SBI4U - Macromolecules 1
advertisement

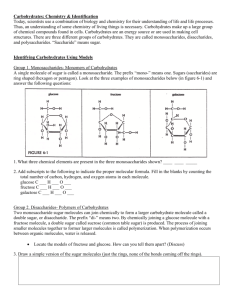
SBI4U - Biochemistry Macromolecules Carbohydrates & Lipids Organic Chemistry • originally the chemistry of compounds produced by living organisms • in general organic compounds contain carbon and hydrogen, and usually other elements such as nitrogen, sulfur and oxygen Electronegativity Homework, p.18 #9,8 • In a bond between nitrogen and hydrogen (N-H), which atom will the electrons be closer to? Explain your reasoning. • How do polar covalent bonds and nonpolar covalent bonds differ? Homework, p.18 #10 • Oxygen plays a major role in biological molecules. Explain how oxygen plays a role in polarity, bond shape, (and redox reactions). Polar vs. Non-Polar • molecular polarity is determined by: – polarity of bonds within molecule – symmetry of molecular structure • polarity of molecules or functional groups determines characteristics such as solubility Homework, p.18 #6,7 • How can the atomic composition and shape of a molecule affect its polarity? • What effect to the polarity, size, and shape of molecule have on the physical properties of the molecule? • How do these factors affect intermolecular forces? Homework, p.24 #1,5 • Water is a polar molecule. Explain how the polarity of water accounts for its lattice structure. • How does polarity influence water’s role as a solvent? H-bonding Homework, p.18 #11 • In what ways do hydrogen bonds produce attractive forces between molecules? Include a labelled diagram to illustrate your answer. • How do hydrogen bonds influence the physical properties of water? Functional Groups • specific clusters of atoms attached to the carbon backbone • functional groups react in characteristic ways, giving chemical properties to macromolecules, and are involved in most reactions in living organisms Functional Groups Homework, p.28 #4 • Explain how functional groups influence solubility and the forces of attraction between molecules. Macromolecules • macromolecules are large molecules that are often composed of repeating sub-units • some of the biologically important macromolecules are: – carbohydrates – proteins -lipids -nucleic acids Carbohydrates • carbohydrates are the most important energy source • animals cannot synthesize carbohydrates; they must be consumed in plant material Structure of Carbohydrates • carbohydrates are made up of either single sugar molecules, or chains of many single sugar molecules – monosaccharides – disaccharides – oligosaccharides – polysaccharides Monosaccharides • single sugars in straight chain or ring form • C:H:O usually in 1:2:1 ratio (glucose is C6H12O6) • examples: fructose, galactose, ribose, deoxyribose Monosaccharides • some monosaccharides are isomers, e.g., glucose, fructose, and galactose Disaccharides • sugar molecules made from 2 single sugars • formed by a dehydration synthesis (condensation) reaction • See animation: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UyDnn D3fMaU Find the sugars… Polysaccharides • oligosaccharides are shorter-chain sugars with 3-10 single sugars • longer chain carbohydrates are called polysaccharides • examples: starch, cellulose, glycogen, chitin Polysaccharides Lipids • 4 groups: – – – – fats & oils phospholipids steroids waxes • Functions: – – – – energy storage insulation absorption of vitamins raw materials Triglycerides • most common type of fat • glycerol + 3 fatty acid molecules • saturated and unsaturated fatty acid chains • See animation: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3xF_L K9pnL0 Phospholipids • key component of cell membranes • 1 glycerol + 2 fatty acid chains + 1 phosphate group • phosphate end is polar and watersoluble, fatty acid end is non-polar Phospholipids Steroids (Sterols) • carbon-based multiple-ring structure • used to make hormones such as estrogen and testosterone Waxes • long-chain fatty acids linked to alcohols/carbon rings • suitable as waterproof coating for plant leaves, animal feathers, etc.