RECEIVABLES & SALES
advertisement

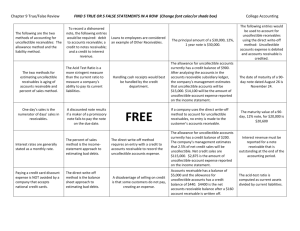
CHAPTER FIVE Homework P1 - Sales Discounts P2 – Sales Allowance P3 – Allowance Method of Uncollectibles P4 – Write Off Uncollectibles P8 – Notes Receivable Credit Sales and discounts Contra Revenues Allowance methods Write Off A/R Aging A/R Direct W/O Receivable Analysis Notes Receivable Percentage of Sales Method- Allowance Accounts Receivable transactions Credit Sales Accounts Receivable (Amount of invoice) Sales Freight-out Receive Payment Cash A/R Contra Revenue Accounts Sales Discount Sales Returns Sales Allowances DISCOUNTS TRADE DISCOUNTS a reduction in the selling price of the item as a reward for buying large quantities. SALES DISCOUNTS (pg 285) a reduction in the amount the customer needs to pay as a reward for paying earlier than required TERMS 2/10 Net 30 2% if paid in 10 days, full amount in 30 days 1/15 Net 60 Sales Discount Transaction Credit Sales – no discount until paid A/R 500 Sales 500 Payment – Discount is recorded when paid Cash Sales Discount(2%) A/R 490 10 500 (take it out for the amount you put it in) Sales Discount exercises Do E5-3, 5-4 page 246 Sales Returns & Allowance SALES RETURNS If it doesn’t work or your customer doesn’t want it, it can returned and the customer will get their money back SALES ALLOWANCE If you give a reduction in the price of the item you sold and they keep the item. Sales Returns & Allow transaction Credit Sale A/R Sales 1000 1000 Return Sales Return and Allowance A/R Customer Payment Cash A/R 700 700 300 300 NET SALES SALES 1500 -- Sales Returns & Allowances 300 -- Sales Discount 10 ----------------------------------------- ------ NET SALES 1190 Sales Return and Allowance Exercise 5-6 page 247 When a customer cannot or will not pay the invoice. Four methods: Direct Write off Method Allowance Methods: Percentage of Receivables Aged A/R Percentage of Sales Direct Write off Method Use when you have only a few uncollectible invoices and it occurs infrequently. Transaction: Bad Debt Expense A/R ALLOWANCE ACCOUNT Set aside of costs that will not occur until the next period but revenue is recorded in current year. Use when you have several customers who do not pay you and it happens frequently during the same year. Can’t charge A/R because we don’t know which one will be uncollectible Fraud Alert or Income Manipulating If overstate the uncollectible –understate income and income tax Do not have to worry until the next year. If audited will need to provide an aged A/R to prove your uncollectible A/C expense Accounts used Uncollectible Account Expense or BAD DEBT Expense Always a debit balance account Non- Cash transaction Allowance for uncollectible – Contra Asset Account Should be a credit balance Setting up or adjusting entry - 2009 Bad Debt Expense 5000 Uncollectible Account Expense 5000 Effects Net Income Writing off bad A/R in 2010 Uncollectible Account Expense 4000 A/R Does not effect net income 4000 Allowance t-account ___________________________________ Write off A/R | Setting up or adding to | | 5000 4000 | ------------------------------------------------1000 Balance Wrote off less than estimated ___________________________________ Write off A/R | Setting up or adding to | | 5000 7000 | ------------------------------------------------2000 Balance Wrote off more than estimated Accounts Receivable Less Allow.for Uncollectible Accts = Net Receivables (Net realizable value) Exercise 5-7 pg 247 Exercise 5-13 page 248 Compare allowance method with the direct write off method and the effect on income tax. Aging Method More accurate Use if you do not have historical data It is the balance in the allowance account – not the adjusting entry See page 228 for Aging schedule Exercise 5-11 page 248 Percentage of Sales Percentage of A/R --- Balance Sheet Method Good because it is closest to net realized value Most accepted method Percentage of Credit Sales – Income Statement Method Good because better matched with revenue Only accepted if the amounts do not differ significantly from Percentage of Receivables Exercise E5-19 page 249 Receivable Analysis Good to get when you first start the job or higher a new person. Later show how you have helped to improve A/R collections Receivables turnover ratio Average collection period Receivables turnover ratio -- # of times during the year the Avg A/R is collected or turned over Net Credit Sales Avg A/R Higher the number of times, the better. Average collection period -- # of days A/R balance is outstanding or how long did it take to collect A/R Average collection period -- # of days A/R balance is outstanding or how long did it take to collect A/R Your Invoice terms are used to see if good or bad If Net 30 is terms you days should be around 30. 365 A/R Turnover Exercise E5-14 page 249 More formal and legally bound form of credit sales. Usually a note is a loan that is signed and has an interest component . Note Terminology Face Value – Principle of the note Due date- date it is to be paid back (DUH!!!) Payee – who is to receive the money Maker – who is to pay the money Interest rate- rate is in annual terms. Note Transactions A note for an accounts receivable Seller Notes Receivable (N/R) A/R Buyer A/P Notes Payable (N/P) Note is paid Cash Interest Income N/R N/P Interest Expense Cash Interest Calculations I=PRT Interest = Principle X rate X time Rate 12% = 1% month 6% = .5% month 18%= 1.5% month 24% = 2% month Principle is $10,000 rate is 12% time is 2 months the interest is: 10000 X 1% X 2 = $200 Exercise 5-16 pg 249 Interest Receivable Adjust Entry Interest earned but not yet paid - ACCRUAL Adjusting Journal Entry – for the month of the year Interest Receivable Interest Income When note is paid Cash N/R Interest Receivable Interest Income Exercise 5-18 page 249