Chapter 7, Part 4
advertisement

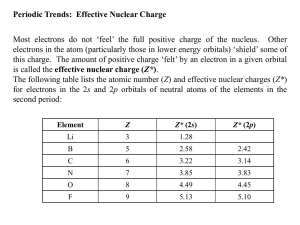
November 6, 2009 •E X A M # 3 M O N D A Y , N O V E M B E R 9 T H •R e s o u r c e s p o s t e d o n c o u r s e w e b s i t e : •Study Guide •Practice Problems (Study group problems and answer key) •Video •T o d a y : Review Periodic Properties Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table Chromium and copper are anomalies Cr Cu Periodic Trends How does the electron configuration lead to the properties of an element? Basic Properties Size Ionization Energy Electron Affinity Ion Size (electron configuration of ions) Keep in mind Coulomb’s Law (force between charges): q q 1 2 Force k e 2 r Trends in Orbital Energies Trends in Orbital Energies Why do energies decrease moving left to right? Overall attraction of nucleus for electrons determines energies and size Less attraction higher energy Attraction dependent on distance and charge Effective nuclear charge (Z*) Z*= Z – S Z=nuclear charge S=shielding q q 1 2 Force k e 2 r Atomic Size What happens to the force of attraction between the outermost electrons and the protons in the nucleus as you go down a group? … as you go across a period? q q 1 2 Force k e 2 r Which atom is the smallest? 1. H 83% 2. He 3. Cs 4. Rn 13% 3% 1 2 3 1% 4 Which atom is the largest? 1. K 81% 2. Ca 3. Rb 4. Sr 12% 4% 1 4% 2 3 4 Electron Configurations of Cations Transition Metal Cations: Lose s electrons first Ion Size