Pharmacy Technician*s Course. LaGuardia Community College
advertisement

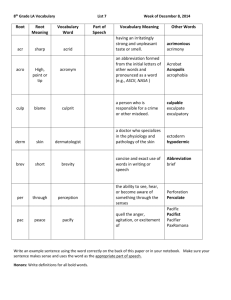
Terminology and Abbreviations Every profession has its own unique language. In the worlds of finance, accounting and equity markets, analysts look at P & L statements, statements of cash flow, accounts receivables, etc. The medical professions have their own unique language. These terms are usually combinations of prefixes, root words, and suffixes. The terms have their roots in Greek and Latin. Prefix A word that when attached to the beginning of a root word modifies it in someway. i.e. Bio means “life” from the Greek word bios (βίος) If you add this to logy meaning “study of” from the Greek logos (λόγος) you get biology meaning “study of life” i.e. geront0 means “old” from the Greek word, γέρων (geront) meaning old man and you add this to logy you get gerontology, meaning the study of the social, physiologically and mental aspects of aging. Geriatrics is the branch of medicine that studies disease in elderly people. A harder one: glio means “gluey” in Greek and glial cells in the brain refers to cells that support other cells in the brain. Blasto comes from a Greek word meaning “sprouting” and refers in science to a developing cell. When this two prefixes are added to “oma” (typically refers to cancer cells) you have the word glioblastoma meaning a cancer of young glial cells in the brain and is the most highly malignant type of brain cancer. Important Prefixes for pharmacy “an” means without/ example: anesthesia “ante” means before/example: anterior “anti” means inhibit/example: antibiotic “brady” means slow/ example:bradycardia, slow heart rate “Contra” means against/ example: contraindicated “dys” means abnormal/ example: dysmorphic, abnormal shape “hyper” means too much/ example: hyperkalemia, too much potassium “hypo” means too little/ exampe: hypokalemia, too little potassium in the blood “Intra” means within/ example: intradermal (within the skin), intervenous (within a vein) “micro” means very small or can mean (1 per 1,000,000) in the metric system i.e. microgram (one millionth of a gram) “neo” means new/ neonate is a newly born baby. “poly” means too many/ polypharmacy is used to mean the practice of prescribing to many medications for the same purpose. “Sub” means below/ sublingual means below the tongue. Subcutaneous means below the skin Tachy means fast/Tachycardia is a rapid heart rate Important root words in Pharmacy ROOT MEANING EXAMPLE Arter Artery Arterial Arthr Joint Arthritis Bronch Airway in the lung Bronchitis Carcino Cancer Carcinogen Cardi Heart Cardiac Derma Skin Dermatitis Enter Intestine Enteral nutrition Gastr Stomach Gastric pain Gluco Sugar Glucometer Hemo Blood Hematology Important Root words in Pharmacy ROOT MEANING EXAMPLE Hepat Liver Hepatitis My Muscle Myalgia Nasa Nose Nasal Nephr Kidney Nephrology Neur Nerve Neurology Oste Bone Osteoporosis Pneu Lung pneumonia Procto Rectum Proctotitis Pulmo Lung Pulmonary Ren Kidney Renal Thromb Clot thrombosis Suffix A suffix is a word that is added at the end of a root word to indicate or qualify its meaning. For example, arthr (joint) plus itis yields the word arthritis which meaning inflammation of a joint. Important pharmacy related suffixes SUFFIX MEANING EXAMPLE Ac Pertaining to Cardiac Al Pertaining to Renal Algia Pain Myalgia Ase Enzyme Protease Cyte Cell Hepatocyte Ectomy Surgical removal Hysterectomy Emia Blood condition hyperkalemia Itis Inflammation Hepatitis Logy Study of Cardiology Rrhea Flowing discharge Diarrhea, rhinorrhea Uro Urine Urology General Pharmacy Abbreviations Meaning Abbreviation Adverse drug reaction ADR Average wholesale price AWP Controlled release CR Discontinue DC Dispense as written DAW Drug utilization review DUR Enteric coated EC Extended release ER Fluid Fl. Maximum allowable cost MAC No known drug allergies NKDA Nothing by mouth NPO General Pharmacy Abbreviations Table 2 MEANING ABBREVIATION Over the counter OTC Pediatric Ped Prescription Rx Schedule 1 CI Schedule 2 CII Schedule 3 CIII Schedule 4 CIV Schedule 5 CV Solution Soln Suppository Supp Wholesame acquisition cost WAC Case in point In 2001, a case was report to the FDA via medwatch, see article, http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/DrugSafety/MedicationErrors/UCM080654 The case involved an infant transferred from an obstetrics unit to a nursery for well babies with an order for DTO 0.7 ml PO q4h. The pharmacist in the case recognized the