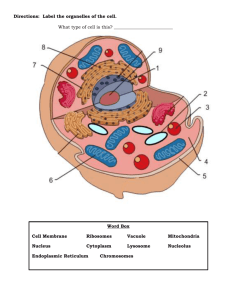
Level 1
advertisement
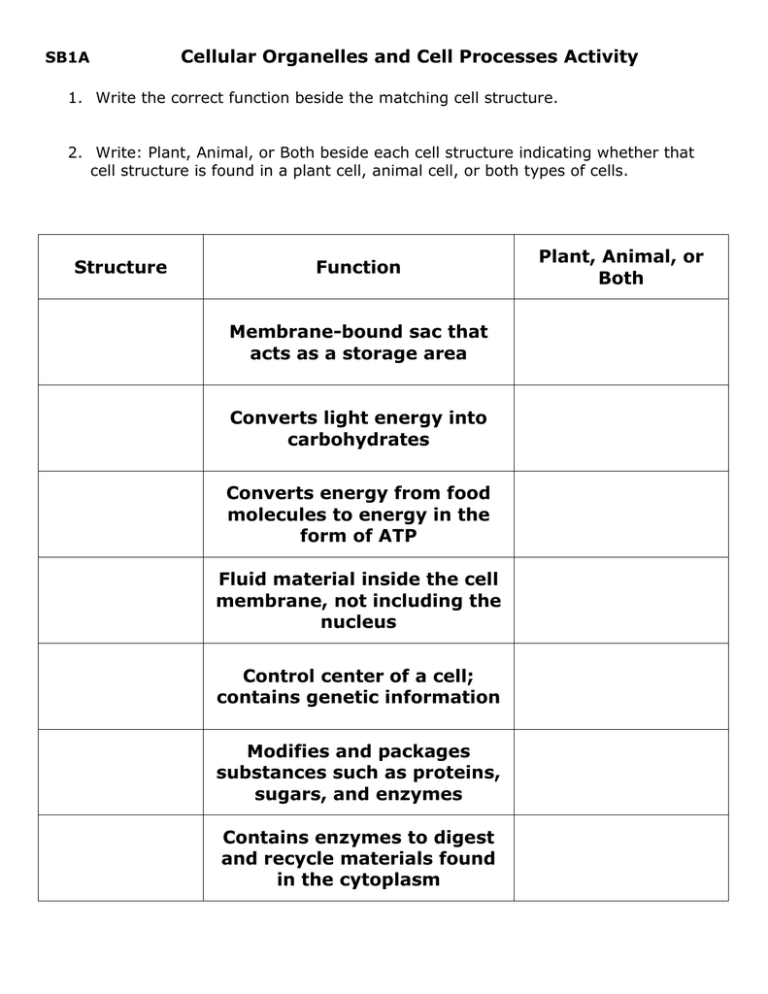
SB1A Cellular Organelles and Cell Processes Activity 1. Write the correct function beside the matching cell structure. 2. Write: Plant, Animal, or Both beside each cell structure indicating whether that cell structure is found in a plant cell, animal cell, or both types of cells. Structure Function Membrane-bound sac that acts as a storage area Converts light energy into carbohydrates Converts energy from food molecules to energy in the form of ATP Fluid material inside the cell membrane, not including the nucleus Control center of a cell; contains genetic information Modifies and packages substances such as proteins, sugars, and enzymes Contains enzymes to digest and recycle materials found in the cytoplasm Plant, Animal, or Both Structure in plants and fungi that protects and supports the organism Responsible for protein synthesis Moves molecules from one part of the cell to another; involved in synthesis of lipids; has not ribosomes Moves molecules from one part of the cell to another including proteins; covered with ribosomes Thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cell. Regulates what materials enter and leave the cell Groups of microtubules important for cell division A framework for the cell within the cytoplasm The site of ribosome production within the nucleus ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS FOR HOMEWORK 1. In what organelle does cellular respiration take place? 2. Name two storage organelles? 3. What is the list of organelles that take part in protein synthesis? 4. How is the nucleus involved in protein synthesis? 5. What organelle is considered a “factory”, because it takes in raw materials and converts them to cell products that can be used by the cell? 6. How does the membrane of the cell differ from the nuclear membrane? What advantages does this difference have for the nucleus? 7. What do ribosomes do? Are they found freely floating in the cytoplasm? OR are they found attached to another organelle? OR both. Explain why this occurs. 8. What does the endoplasmic reticulum do? 9. What is the difference between rough ER and smooth ER? What is the ER doing that is different in each case? 10. What are lysosomes? What types of molecules would be found inside a lysosome? 11. Why might a lysosome fuse with or link up with a food vacuole? 12. In what organelle do molecules move from the ER to the Golgi bodies? 13. What is a centriole? In what type of cell (plant or animal) is it found? What does it do for the cell?