M1_prep - UCSD Cognitive Science
advertisement

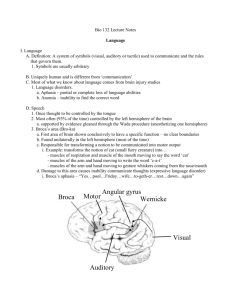
(Questions from quizzes) Coulson 14 If a patient has language localized in their left hemisphere, what would happen if they were given an anesthetic to their right hemisphere? a. The patient would be able to move their right hand only and have speech unaffected. b. The patient would be able to move their right hand only and have speech unaffected. c. The patient would not be able to move both hands and speech would be unaffected. d. Two of the above are correct. e. None of the above. Generally speaking, production of speech is lateralized such that which hemisphere of the brain is primarily involved in it? a. Left b. Right c. Language is weakly lateralized/not lateralized at all such that both hemispheres are equally involved. d. Anterior e. Posterior Which of the following is NOT a typical symptom of Wernicke's aphasia? a. Halting speech b. Difficulty in comprehension c. Reduced vocabulary d. Unawareness of garbled speech True or False: Those who suffer from Broca's Aphasia always have complete loss of ability to articulate ideas. a. True b. False Will a Wada test on the left hemisphere of the brain of a right-handed person typically result in temporary aphasia? Which side of the body would usually lose motor function? a. No; Left side b. No; Right side c. Yes; Left side d. Yes; Right side e. Not enough information to tell Broca’s Aphasic patients: a. Show no comprehension of meaning b. Speak rapidly with made-up words c. Are unaware of their condition d. Mainly rely on nouns and pronouns to express thoughts e. Exhibit repetitive speech True or False: The homunculus is a cortical representation of the body, in which the size of representation correlates with actual body size. a. True b. False Wernicke’s Aphasia is also known as ______ and Broca’s Aphasia is also known as_______ a. Expressive Aphasia/Receptive Aphasia b. Receptive Aphasia/Expressive Aphasia c. Expressive Aphasia/Talkative Aphasia d. Talkative Aphasia/Receptive Aphasia e. None of the above. The structure of fiber bundles that conveys information from one side of the brain to the other is called: a. Corpus callosum b. Broca’s area c. Brodman’s area d. Wernicke’s area e. Central sulcus Damage to which cortical lobe would be most likely to impair vision? a. Frontal b. Pre-frontal c. Parietal d. Temporal e. Occipital According to the Wernicke-Geschwind model, which sort of Aphasia is caused by damage to the area responsible for comprehending heard words? a. Wernicke's Aphasia b. Broca's Aphasia c. Production Aphasia d. Conduction Aphasia e. Wada's Aphasia The Wada test was described as a. When you anesthetize one hemisphere and test motor and speech ability. b. When you put a person under general anesthesia and examine their EEG. c. An acronym for “Working Associative Disorder Assay.” d. When you show people movies while imaging their brain. e. When you show people different sizes of cubes and ask them to match the sizes. Damage to the arcuate fasciculus leads to difficulty in the ability to repeat speech, while the patient is still able to understand and produce speech. The disorder is known as: a. Conduction aphasia b. c. d. e. Broca’s aphasia Broca-Wernicke’s aphasia Wernicke’s aphasia Wada aphasia Which of the following statements correctly describe self-awareness in different types of aphasia? a. Broca’s aphasics are aware of their deficits, while Wernicke’s aphasics are unaware of their deficits. b. Broca’s aphasics are unaware of their deficits, while Wernicke’s aphasics are aware of their deficits. c. Both Broca’s aphasics and Wernicke’s aphasics are unaware of their deficits. d. Both Broca’s aphasics and Wernicke’s aphasics are aware of their deficits. e. Broca’s and Wernicke’s aphasics will frequently indicate different levels of awareness of their deficits. Creel 14 What is language-specific refinement? a. Infants are better at distinguishing between vowels sounds as they get older compared to consonants. b. Infants are only able to learn the first language they are exposed to. c. Infants get better at distinguishing all sounds, as they get older. d. Infants become worse at distinguishing sounds that are not contrastive in their language, and better at those in their own language. e. None of the above. Three-year-old Jenny says "blowed up" instead of the (correct) "blew up." This is an example of: a. Categorical perception. b. Habituation. c. Over-pronunciation of verbs. d. Over-regularization of verbs. e. Narrative confusion. True or False: Categorical perception refers to the uniquely human innate ability to discriminate sound categories. a. True b. False True or False: As they get older, monolingual infants get worse at discriminating sounds that are not contrastive in their native language. a. True b. False True or False: Bilingual children, unlike monolingual children, do not see a narrowing of their phonemic discrimination ability around the time that they start to speak. a. True b. False When someone encounters ________ they become used to a particular event and express relatively little interest toward it. a. introspection b. visual acuity c. habituation d. primes e. aphasia" Canadian infants can distinguish German /u/ versus German /y/ at: a. 4 months b. 6 months c. 8 months d. 10-12 months" Japanese speakers have only one category for r vs. l sounds. Because they do not separate these sounds, we would expect they would not show a __________ in the same place as native English speakers. a. Category boundary b. Segmentation boundary c. Sonorant d. Frictative True or False: Children's inability