American Imperialism
advertisement

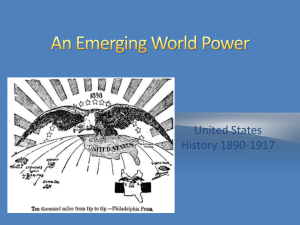
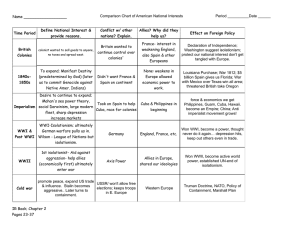
American Imperialism AP PARTS From LEGACION DE ESPAÑA.,WASHINGTON, D.C. To His Excellency, Don José Canalejas (Spanish Foreign Minister) The situation here remains the same. Everything depends on the political and military outcome in Cuba... Until then, nothing can be clearly seen, and I regard it as a waste of time and progress, by a wrong road, to be sending emissaries to the rebel camp, or to negotiate with the autonomists who have as yet no legal standing, or to try to ascertain the intentions and plans of [the US] government... Besides the ingrained and inevitable bluntness with which is repeated all that the press and public opinion in Spain have said about Weyler, it once more shows what McKinley is, weak and a bidder for the admiration of the crowd besides being a would-be politician who tries to leave a door open behind himself while keeping on good terms with the jingoes of his party.... Stirrings of Imperialism The New Manifest Destiny Attention to foreign lands, closing of the frontier Social Darwinism Admiral Alfred Thayer Mahan (1890) ‘Influence of Sea Power’ Foreign commerce, navy & colonies, Pacific bases Josiah Strong’s ‘Our Country; Its Possible Future & Present Crisis WASP values of liberty & Christianity –duty to spread them Controlling the Hemisphere Secretary of State James Blaine sought Latin American markets for excess goods Organized Pan – American Congress Leads to border dispute w/Venezuela in 1895 Control of the Pacific: Hawaii US wants naval base at Hawaii After 1840, Americans & Europeans dominated political & economic life Disease decimates 50% of native pop. SUGAR (major export); rise of plantations 1890, US eliminates sugar tariff US annexes Hawaii in Dec. 1898 Queen Liliuokalani protests Control of the Pacific: Samoa US presence since 1878, share w/ Germany & GB 1899 buys out GB & splits island w/Germany ‘you furnish me the pictures, I’ll furnish the war’ War with Spain: Causes Cuba Controversy Civil war b/w native Cubans & Spanish since 1868 Spanish General ‘Butcher’ Weyler used concentration camps against Cubans Yellow Journalism Pultizer’s NY World & Hearst’s NY Journal De Lome Letter Sinking of the Maine “Splendid little war” –Sec. of State John Hay Lasted from April to August 1898 US military not prepared –supply issues, few regular army, many soldiers had never fought in-large scale attack Racial conflicts w/ black soldiers Seizing of Philippines Comm. George Dewey ordered by Sec. of Navy, T. Roosevelt Captured Manila Bay after war declared Becomes a war to strip Spain of its colonies Battle for Cuba & Control of the Caribbean American forces land in June Fight at Santiago, El Caney & Kettle Hill (San Juan Hill) in July Rough Riders led by TR charge up San Juan Hill US takes Puerto Rico & Guam Rising anti-imperialist sentiment by Twain, Carnegie, Gompers, Sen John Sherman Armistice w/Spain –Treaty of Paris of 1898 Cuban independence Ceded PR & Guam to US Jones Act (1917) Puerto Ricans become US citizens Another source of sugar w/ no tariff US buys Philippines for $20 mil 3 years guerilla war led by Emilio Aguinaldo Islands become dependent on US goods -Effects Open Door Policy Gain concession/sphere of influence in China like other Europeans had since the 1850s Philippine occupation increased US interest in Asian markets Sec. Hay proposed “open door notes” in 1898 to European nations to allow free trade w/Chinese w/o no colonies or military Development of modern professional military; officer training schools, role of Joint Chiefs of Staff 1899 Boxer Rebellion against foreigners US military rescue Republic as Empire Panama Canal 1903 Panamanian Revolution TR sends forces ‘to maintain order’ Panama becomes independent & signs favorable treaty w/ US “Speak softly and carry a big stick’ -TR Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine (1904) US will oppose European intervention in our hemisphere US had a right to intervene in the western hemisphere to preserve order & stability ‘Dollar Diplomacy’ –Taft administration US investment in lesser developed nations Criticized by some who felt the US should intervene, especially with troops Honduras 1909; Nicaragua 1912 Now, Will You Be Good? Uncle Sam (to Filipino) — "See what I do for a good little boy?" Something Lacking. Uncle Sam: "Well, Sonny, What Is It?" Philippines: "Where Do I Come In On This?" Panama--A New Sister Republic. “The News Reaches Bogota," 1903 A Fair Field and No Favor Uncle Sam: ‘I am out for commerce, not conquest TR Big Stick http://www.authentichistory.com/1898-1913/4imperialism/7-bigstick/index.html