Distillation Lab distillation_lab2
advertisement

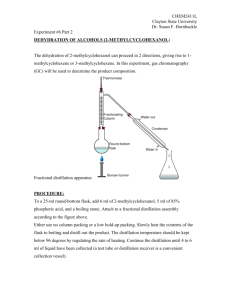
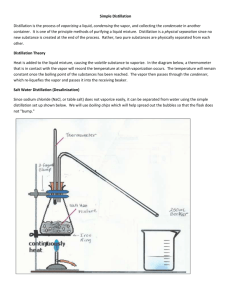
Distillation Lab How Distillation Works • Distillation separates liquids based on their different boiling points. • Liquids are boiled and then recondensed in a separate location. • Water is distilled to remove its impurities. • Processing of crude oil is mostly distillation. Gases like propane boil off at less than 40oC, gasoline boils off from 40-200oC, kerosene boils off from 2-300oC, diesel boils off from 250350oC, etc. Lab Procedures I 1. Remove the 250 ml round bottom flask. 2. Use the graduated cylinder to add 25 ml of isopropanol and 25 ml of tap water. 3. Add 4 fresh boiling chips and 2 drops of food color. 4. Reconnect the 250 ml flask. 5. Turn on the water as low as possible. 6. Turn on the hot plate as high as possible. 7. Place a bowl of ice water around the collection flask. Lab Procedures II 6. Set up the temperature probe on the Labpro. 7. Set the temperature probe at the intersection above the boiling flask. 8. *Record the time, temperature and observations every 60 seconds in each individuals notebook. 9. *Sketch the distillation apparatus between measurements and figure out the role of water. 10. The temperature will flatten out while boiling for several minutes. 11. When it rises 3 more degrees, turn off the heat and move the hot plate to stop the boiling. Lab Procedures III 10. Place the collected distillate in the collection bottle labeled 88% Isopropanol. 11. Place the colored liquid remaining in the boiling flask in a bottle labeled “Waste Bottoms.” 12. Reattach all the flasks securely. Lab Analysis • Prepare a graph using Excel. Select XY scatter and connect the dots with curved lines. • Label observations on your graph with text boxes. • Print and tape a copy of the graph in each person’s lab notebook. • Answer the following questions in your lab notebook. Distillation Lab Questions 1. Describe the physical changes that isopropanol does in order to move to the collecting flask. 2. What is the role of water from the faucet? 3. How is the isopropanol extracted or purified from the water & food color in this process? 4. Find out 3 uses of distillation. 5. What are the manipulated and responding variables in distillation? Teacher Notes • High output hot plates are required. • Temperature probes need clay or electricians tape to seal the top. • Set up each distillation apparatus to rest ¼ or ½ inch above the hot plate with enough room to put ice baths below the collecting flasks. Use bricks from Phys under low hot plates. • Prepare used isopropanol to distill by taking 1 part of 88% isopropanol and mix with 1 part of water. • Waste bottoms are primarily food coloring and water with a small amount of isopropanol. • Use black rubber hoses for water connections. Water cools the vapor to liquid In the condensing tube. Thermometer measures vapor Excess pressure is released out opening. Isopropanol boils At 82.5oC, water at 100oC, food color? 44% isopropanol boiling chips Food coloring Ice condenses last of vapor to minimize escape.