What is matter?
advertisement
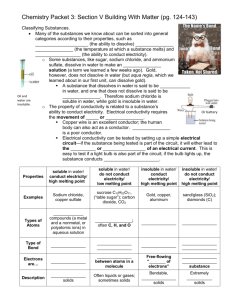
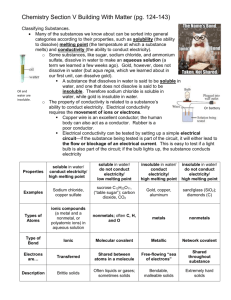
Chemistry Last year you were expected to: •Classify matter based on its physical properties including magnetism, physical state, and the ability to conduct or insulate heat, electricity, and sound; •Demonstrate that some mixtures maintain the physical properties of their ingredients; •Identify changes that can occur in the physical properties of the ingredients of solutions such as dissolving sugar in water ; and •Observe and measure characteristic properties of substances that remain constant such boiling point and melting point. Everything in the universe is made of matter. Some examples of matter are water, soil, air, and even you. What is matter? Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space (volume). Matter is identified by its physical properties. What is a property? Properties are the characteristics of matter. What is a physical property? A characteristic of a substance that can be observed with the five senses or measured without changing the substance into something else is called a physical property. Some common examples of physical properties of matter are odor, taste, hardness, texture, color, shape, mass, and volume. What is mass? Mass is how much matter is contained in an object. It is measured in grams using a balance. What is volume a measurement of? Volume is a measurement of how much space an object takes up. Volume of a rectangular prism can be found by multiplying length x width x height using cm3. Volume of a liquid is measured in a graduated cylinder using the metric unit milliliters. Volume of irregular objects can be found by dropping the object into a graduated cylinder containing water and measuring the change in the volume of water. This method is called water displacement. 1 mL = 1 cm3 Some other physical properties are: Magnetism is the ability of a material to exert a force that either attracts or repels other materials. Some well know materials with magnetic properties are iron, some steels, and the mineral lodestone. The state of matter a substance is in is another example of a physical property. There are 5 states (or phases) of matter. The most common are solid, liquid, and gas. The other two are plasma and BoseEinstein condensate. A substance can change states by adding or taking away energy. Each state has definite characteristics. A solid has a definite shape and volume. A liquid has a definite volume but takes the shape of the container it is in. A gas takes the volume and shape of the container it is in. Read more @ http://www.chem4kids.com/files/matter_intro.html Each substance has a specific boiling point, melting point, and freezing point. Boiling point is the temperature where a substance changes from a liquid to a gas. Melting point is the temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid. Freezing point is the temperature at which a liquid changes to a solid. Melting, Freezing, and Boiling Point of Common Substances Substance Melting/Freezing Point Boiling Point Water 0°C 100°C Hydrogen -259°C -253°C Oxygen -219°C -183°C Alcohol -112°C 78°C Ammonia -78°C -35.5°C Gold 1,063°C 2,600°C Mercury -39°C 357°C Olive Oil -6°C 300°C Another physical property is a substances ability to conduct or insulate heat, electricity, and sound. Metals are good conductors of heat, electricity, and sound. Plastic, fiberglass, rubber, Styrofoam, and cotton are examples of good insulators. Some other physical properties are: Brittleness – substance is easily broken or shattered chalk Ductility – ability to be drawn into a wire Malleability – can be hammered or pressed without breaking Elasticity – stretches Luster – quality or condition of shining by reflected light dull shiny Electrolyte - liquid that conducts electricity Viscosity – the resistance of a liquid to flowing under applied force Opacity – the degree to which a substance reduces the passage of light opaque vase Transparency – the degree to which a substance freely permits the passage of light transparent butterfly transparent vase A mixture is a composition of two or more substances that are not chemically combined with each other and are capable of being separated. Heterogeneous mixtures do not have a uniform composition or even distribution of each substance in the mixture. birdseed fruit salad Coke with ice air oil & water Solutions are mixtures with the molecules in a completely even distribution making them homogeneous. Salt mixed with water creates a solution because the salt will evenly distribute throughout the water molecules. This solution can be separated by evaporating the water leaving the salt behind. Solutions can be solids dissolved in liquids or even gases dissolved in liquids. There can also be gases in other gases and liquids in other liquids There are two parts to a solution. A solute is the substance that gets dissolved. The solvent is the substance that does the dissolving. In the example of the salt and water solution, the salt is the solute and the water is the solvent. solute = salt solvent = water 6th grade Objectives: In sixth grade you are expected to: •Demonstrate that new substances can be made when two or more substances are chemically combined and compare the properties of the new substances to the original substances; •Classify substances by their physical and chemical properties; and •Define matter and energy. What is matter? Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space (volume). What is a chemical property? A chemical property is a characteristic that is observed when a substance interacts with another substance. An example of a chemical property is the way some substances burn and some do not called flammability. Another chemical property is reactivity. Some substances that chemicals react to are water, oxygen, light, electricity, heat, and acids. Describe a physical change. A physical change is a change in the appearance of matter, like size, shape, or state, but the type of matter is unchanged. What are some examples of physical changes? Some examples of physical changes might be chopping wood, bending wire, sugar or salt dissolving in water, and ice melting. Describe a chemical change. A chemical change is a change that produces a new substance with properties that are different from the original substances. Chemical changes usually release energy in the form of heat, light, or electricity. A substance going through a chemical change can change color. Give some examples of chemical changes. Some examples of chemical changes are milk souring, burning wood, iron rusting, and a cake baking. What is required for physical and chemical changes to occur? Energy is required for matter to move, react, or transform in physical or chemical changes. What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. What is an acid? An acid is a substance that has a sour taste and is corrosive. What are some examples of an acid? Lemon juice, vinegar, citric acid, and HCl or hydrochloric acid are examples of acids. What is a base? A base is a substance that feels slippery, tastes bitter, and denatures proteins. What are some examples of bases? Laundry detergent and shampoo are examples of bases. What is an indicator? An indicator is any chemical that changes color in an acid or a base. What is an example of an indicator? BTB, Universal Indicator, Phenol Red, and Red Cabbage Juice are examples of indicators. Describe an element. An element is a type of substance with only one kind of matter. What is a substance called that has more than one kind of matter? A compound has more than one kind of matter. Water (H2O) and salt (NaCl) are examples of compounds.