order as deodorized tincture of opium USP, which has a concentration of 60 mg/ml morphine. The prescribed dose translates into give 0.7 ml (42 mg) by mouth every four hours. This dose is 252 mg per day of morphine, a dose that can kill or send a newborn baby to the nicu for respiratory arrest. The pharmacist verified the order as diluted tincture of opium which is 25 fold dilution of the original drug. The actual dose is 0.7 ml(1.6 mg) by mouth every four hours. Most commonly abbreviated medical conditions you will see Medical Conditions Abbreviation Common meaning Myocardial Infarction MI Heart attack Congestive Heart failure CHF Heart muscle is dying Atrial fibrillation AFib A cardiac heart beat that is fast and abnormal Ventricular Fibrillation VF A cardiac heart beat that is fast and almost always fatal Cerebral Vascular Accident CVA Stroke/loss of blood flow to brain Diabetes Mellitus DM A disorder of carbohydrate metabolism Hypertension HTN High blood pressure Medical Conditions Abbreviation Common meaning CABG Coronary artery bypass graft Surgery to re-establish blood flow to the heart ATN Acute tubular necrosis A disorder of the kidney RA Rheumatoid Arthritis A joint disease that effects older people RI Renal Insufficiency Poorly functioning kidneys PE Pulmonary Embolism A blood clot that travels to the lung DVT Deep vein Thrombosis A blood clot in the leg that often travel to the lung Not an all inclusive but include very common conditions Medication Abbreviations Abbreviation Drug Indication ASA Aspirin Pain, post MI use APAP Acetaminophen Pain, fever reducer in children 5FU Flurouracil Anti cancer drug SMX/TMP Sulfamethoxazole/trimeth oprim Antibiotic HCTZ Hydrochlorothiazide diuretic INH Isoniazid Anti-TB (tuberculosis) drug 6-MP 6 mercaptopurine Immune suppressant Medication Abbreviations Abbreviation Drug Indication NTG Nitroglycerin Chest pain (angina) SSKI Super saturated potassium iodide Hyperthyroidism T4 Levothyroxine (synthroid®) hyperthyroidism KCL Potassium chloride Potassium deficiency MgSO4 Magnesium Sulfate Magnesium deficiency MSO4 Morphine sulfate Pain killer PCN Penicillin antibiotic Medication Abbreviations Abbreviation Drug Indication AZT Zidovidune HIV NS Normal Saline IV fluid D5W Dextrose 5% in water IV fluid D5WNS Dextrose 5% in water with normal saline IV fluid MVI Multiple vitamins Vitamin replacement ISDN Isosorbide dinitrate Chest pain MTX Methotrexate Cancer drug Most Common Sig Codes in Pharmacy Sig Code Meaning Sig: Let it be written PC Post Cena (after meals) AC Ante Cena (before meals) UD As directed Ad lib As desired PRN As needed HS At bedtime Qd daily Sig Meaning Q Every Q+blank+H Every blank hours BID Twice a day TID Three times a day QID Four times a day QOD Every other day QW Every week (once) BIW Twice a week TIW Three times a week Common Routes of Administration Route Meaning PO By mouth SL Sublingually BU Buccally INH or IN Inhalation IVP Intravenous Push IVPB Intravenous Piggyback IM Intramuscular SC or SubQ Subcutaneously Opth Via the eyes Route Meaning OT Otic (via ears) PR Rectally PV Vaginally EX Topically IP Intraperitoneal Uncommon Routes of administration Certain routes are not commonly used Often to avoid confusion and the potential for error the routes are spelled out on medical orders Example 1 Epidural Medication is given just outside the spinal cord next to the dura mater. Used in cases where high doses of pain medications are needed but side effects need to be minimized. Used in obstetrics ward in women undergoing labor Used for post operative patients in PACU Example of a drug is Fentanyl 2 mcg/ml with 0.0625% bupivacaine in 250 ml of NS Example 2 Intrathecal Route Involves passing the medication through the spinal cord into the subarachnoid space to allow for direct bathing of the neural tissue in the drug Intrathecal chemotherapy i.e. methothexate, cytarabine Intrathecal Baclofen in cerebral palsy patients Advantages are that very small amounts of drug can be used leading to less side effects Disadvantages are high risk for infections and inadvertent overdoses Epidural Injection Courtesy of: http://richardspatafora.com/2011/05/19/lumbar-epiduralcortisone-injection/ Common Abbreviations for quantities Abbreviation Meaning Mg Milligrams G Grams Gr Grains Ml Millilter L Liter Fl. OZ Ounces (fluid) Tab Tablets mEq Milliequivalents Tsp Teaspoon TBSP Tablespoon cc Cubic centimeter (= 1 ml) Gtt(s) Drop(s) JCAHO’s Minimum Do not use List In 2004, JCAHO published its minimum do not