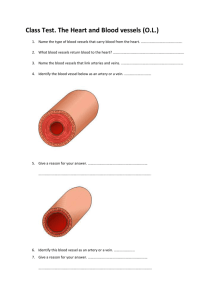
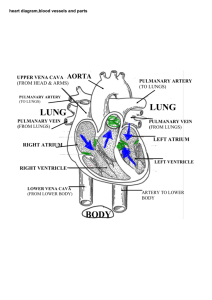
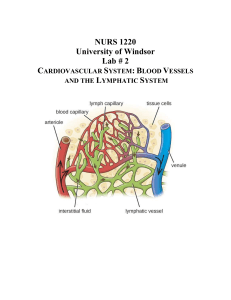
File
advertisement
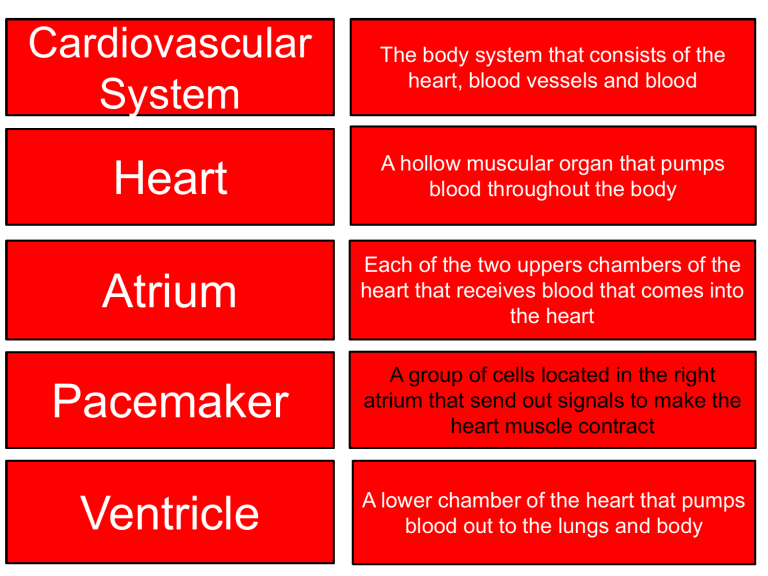
Cardiovascular System The body system that consists of the heart, blood vessels and blood Heart A hollow muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body Atrium Each of the two uppers chambers of the heart that receives blood that comes into the heart Pacemaker A group of cells located in the right atrium that send out signals to make the heart muscle contract Ventricle A lower chamber of the heart that pumps blood out to the lungs and body Valve A flap of tissue in the heart or vein that prevents blood from flowing backward Artery A blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart Capillary A tiny blood vessel where substances are exchanged between the blood and the body cells Vein A blood vessel that carries blood back to the heart Aorta The largest artery in the body Coronary Artery An artery that supplies blood to the heart itself Pulse The alternating expansion and relaxation of an artery wall as blood travels through it Diffusion The process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration Blood Pressure The pressure that is exerted by the blood against the walls of the blood vessels Plasma The liquid part of the blood Red Blood Cell A cell in the blood that takes up oxygen in the lungs and delivers it to the cells elsewhere in the body Hemoglobin An iron containing protein that binds chemically to oxygen molecules White Blood Cell A blood cell that fights disease Platelet A cell fragment that plays an important part in the forming of clots Lymphatic System A network of vein like vessels that return fluid that leaks out of blood vessels to the bloodstream Lymph The fluid that the lymphatic system collects and returns to the bloodstream Lymph Node A small knob in the lymphatic system that filters lymph, trapping bacteria and other disease causing microorganisms Atherosclerosis A condition in which an artery wall thickens from a buildup of fatty material Heart Attack A condition in which blood flow to part of the heart muscle is blocked causing heart cells to die Hypertension A disorder in which a person’s blood pressure is consistently higher than normal