Chemistry Packet 3: Section V Building With Matter (pg. 124
advertisement
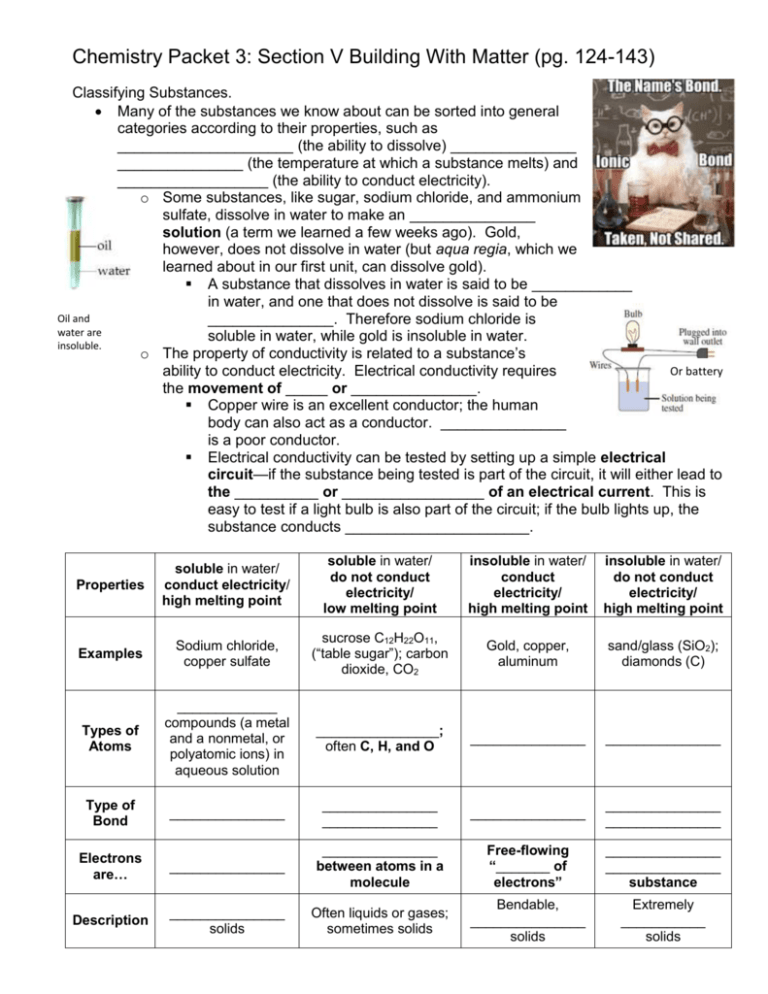
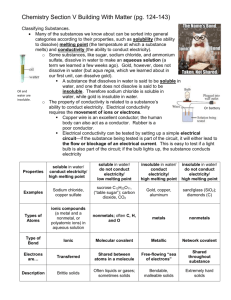
Chemistry Packet 3: Section V Building With Matter (pg. 124-143) Classifying Substances. Many of the substances we know about can be sorted into general categories according to their properties, such as _____________________ (the ability to dissolve) _______________ _______________ (the temperature at which a substance melts) and __________________ (the ability to conduct electricity). o Some substances, like sugar, sodium chloride, and ammonium sulfate, dissolve in water to make an _______________ solution (a term we learned a few weeks ago). Gold, however, does not dissolve in water (but aqua regia, which we learned about in our first unit, can dissolve gold). A substance that dissolves in water is said to be ____________ in water, and one that does not dissolve is said to be Oil and _______________. Therefore sodium chloride is water are soluble in water, while gold is insoluble in water. insoluble. o The property of conductivity is related to a substance’s Or battery ability to conduct electricity. Electrical conductivity requires the movement of _____ or _______________. Copper wire is an excellent conductor; the human body can also act as a conductor. _______________ is a poor conductor. Electrical conductivity can be tested by setting up a simple electrical circuit—if the substance being tested is part of the circuit, it will either lead to the __________ or _________________ of an electrical current. This is easy to test if a light bulb is also part of the circuit; if the bulb lights up, the substance conducts ______________________. Properties soluble in water/ conduct electricity/ high melting point soluble in water/ do not conduct electricity/ low melting point insoluble in water/ conduct electricity/ high melting point insoluble in water/ do not conduct electricity/ high melting point Examples Sodium chloride, copper sulfate sucrose C12H22O11, (“table sugar”); carbon dioxide, CO2 Gold, copper, aluminum sand/glass (SiO2); diamonds (C) Types of Atoms _____________ compounds (a metal and a nonmetal, or polyatomic ions) in aqueous solution ________________; often C, H, and O _______________ _______________ Type of Bond _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ Electrons are… _______________ _______________ between atoms in a molecule Free-flowing “_______ of electrons” _______________ _______________ substance Description _______________ solids Often liquids or gases; sometimes solids Bendable, _______________ solids Extremely ___________ solids Packet 3 Example 1: Predicting Properties Predict whether the following substances will dissolve in water, and whether they will conduct electricity. Lead soluble / insoluble conduct / not conduct Potassium bromide soluble / insoluble conduct / not conduct Bonding Chemists call the attraction that holds atoms together a __________________ ______________. Several types of bonds exist, and they all involve electrons in some way. Carbon dioxide exists as separate CO2 molecules; silicon dioxide exists as a network of silicon and oxygen. We’ve seen that most substances can be divided into four categories based on their physical properties. These categories can be explained by different models of _______________. You can see these in the table on the previous page. Some properties are directly related to the _______________ of bonds the atoms in the substances have. Therefore, it is possible to match the bonding with the _______________ _______________ observed in different substances. o _______________ requires the movement of charged particles. Ionic substances in aqueous solution contain free-moving _______________ and _______________, so they conduct electricity. Metallic substances conduct electricity because their valence electrons are ____________ ____ __________ within the solid. Network covalent substances and molecular covalent substances ____ ________ contain ions or transfer electrons, so they do not conduct electricity. o _______________ _______________depends on the attractive forces between the particles. The higher the melting point, the stronger the attractive forces. Packet 3 Example 2: Identifying Types of Bonds Determine the type of bond in each of the following substances. Then decide the physical properties each substance would have. Substance Type of Bond Soluble in Conducts Electrons Description water? electricity? are… Magnesium chloride, MgCl2 Rubbing alcohol, C3H8O Electroplating Metals Most metals are dug out of the ground as ionic compounds (_______________); in other words, they cannot be found in nature in their _______________ forms. Through the ages, people have struggled to extract the pure metals from these ores; some are easier to purify than others. o Despite being the third most common element in Earth’s crust, _______________ was one of the most difficult metals for scientists to isolate. It was first purified in 1827 by a German chemist named Friedrich Wöhler. Processing aluminum was still difficult and inefficient, making it more expensive per ounce than ______________ for quite some time. Napoleon III famously let only his favorite guests use his aluminum cutlery, while the rest had to use gold. The Washington Monument was also capped with aluminum which (at the time) was as expensive as silver. It was not until the advent of _____________________ (running an electric current through aluminum ore), that the isolation of aluminum became more efficient, therefore dropping the price of aluminum. _______________ can be used to extract metal from compounds by “giving” electrons back to metal ions, which converts them to neutral metal atoms. This process is called _______________________. o Ex. Copper metal can be extracted from a copper sulfate solution by running an electrical current through the solution.