to produce a sound correctly (e.g. "wif" instead of "with") reflects not knowing how the sound is actually pronounced in English. a. True b. False Using the high amplitude sucking paradigm, researchers found that babies would only respond to a 20 ms VOT difference if the difference corresponded to a phoneme boundary. A 20 ms VOT difference that didn’t span a phoneme boundary was not perceived. Eimas argued that this was evidence that: a. Human babies are not born with innate phonetic feature detectors. b. Our auditory system is particularly adapted to detect phonemic contrasts found in human speech. c. Infants are not sensitive to very subtle (20 ms) VOT differences. d. Listeners are much worse at discriminating between categories than within categories. e. Two of the above are correct. In lecture, Dr. Creel showed a video with a three year old describing the star wars narrative as an example of how children tend to speak. Which of the following was NOT a point she was trying to make about the three year old to illustrate how children tend to speak? a. She uses overregularized verb forms. b. She uses social phrases. c. She uses new words for new concepts. d. She misremembers aspects of the story line. e. She has good narrative skills True or False: Innate ability to distinguish speech sounds is a uniquely human trait. a. True b. False Using Head-turn- preference procedure, Juscyk & Hohne found the result that: a. 8-month olds remember some words they’ve heard, but only if they have an idea of what it means. b. 8-month olds do not remember any words they’ve heard c. 8-month olds remember all words that they’ve heard, even if they don’t know what they mean d. 8-month olds remember some words that they’ve heard, even if they don’t know what they mean e. 8-month olds will remember all words that they know the meaning of. Transitional probability, in Professor Creel’s lecture, was suggested to be important as a clue for a. Word boundaries b. Speaker’s excitement c. Phoneme recognition d. Specific vowels e. Predicting words Kirsh 14 Who is most likely to perform marking? a. Ballet dancer b. Cellist c. Irish river dancer d. All of the above e. None of the above In which of the following assessment categories did practicing full-out produce the best results in? a. Memory b. Technicality c. Timing d. Dynamics e. Reactivity Dr. Kirsh showed a video of two people making their fingers dance to music. Which of the following was he trying to illustrate? a. Marking b. Purely mental simulation c. Riffing d. Leakage e. Digital computation What is the phenomenon of “marking” in dance? a. Practicing movements with reduced energy. b. Marking off your designated space in the dance floor. c. A method of practicing a dance move by focusing on a specific aspect. d. Both a and c e. None of the above. What is the evidence suggesting that external structure helps thinking and performance? a. Weak visualizers spend more time to play a tic tac toe game than strong visualizers b. Weak visualizers take longer to play a tic tac toe game when they are asked to play the game with a pen on paper than via the internet c. Weak visualizers spend less time to play a tic tac toe game when they are allowed to look at a table drawing on paper than nothing on paper. d. The benefits of perception decrease as the complexity of the thing to be imagined decreases. e. None of the above. Which of the following is an example of marking? a. Fully executing a dance, as in a final performance in front of an audience b. Dancer abstracts from full phrase c. Leakage d. Purely mental simulation e. Riffing True or False: While embodied cognition mainly utilized environmental factors, distributed cognition occurs mainly in the brain. a. True b. False What were the results of Kirsh' projection experiment? a. In the 3x3, projection subjects performed worse than the imagination group, but did better than the imagination group in the 4x4 trial. b. Projection subjects performed better in both trials compared to the imagination group c. Projection subjects performed worse in both trials compared to the imagination group d. In the 4x4, projection subjects performed worse than the imagination group, but did better than the imagination group in the 3x3 trial. e. Projection subjects shown an 'X' and 'O' unanimously performed better. The following are attributes that apply to the phenomenon of marking in dance: a. Dancers use it as a technique to not fully go all out and risk injury during practice. b. Dancers represent a full dance phrase with less effort and detail in motion c. Marking is less physically expressive than mental simulation. d. a & b. e. b & c. Which of the following is considered a possible explanation for the continued use of multiple modalities in embodied cognitive processes such as the dancing discussed by Dr. Kirsh? a. Using multiple modalities helps foster creativity in the activity. b. One modality may include information on aspects the other cannot. c. “Leakage” prevents practice in only one modality. d. a & b e. None of the above. In the phenomenology of projection, perception is ____ while imagination _____. a. the interpretation of an object in our mind; is the knowledge that an object really exists b. the feeling that we are one with the object; is the knowledge that an object really exists c. seeing an object that really exists; of an object is the feeling that we are the sole cause of the experience d. a way of anchoring and object to a target; of an object is the feeling that we are the sole cause of the experience e. None of the above. What is the evidence suggesting that external structure helps