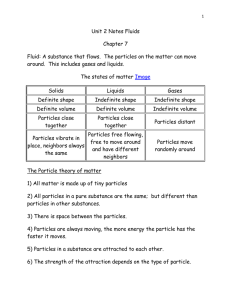
Unit 3 - Section 5.1 2014 States of Matter
advertisement
Grade 9 Academic Science – Chemistry Particle Theory and Physical Properties of Matter Section 5.1 and Section 5.2 Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. NOTE: In the entire universe, anything . can be classified as either matter or energy. The Particle Theory of Matter 1. Matter is made up of tiny particles: atoms and molecules 2. Particles of matter are in constant motion 3. Particles of matter are held together by very strong electrical forces 4. There are empty spaces between the particles of matter that are very large compared to the particles themselves. 5. Each substance has unique particles that are different from the particles of other substances 6. Temperature affects the speed of the particles. The higher the temperature, the faster the speed of the particles. The particle theory of matter explains the following scientific phenomena. 1. Pure substance are homogeneous (one phase - one unique kind of particle) 2. Physical Changes such as melting, evaporating, sublimating, dissolving, etc. 3. Physical Properties including density, viscosity, electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, boiling point, melting point, etc. We are concerned mainly with the three primary states of matter: (1) solid, (2) liquid and (3) gas. Task Use your textbook to complete Table 1. Table 1. Physical Properties of Each State of Matter Property Solid Liquid Gas Shape Volume Ability to flow Can be compressed Volume change with heating Physical Properties A physical property is a characteristic of a substance that can be determined without changing the composition of the substance. They can be either qualitative (not measurable, descriptive) or quantitative (measurable such as mass) Table 2. Examples of Physical Properties Physical State Solid, liquid, gas Colour Green, blue, yellow, reddish-brown, etc Odour Odourless, spicy, nauseating, etc. Clarity Ability to let light through - clear, cloudy, opaque Lustre Shiny, dull Form Regular (crystalline), irregular (amorphous) Texture Fine, coarse, smooth, waxy, etc. Hardness Ability to be scratched easily…scale 1-10 (e.g., diamond – 10) Brittleness Ability to break apart / Shatter easily Malleability Ability to be folded into different shapes Ductility Ability to be stretched Viscosity Ability to flow or pour readily Electrical Conductivity Ability to allow electric current to pass through it Properties of Matter 1. Match the description with each of the physical properties listed below by placing the appropriate letter in the blank _________ “feel” of a substance A. Physical state _________ hammered into a sheet _________ ketchup stuck in a bottle _________ ice _________ a frosted window in a bathroom _________ fermented milk _________ stretching gold into a thin, long wire _________ sour, sweet and salty _________ a diamond reflecting light _________ a diamond etching in glass _________ copper burning green when in a flame B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. Odour Clarity Texture Viscosity Malleability Taste Hardness Colour Lustre Ductility 2. Write the physical property beside each of the following The sheet of glass is clear The sandpaper feels rough The milk tastes sour The cold syrup flowed very slowly The powder is blue-gray Her perfume is very strong The molten steel was stretched into a wire Mercury is a liquid at room temperature The sheet of gold foil was hammered very thin by the artist The diamond sparkled brilliantly 3. Describe each of the following objects using three different physical properties A pearl A snowflake A lemon Aluminium foil