
600
Fixed
Cost
500
400
Total
Cost
300
Variable
Cost
200
100
TFC
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Q
8-14
Short-Run Production Costs
$200
MC
Costs
150
ATC
AVC
100
AFC
50
AVC
AFC
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Q
8-15
Graphical Relationships
Average Product and
Marginal Product
Production Curves
AP
MP
Quantity of Labor
MC
Cost (Dollars)
AVC
Cost Curves
Quantity of Output
8-16
Production Relationships
• Marginal cost and diminishing returns
• Marginal cost and marginal product
• Marginal cost and average variable cost
• Marginal cost and average total cost
• Production curves and cost curves
8-17
Shifts in Cost Curves
• Shifts in cost curves – Which curves shift and where?
– Change in cost of variable inputs?
– Change in cost of fixed inputs?
• Examples
– Decrease in union wage requirements?
• AVC, ATC, MC shift DOWN
– Increase in rent?
• AFC, ATC, shift UP
– Increase in cost of materials?
• AVC, ATC, MC shift UP
– More efficient production technology is discovered?
• AVC, ATC, MC shift DOWN
Long-Run Production Costs
• Choose your plant size
– What would generally happen to cost curves
if we open a larger plant?
• Minimize ATC
• Different ATC curves
–Short run
• Long run ATC
–Envelope of short run ATC
8-19
Average Total Costs
Long-Run ATC Curve
ATC-1
ATC-5
ATC-2
ATC-3
ATC-4
Output
Any number of short-run optimum
size cost curves can be constructed
8-20
Average Total Costs
Long-Run ATC Curve
ATC-1
ATC-5
ATC-2
ATC-3
ATC-4
Long-Run
ATC
Output
The long-run ATC curve just
“envelopes” the short run ATCs
8-21
Long Run Production Cost
• Economies of Scale
– Labor specialization
– Managerial specialization
– Efficient capital
• Diseconomies of Scale
– Difficulty in communicating and
coordinating
– Workers can feel less
attached/motivated
• Constant Returns to Scale
8-22
Average Total Costs
Long-Run ATC Shapes
Constant Returns
To Scale
Economies
Of Scale
Diseconomies
Of Scale
Long-Run
ATC
q1
q2
Output
Long-run ATC curve where economies
of scale exist
8-23
Average Total Costs
Long-Run ATC Shapes
Economies
Of Scale
Diseconomies
Of Scale
Long-Run
ATC
Output
Long-run ATC curve where costs are
lowest only when large numbers are
participating
8-24
Average Total Costs
Long-Run ATC Shapes
Economies
Of Scale
Diseconomies
Of Scale
Long-Run
ATC
Output
Long-run ATC curve where economies
of scale exist, are exhausted quickly,
and turn back up substantially
8-25
Industry Structure
• Minimum efficient scale (MES)
–Minimum level of output
necessary to minimize LRATC
• Natural monopoly
–One large firm
• Pure Competition
–Many small firms
• Monopolistic Competition
–Some small, some large firms
8-26
Sunk Costs
• Irrelevant in decision making
• Cannot be recovered
• Do not affect marginal
benefit and marginal cost
• Firm example:
–R&D costs
8-27
Key Terms
• economic (opportunity)
cost
• explicit costs
• implicit costs
• normal profit
• economic profit
• short run
• long run
• total product (TP)
• marginal product (MP)
• average product (AP)
• law of diminishing returns
• fixed costs
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
variable costs
total cost
average fixed cost (AFC)
average variable cost
(AVC)
average total cost (ATC)
marginal cost (MC)
economies of scale
diseconomies of scale
constant returns to scale
minimum efficient scale
(MES)
natural monopoly
8-28
Next Chapter Preview…
Pure
Competition
8-29