thinking and performance? a. Weak visualizers spend more time to play a tic tac toe game than strong visualizers b. Weak visualizers take longer to play a tic tac toe game when they are asked to play the game with a pen on paper than via the internet c. Weak visualizers spend less time to play a tic tac toe game when they are allowed to look at a table drawing on paper than nothing on paper. d. The benefits of perception decrease as the complexity of the thing to be imagined decreases. e. None of the above. In Dr. Kirsh’s study of the effectiveness of marking compared to full practice and mental simulation among dancers, he collected data from dancers. Which of the following was NOT a performance measure in this study? a. b. c. d. e. Technicality Memory Dynamics Timing Leakage In Dr. Kirsh’s study of the effectiveness of marking, full practice, and mental simulation among dancers, which of the following did he find? a. Marking, full practice, and mental simulation were equally effective. b. Marking and full practice were equally effective, but mental simulation was not as effective. c. Mental simulation and full practice were equally effective, but marking was not effective at all. d. Full practice was most effective, followed by marking, and then mental simulation. e. Marking was most effective, followed by full practice, and then mental simulation. Elman 14 Which of the following is not a primitive form of communication? a. Kanzi the chimpanzee following cooking commands b. Vervet alarm calls c. Bee dance d. Protective coloration in butterflies e. None of the above Which of the following is true? a. There is neither a language gene nor a language organ b. There is a language organ in Broca's area c. There is a language gene controlling voluntary localiztion d. FOXp2 is a language gene e. There is no language gene, but there is a language organ in Broca's area Kanzi the bonobo can do all but which of the following: a. Understanding simple English words b. Point to lexigrams corresponding to spoken words c. Vocalize simple English words for communication d. Comprehend simple syntax in English Enculturation refers to: a. Controlled growth of bacteria in a petri dish b. Being raised in a certain cultural environment and learning about accepted behavior in that environment c. Integration of cultural values from multiple independently developed cultures d. Language learning in the context of a foreign culture The McGurk effect shows that the speech processing brain is: a. b. c. d. Opportunistic Plastic Intelligent Integrative WC3. Which of the following evidence suggests that the idea of language organ in the brain could not be right? a. A 45 yrs. old Broca’s aphasia patients have troubles articulation. b. Animals do also use languages like human. c. A 6 month old baby with his left hemisphere lesion does not show language disability when he is an adult. d. A kanzi grown up with human is capable understanding human language. e. Words and vocabulary are organized as category of concepts. WC5. The scanning project of Leborgne’s brain found different degrees of superior longitudinal fasciculus deformity in the left and right hemispheres: the left side is gone. What would this finding suggest? a. There is a language organ in the brain. b. Broca area has nothing to do with language processing. c. Not only acting area but also connecting area of brain plays a role for language processing. d. Cell morphology is highly relevant to its functionality. e. Our brain has flexibility and reorganize in the childhood. WC1. Human language is very different from other types of communication used among animals. For example, human language could use metaphors. Which of the following sentences is a good example? a. The dog the mouse sees barked. b. If I were you, I’d hate myself. c. This car is a lemon. d. The man returned to his house was happy. e. Me are six. KC5. The lecture mentioned a family that had speech impairments. After genetic testing, the researchers found that the FOXP2 gene accounted for their deficits. This was an important finding in language research because a. This showed there was a clear gene for language. b. The gene was responsible for the motor output and controlling muscles to produce language, indicating that there is a “team” of cells and connections to produce language and not just a gene or a language “area” responsible. c. The finding showed that humans are the only animals with language capability d. All of the above. e. None of the above. BT5. True or False: The basal ganglia in the brain accounts for motor movements as well aspects of sequential behavior. a. True b. False SD2. What is an example of language? a. Kanzi understanding cooking directions. b. Bee waggle dance that directs other bees to flowers. c. Humans talking in line at the grocery store. d. Protective coloration on a butterfly. e. All of the above. JS 2. The FOXp2 gene has its effect on enabling language via: a. Allowing rapid and complex movements required for controlled vocalization. b. Promoting brain development in Broca’s area and other language centers. c. Creating connections in the brain vital to developing a wide, associative vocabulary of words. d. Permitting the high-level formation and consolidation of memories required for remembering a lexicon consisting of thousands of words. e. Encouraging joint attention and other behaviors associated with normal speech development in early years. JS 3. Kanzi (the bonobo seen in the video in class) was able to follow verbal cues and help her handler to cook. Dogs are also known to follow verbal cues in many instances. According to what