Domain Eukarya - Cloudfront.net
advertisement
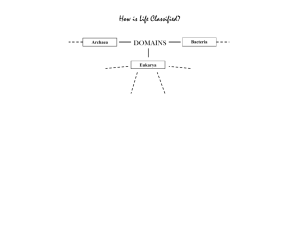
Kingdom Protista Weird things: has eukaryotic cells, so they aren’t bacteria or archaea doesn’t fit in with the fungi, plants, or animals either this kingdom is a ‘catch-all’ for things that we don’t fully understand their relationships to the rest of life Very diverse, so we tend to think of them as which other kingdom they are most like: fungus-like plant-like (algae and seaweeds) animal-like (protozoans) not classified as fungi for various reasons have a stage in their life cycle where they are mobile sometimes unicellular, sometimes multicellular most reproduce using spores Two main groups (thought there are more) Slime molds Water molds Mostly heterotrophic decomposers Many water molds are parasitic and cause numerous plant diseases, among other things Sudden Oak Death probably the most familiar protists; include algae and seaweed not classified as plants due to various reasons: some are unicellular some lack certain tissues that true plants have must live in water use photosynthesis to obtain food many different groups: diatoms euglena green, red, brown, and golden-brown algae Uses: Diatoms are used in forensics, nanotechnology, and agriculture Seaweeds are an important source of food and have applications in green energy again, not classified as animals for a variety of reasons: mostly unicellular mostly heterotrophs that live in water often grouped by how they move: flagellates (move using a flagella) ciliates (move by using cilia) amoebas (move using pseudopodia) there is an additional group that is entirely parasitic: sporozoans Giardia lamblia Paramecium Amoeba Plasmodium Relevance to people: disease: giardiasis, malaria, Chagas disease scientific research: Paramecium is used as a model organism in labs ecological: many eat bacteria, helping keep their numbers in check