Cold War Conflicts
advertisement

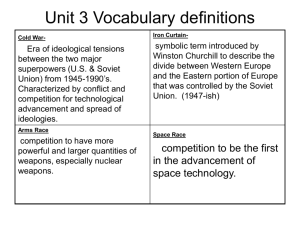
Cold War Conflicts Korean War, Vietnam War, and Cuban Missile Crisis Korean War - Background Korea was a Japanese colony After World War II, U.S. and Soviet Union divided Korea into two sections (38th parallel) a. North Korea (Soviet Union) b. South Korea (U.S.) Korean War Korean War – Cause 1950 North Korea invaded South Korea in order to unite Korea Korean War – Key Events 1950 U.S. and United Nations forces pushed North Korean forces back behind the 38th parallel 1951 Chinese and North Korean forces pushed United Nations forces back behind the 38th parallel and into South Korea Korean War - Result 1953 Korean War ended (38th parallel divides North Korea from South Korea) Korean War – Key Terms United Nations (peacekeeping organization) Korean War represented first UN action Vietnam War - Background Vietnam was a French colony (French Indochina) Vietnamese forced the French to leave Ho Chi Minh (communist leader) dominated North Vietnam Geneva Conference (1954) temporary division of Vietnam a. North communist b. South non-communist Vietnam War - Causes Ho Chi Minh wanted to unite Vietnam under Northern rule (communist rule) Ho Chi Minh encouraged communist rebels to overthrow South Vietnamese government Vietnam War - Events Increased American involvement a. President Eisenhower sent military advisors and supplies to South Vietnam b. President Kennedy more military advisors and weapons to South Vietnam c. President Johnson sent American troops to fight the North Vietnamese d. President Nixon cease-fire and the withdrawal of American troops beginning in 1973 Vietnam War - Results U.S. troops left Vietnam Unification of Vietnam (communist country) Vietnam War – Key Terms Gulf of Tonkin Resolution (1964) Congress authorized President Johnson to increase American involvement in Vietnam Vietnamization Nixon's administrations policy of building up South Vietnamese forces while gradually withdrawing American troops Domino Theory If Vietnam became a communist country, the countries adjacent to (surrounding) Vietnam would also become communist countries http://www.history.com/topics/cold-war/cold-war-history/videos/the-road-to-war?m=528e394da93ae&s=undefined&f=1&free=false Vietnam War – Key Terms Dove Someone opposed to American involvement in the war Hawk a person who supported American involvement in the war Cuban Missile Crisis – Background 1959 Fidel Castro came to power in Cuba Cuba became a communist state 1961 Bay of Pigs a. U.S. (President Kennedy) supported a plan by anti-Castro exiles (people forced to leave Cuba when Castro came to power) to invade Cuba and lead an "uprising" against Castro b. Failed http://www.history.com/topics/cold-war/cold-war-history/videos/bay-of-pigs-cias-perfect-failure?m=528e394da93ae&s=undefined&f=1&free=false 1962 U.S. imposed a trade embargo on Cuba CIA Tries to Kill Castro http://www.history.com/topics/coldwar/cold-war-history/videos/history-rockscastro-mustdie?m=528e394da93ae&s=undefined&f=1 &free=false Cuban Missile Crisis - Cause Castro asked the Soviet Union for help Soviet Union built nuclear missile bases in Cuba Cuban Missile Crisis October 1962 President Kennedy demanded the immediate removal of nuclear missiles U.S. created a naval blockade of Cuba. Period of tension between Soviet Union and United States Cuban Missile Crisis - Results Soviet Union removed nuclear missiles U.S. promised not to invade Cuba