introduction
advertisement

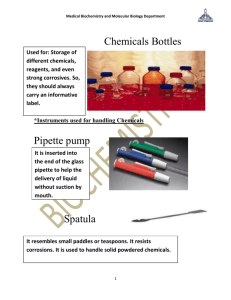
MEDI 2130 INTRODUCTION Biochemistry • Biochemistry is the application of chemistry to study biological processes at the cellular and molecular level. Biochemistry is also concerned with the study of the structure and function of cellular components, such as proteins, carbohydrates and lipids. Biochemistry is both a life science and a chemical science; it has provided explanations for the causes of many diseases in humans. • Biochemistry is the study of molecular structures and interactions in living organisms. • Biochemists seek to understand living organisms in terms of chemical reactions. Biochemistry The objective of this course: • To learn fundamental techniques used in biochemistry. • To learn some biochemical procedures and experiments commonly used in biochemistry laboratories. • To provide a basis for understanding how biochemical data is obtained, analyzed and presented. Attendance and activity midterm 10 Reports 10 Quizzes 10 Final 40 30 Safety rules 1. Listen to or read instructions carefully before attempting to do anything. 2. Clean up your lab area at the conclusion of the laboratory period. Wear lab coat • After handling chemicals, remove gloves and always wash your hands with soap and water. • Never taste any chemicals (you should never taste anything in the lab). Sign for cautions Please read the warning signs and symbols placed on the reagents. Chemical hazards 1. 2. 3. Never mix chemicals together unless you are told to do so (and then only in the manner specified). Never pour water into a concentrated acid. Acid should be poured slowly into water. Check labels on containers twice to make sure you use the right chemical and of the correct concentration. Dispose of chemicals in proper receptacle. • If you need to smell the odor of a chemical, waft the fumes toward your nose with one hand. Do not put your nose over the container and inhale the fumes. • Before leaving the lab, the workplace, reagents and equipment should be put in order. • Wash the lab glass. Close the gas valves. Turn off the taps. Team work Instruments The only type of glassware that may safely be heated is either Kimax or Pyrex. When heating a test tube, move it around slowly over the flame to distribute the heat evenly. Keep burners in the middle of the lab table, not on the edge. When heating liquids in test tubes, never point the tube toward yourself or anyone else. Never heat the test tube directly at the bottom but tilt the tube and heat it gently between the bottom of the tube and the top of the liquid. Use boiling chips when boiling liquids in a flask or beaker to prevent bumping. Droppers cylinder Balance Filter paper Test tube brush Rack Clamps • Centrifuge - separates materials of varying density. • Test tube - used as holder of small amount of solution. • Thermometer - measures temperature. • Wire gauze - used to spread heat of a burner flame. • burette - measures volume of solution. Certainty vs. Uncertainty The smallest division of this graduated cylinder is 1 mL. These values are CERTAIN. Note: There are no graduation lines between 36 and 37 mL. This value must be ESTIMATED. • The error in reading the measurement will be ± 0.1 mL or 1/10 of the smallest division. • A reading of the volume is: 36.5 ± 0.1 mL One person may read this as: 36.6 mL One person may read this as: 36.4 mL • NOTE: The value of 36 is CERTAIN The value of .5, .6 or .4 is ESTIMATED OR UNCERTAIN • The certainty of a measurement depends on the precision of the instrument. Accuracy vs. Precision • Accuracy • Accuracy is defined as the degree of conformity to the truth and expressed as absolute error. • Absolute error = experimentally measured value – true value • Precision is defined as the degree of agreement between replicate experiments and expressed as standard deviation. • Precision does not mean accuracy, since measurements may be highly precise but inaccurate due to a faulty instrument or technique. chemical reaction • A chemical reaction :change of a substance into a new one that has a different chemical. • signs of chemical reaction: 1-formation of a precipitate 2-color change 3-evolution of gas 4-temperature change Exothermic reaction :give off energy and generally cause the surroundings to get hotter Endothermic reactions: require energy and generally cause the surrounding to become cooler Types of biochemical compounds • • • • Carbohydrates Amino acids and proteins Nucleotides and nucleic acids Lipids How to make report • • • • • • • Name of test Introduction Aim Principle Procedure Results Comments