IMPERIALISM_2
advertisement

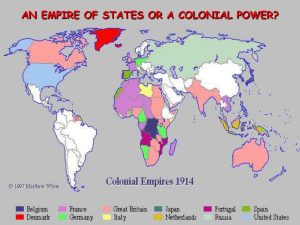
IMPERIALISM BECOMING A WORLD POWER IN THE LATE 1800s What is Imperialism? Policy of extending the rule or authority of an empire or a nation over foreign countries, or of acquiring and holding colonies Under imperialism stronger nations attempt to create empires by dominating weaker nations (economically, politically, culturally and militarily) Why did imperialism grow? Growth of industry – creates need for more natural resources (U.S. looks overseas) Nationalism – countries (especially in Europe) competition for large empires, goal to be superior over other nations Military factors – military technology led to more advanced armies and navies than those in Africa or Asia, and need for military bases Duty to spread humanitarian aid and religion (Western civilizations laws, medicine and Christian religion) Forms of Imperial Rule Colonies: direct or indirect rule of controlling nation Protectorates: local rulers left in charge, but followed the foreign advisors advice Spheres of Influence: outside power claimed exclusive investment or trading privileges Hawaii Why Hawaii? Tropical climate, fertile soil Good location for naval base and coaling station for travel to and from Asia US begins to send missionaries and grow crops (sugar) Sugar exempted from US tariffs 12 years later, US demands control of Pearl Harbor in exchange for tax free status; Hawaii refuses Force King Kalakaua to sign new constitution at gun point; US gets rights to Pearl Harbor Queen Liliuokalani tries to regain Hawaii, US Minister to Hawaii places marines around palace Queen surrenders Hawaii annexed in 1898, despite opposition of most of Hawaii’s population Became territory in 1900 and 50th state in 1959 Becoming a World Power EVENT/ AREA DATE OF EVENT Spanish- 1898 American War: “A Splendid Little War” Treaty of Paris 1898 Philippine 1899 Islands SUMMARY OF EVENTS OUTCOME OF INCIDENT AFFECT ON THE NATIVE PEOPLE -The de Lome letter - Explosion of the USS Maine -Preparing in the Philippines - War against Spain -Fighting in Cuba and the Philippines -U.S. destroyed the Spanish Navy - Thought the Americans were helping but found themselves under a new ruler -Spain recognized - U.S. gains new “unincorporated territories” - Caused debate in the U.S. over acquiring new territories Cuba’s independence -Sold the Philippines, Puerto Rico and Guam to the U.S. for $20 mil. -Filipinos declare independence from the U.S. - U.S. v. Filipinos - U.S. wins (Cuba, Philippines, Guam and Puerto Rico) - U.S. will control the Philippines until 1946 - Filipinos are unhappy and continue to fight sporadically until 1946 1898 1900 1900 -America established a military gov’t. after Spain was defeated - Platt Amendment - U.S made military bases and kept right to intervene in Cuba’s affairs - Cubans feel betrayed -U.S. established a military gov’t. - slowly gave them their independence -1917, Jones Act - Puerto Ricans can be U.S. citizens - Still under U.S. control Hawaii 1893 -U.S. used Hawaii for trade and Pearl Harbor - overthrew Queen Liliuokalani -U.S. annexed Hawaii (1898) - People very unhappy Samoa 1878 1899 -three-power protectorate, U.S., Germany and Britain - Britain pulls out in 1899 - U.S. acquired the harbor at Pago Pago - Open Door Policy in China for trade with all other nations -continued Cuba Puerto Rico Open Door 1899to China 1900 open trade policy with china - Chinese unhappy with foreign involvement (Boxer Rebellion)