we discussed in class, how would these animals respond if told to do the opposite of their routine actions? a. Kanzi would respond by performing the correct (opposite) action, while a dog would perform the incorrect (routine) action. b. Kanzi would respond by performing the incorrect (routine) action, while a dog would perform the correct (opposite) action. c. Both Kanzi and a dog would perform the correct (opposite) action. d. Both Kanzi and a dog would perform the incorrect (routine) action. e. The animals will respond different to the opposite cues each time. JS 1. Humans’ ability to produce language is thanks to our superior and unique ability to: a. Imitate others’ actions b. Control our respiration c. Remember a vast amount of information d. Process auditory stimuli at a high level e. None of the above; the emergent property of language came from a combination of these factors Boyle 14 What properties contribute to movement of ions across a cell membrane? a. Diffusion of concentration. b. Selectively permeable ion channels. c. The electrical field. d. The magnetic field. e. a, b, and c What is the function of myelin? a. b. c. d. e. Faster conductance of electrical signals along the axon. Slower conductance of electrical signals along the dendrites. No conductance of electrical signals along the axon. Shortening of the axon. Elongation of the axon Which structures does the synapse involve? a. Dendrite of the pre-synaptic neuron and the dendrite of the post-synaptic neuron. b. Axon of the pre-synaptic neuron and the axon of the post-synaptic neuron. c. Dendrite of the pre-synaptic neuron and the axon of the post-synaptic neuron. d. Axon of the pre-synaptic neuron and the dentrite of the post-synaptic neuron. e. Axon hillock of the pre-synaptic neuron and the dendrite of the post-synaptic neuron. WC1. If two electrodes are both placed just outside the membrane of a resting neuron, what will be the potential difference will be measured? a. 0 b. -70 mV c. +70 mV d. -65 mV e. +50 mV WC 2. Action potentials begin by the a. Opening of sodium channels b. Closing of chloride channels c. Closing of potassium channels d. Opening of potassium channels e. Closing of calcium channels DM 2. a. b. c. d. e. What are the two forces that allow for action potentials to occur? Concentration gradient and electrostatic pressure Concentration gradient and driving force Driving force and electrostatic pressure Normal force and electrostatic pressure Normal force and concentration gradient DM 5. How many sodium and potassium ions are pumped across the membrane by the sodium potassium pump described in class, and in what direction? a. Three sodium out, two potassium in b. Three sodium in, two potassium out c. Two sodium in, three potassium out d. Two sodium out, three potassium in e. Depends on the individual sodium-potassium pump DM 4. Which component of the cell integrates all inputs to it decides whether or not the cell will communicate? a. b. c. d. e. Cell body Synapses Axon Nucleus Terminal button BT2. Which of the following is INCORRECT about the membrane potential? a. The resting membrane for most neurons is approximately -70 mV. b. The extracellular membrane has a higher concentration of sodium compared with the intercellular space. c. The extracellular membrane has a higher concentration of potassium compared with the intercellular space. d. The membrane potential must pass a certain threshold in order to fire an action potential. e. The voltage gated sodium channel opens when the potential surpasses the firing threshold. LS 1. Santiago Ramon y Cajal is famous for which of the following: a. Psychoanalysis b. Discovering that babies understand language c. Discovering Broca’s area d. Describing organization and function of neurons the cortex using golgi staining e. His extensive work in muscle movement JS 2. Early researcher Santiago Ramon y Cajal is considered one of the most important neuroscientists ever for which of these contributions to the field? a. Developing the method for production of sharp, strong electrodes for accurate measurement of neuronal potentials. b. Creating a theory of mind that helped scientists understand the way the human mind could process abstract thought about other individuals. c. Discovering and labeling areas of the brain defined by their different anatomical characteristics using a variety of stains. d. Measuring the voltage difference across neuron cell membranes as -70mV. e. Researching and proposing the neuron as the fundamental unit of the brain, and implicating their connectivity, specificity and synaptic connections as crucial to function. JS 5. True or False: Ligand-gated channel proteins are activated by ions such as Na+ and Cl-. a. True b. False JS 4. Which of the following correctly describes the chemical and electrical gradient directions for each ion? a. Na+: chemical in, electrical in; K+: chemical out, electrical in; Cl-: chemical in, electrical out b. Na+: chemical out, electrical in; K+: chemical in, electrical in; Cl-: chemical out, electrical out c. Na+: chemical out, electrical out; K+: chemical in, electrical in; Cl-: chemical out, electrical out d. Na+: chemical in, electrical out; K+: chemical in, electrical out; Cl-: chemical out, electrical in e. Na+: chemical out, electrical in; K+: chemical out, electrical out; Cl-: chemical in, electrical in SD2: What are the three functional units of the neuron listed in the order of the direction of most common electoral flow? a. Cell Body (Soma), Axon, Dendrites b. Synapse, Action Potential, Cell Body (Soma) c. Dendrites, Cell Body (Soma), Axon d. Axon, Cell Body (Soma), Dendrites