use list which the joint commission encourages health care institutions it accredits to use (at a minimum) Abbreviation Problem Preferred IU Mistaken as IV or 10 International units MS, MSO4 or MgSO4 Confused for each other Morphine sulfate/magnesium sulfate Q.D. and QOD Confused for each other Daily and every other day Trailing zero and no preceding zero (3.0 or .3) 10 fold overdose possible 3 or 0.3 U Look like 0 Use “units” Mistake for mg Write microgram Mistaken for every hour Write at bedtime g HS or qHS Abbreviation Problem Preferred AS, AD, AU and OS, OD, OU Mistaken for each other Use “left eye”, “left ear”, etc DC or D/C Mistaken for discontinue meds Write discharge Cc Mistaken for zero’s Write mls SC or SQ Mistaken for SL or 5 every Use subQ or write subcutaneously TIW Mistaken for three times a Write three times a week day Less commonly known pharmacy terminology Term Meaning Analgesic A drug for pain Anorectic A drug for appetite suppression Analeptic A drug that stimulates the CNS IV Admixture A drug product made by adding the drug to an IV bag Anesthetic A drug that block sensations of pain or feeling in general Anaphylactic Shock A severe allergic reaction to a drug Anticoagulant A drug that blocks blood clotting Antitussive A drug that blocks coughing Antiemetic A drug that stop N/V Antipruritic A drug that stop itching Term Meaning Aseptic Techniques Techniques used in making parenteral drug products that minimizes microrganism contamination Clinical Trials Mandated by the FDA for the marketing of new drugs in the US Contraindication An aspect of a patient’s condition that is not compatable with the treatment Emulsion A pharmaceutic dosage form where two immiscible liquid drugs are mixed together NSAID Non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs Corticosteroids Steroid drugs used in autoimmune conditions Glucocorticoids Same as above. Two terms are used interchangeable Neuroleptics Drugs that cause an effect on the CNS used to refer to old type of anti psychotic drugs like Haldol® Term Meaning Narcotic A drug that induces sleep (from the greek word for “stupor”) Antisialagogue A drug that dry mucus and saliva secretion. Used before anesthesia to dry secretions. NMB Neuromuscular blocker Suspension A drug dosage form that consists of suspended drug particles in aqueous solution Solution A uniform homogenous mixture of a drug in water Ointment A semisolid mixture of drug in oily solid base Troche A drug made into a lozenge dose form Tincture An alcoholic mixture of a drug with at 25% V/V alcohol Enema A drug in a fluid vehicle delivered into the rectum Term Meaning NACDS National Association of chain drug stores AphA American Pharmaceutical Association NDC National drug code issued by the FDA. The first five digits are the manufacturer; the second set of four digits are the drug, dose, dosage form; the third set of two number is the package size UPC code Barcoded drug information COGS Cost of goods sold MAR Medication administration record eMAR Electronic medication administration record ASHP American society of health system pharmacists Term Meaning Bioavailability The amount of drug that reaches the blood stream from a route of administration other than intravenous Bioequivalence The comparison of bioavailability between two dosage forms Enterohepatic circulation The excretion of the drug from the liver in the bile flow and its reaborption back to the liver First Pass The amount of drug that is metabolized by the liver before it reaches the blood, i.e. expressed as a percentage. Example is Lidocaine Geometric dilution The mixing of powder of unequal sizes Glomerular Filtration The process of kidney filtration of the blood Orange Book The FDA official collection of approved drugs OBRA 90 Omnibus budget reconciliation act of 1990 which require pharmacist’s counseling Term Meaning Enteral or Alimentary Describes the organs of digestion and nutrient absorption from the mouth to the anus Aseptic technique A technique used in the manipulation of a IV products to maintain their sterile condition USP 797 A standard published by the USP to provide guidance in the use of aseptic technique Auxiliary Label An extra label placed on a dispensed product that may add information for the patient Extemporaneous Compounding The preparation of a patient specific drug product Hypersensitivity Equal to allergic drug reaction; anaphylaxis is the most severe type Teratogenicity A characteristic of drug that produces known birth defects