Patterns of Organization
advertisement

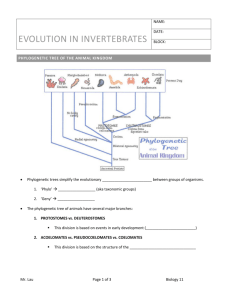
Patterns of Organization 1. ASYMMETRICAL, RADIAL, OR BILATERAL 2. UNICELLULAR, DIPLOBLASTIC, OR TRIPLOBLASTIC 3. ACOELOMATE, PSUEDOCOELOMATE, OR COELOMATE The Three Arrangement of Appendages Asymmetrical – appendages are arranged in no set pattern. Examples – sea sponges & many protists These animals do not have complex sensory, communication, or locomotor functions. Arrangement of Appendages Radial – appendages are arranged in a circular or spherical pattern Examples – octopus, sea stars, sea urchins, etc. Advantages – can sense predators or prey coming from any direction. Disadvantages – these animals are usually sedentary or have minimal locomotion. Arrangement of Appendages Bilateral – Animals with a distinct left and right side, front and back, and head and foot regions. Examples – us, dogs, whales, squirrels, tigers, etc. Advantages – have excellent locomotion. Disadvantages – can only see the world primarily in one direction. The evolution of a distinct “head” with many sensory inputs is called cephalization. Unicellular, Diploblastic, or Triploblastic Unicellular – the whole animal is just one tiny cell. Example – protists Diploblasts – Animals who only have an endoderm and ectoderm, no mesoderm. Only have tissue level organization, no real organs. Examples – jellyfish, hydra. Picture Triploblasts – animals with all three layers of tissue and true organ systems. Usually display bilateral symmetry. Examples – us, horses, cows, llamas, etc. Triplobalsts are further classified based upon whether or not they have an internal body cavity! Next slide Go back Advantages of Having an Internal Body Cavity Body cavity – a fluid-filled space in which the internal organs can be suspended and separated from the body wall. 1. provides more room for organs to grow and develop. 2. allows for an increase in overall body size. 3. provides more surface area for gas, nutrient, and waste exchange. 4. acts as a hydrostatic skeleton. Acoelomates, Pseudocoelomates, & Coelomates Acoelomates – triploblasts with no body cavity, flatworms. Pseudocoelomates – triploblasts with a body cavity that is NOT connected to their mesoderm, roundworms. Pseudo means “false”. Coelomates – triploblasts with a body cavity that IS connected to their mesoderm, most animals.