File
advertisement

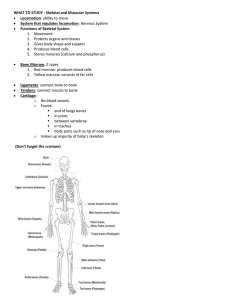
Name: _______________________________ Date: _____________________ Muscles 2 1. Skeletal Muscles (striated) 2. Smooth Muscle 3. Cardiac Muscle Antagonistic Muscles: All muscles work in pairs. Whether they are striated muscle, smooth muscle or cardiac muscle makes no difference, all muscles must work in pairs. Review Questions- Musculoskeletal System: What are the main functions of the skeletal system? Provides shape and support Protects internal organs Moves body Forms blood cells Stores calcium and phosphorous compounds for later use 2) What is the only moveable bone in the head? The mandible 3) Which bones make up the thorax or rib cage? the ribs, sternum and thoracic vertebrae 4) Describe the 3 living layers of bone. Diaphysis: middle section of the bone; where yellow marrow is produced Epiphyses: ends of the bone; where red marrow is produced Periosteum: thin membrane that encloses the bone. Responsible for growth in width of the bone 5) Compare and contrast compact bone and spongy bone. Compact Bone: Directly under the periosteum, Hard, strong layer, Gives bones strength, Contains deposits of calcium phosphate, Contains bone cells and blood vessels Spongy Bone: Located under the compact bone, Has many small, open spaces that make bones lightweight, Filled with a substance called marrow. 6) What is cartilage and what is its function? Cartilage is a smooth, slippery, thick layer of tissue that covers the ends of bones. It acts as a shock absorber and makes movement easier by reducing friction. 7) What would you recommend to a friend who was always breaking their bones? Eat a diet rich in calcium, phosphorus, vitamin A and D and maintain good posture 8) What are the different types of joints and what are some examples of each in your body? Immovable joint: cranium Moveable joints: ball and socket (shoulder), hinge (elbow), pivot (neck), gliding (wrist) 9) What is a muscle? A tissue composed of bundles of elongated cells capable of contraction and relaxation to produce movement in an organ or body part. 10) Describe the 3 parts of a muscle. Tendon: •white cord made up of extremely strong tissues •Connects muscle to the bone Body: •thick part of the muscle Aponeurosis: •membrane of connective tissue separating the muscle from the adjacent muscles 11) What is the difference between a tendon and a ligament? Tendons connect muscle to bone and ligaments connect bone to bone. 12) What are the 4 functions of muscles? A. Movement of limbs and organs B. Posture maintenance C. Joint stabilization D. Heat Release 13) What are the 3 different types of muscles and where can they be found in the body? Skeletal- attached to bone. Cardiac- heart Smooth muscle – internal organs 14) Give an example of an antagonistic muscle pair. Bicep and tricep, quadriceps and hamstrings, etc. 15) What happens to the shape of a muscle when it contracts? And when it relaxes? The muscle shortens during contraction and extends when relaxed.