Nervous Tissues
advertisement

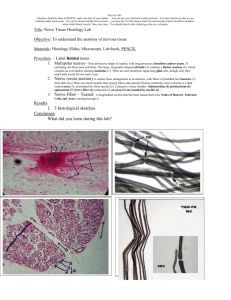
Nervous Tissues Department of Biology Introduction Nervous tissues are formed of cell specialized to receive external and internal stimuli and to transmit them between different parts of the body. Coordination of the different activities of body organs. Introduction Originate from the ectoderm. The cells become differentiated in one of 2 way: 1. Some ectodermal cell differentiated into neuroblasts. Multiply actively and transform gradually into nerve cells (neurons) do not multiplication. 2. Other ectodermal cell differentiated into spongioblasts. Continue modification forming neuroglia cells (bind and protect the neurons) Structure of the nerve cell The nerve cell or Neuron consist of two parts: The cell body (Cyton). Cytoplasmic processes: 1. Dendrites, receive the stimuli and transmit the impulses to the nerve cell body. 2. Axon, extend from the cell body and ends in a number of small branches (terminal arborizations) carry the nerve impulses from the nerve cell outwards. The axons of several neurons collect together to form Nerves. Cell body (Cyton) Located in certain nervous organs (brain, spinal cord and nerve ganglia. From these organs nerves extend to different tissues. The cytons differ in size and shape, some few microns and other hundreds microns in diameter. May be round, ovoid, spindle, star-shaped Cell body (Cyton) The cell body contain central spherical nucleus with one or more nucleoli. Cytoplasm contains: Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, lysosomes as well as other common cytoplasmic organelles and inclusions No centriole. Cell body (Cyton) Nissel bodies: granules, found also in dendrites, but not in axons, rich in ribonucleic acid. Neurofibrils: fine threadlike structure, form network, provide pathway for the nerve impulses within nerve cells. Nerve Fibers Nerve fiber consists of an axis cylinder surrounded by myelin sheath. This layer covered by neurilemma. Node of Ranvier Internode. Nerve Fibers Schwann’s cell, responsible for the formation of myelin sheath and neurilemma. Nerve Fibers The nerve fibers two types 1. Meduullated nerve fibers have myelin sheath, found in cranial and spinal nerves. 2. Non -meduullated nerve fibers which lacks myelin sheath. Found in the sympathetic nerves. Nerves A nerve consist of bundles of myelinated nerve fibers extend parallel to each other. Each nerve fiber appears circular in cross section and the axon in the center Endoneurium: Loose C.T.surround the nerve fiber. Perineurium: C.T. surround the nerve bundle. Epineurium: C.T. surround the whole nerves Peripheral Nerve (cross section) 40X epineurium perineurium Spinal Cord 1. 2. Surrounded by C.T., pia mater and has central canal. Dorsal fissure above the central canal and ventral fissure below it. The substance of the cord is differentiated into: Inner region Gray matter with 2 dorsal horns and 2 ventral horns. This region contains nerve cell bodies and some dendrites all supported by neuroglia cells. White matter surround the gray matter, composed of myelinated nerve fibers supported by the neuroglia projecting from the gray matter.