New Nation and Early Antebellum Era
advertisement

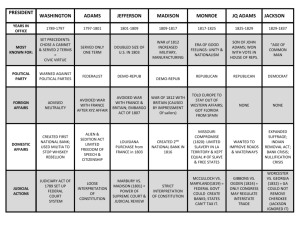
US History Fall Midterm Review Unit 3: The New Nation The United States, 1783 America’s 1st national gov’t was the Articles of Confederation (1777-1789) The Articles established a weak national gov’t in order to protect state power The Successes of the Articles Land Ordinance of 1785 Northwest Ordinance of 1787 Shays’ Rebellion America’s First National Government: The Articles of Confederation James Madison helped broker many the compromises thatwas made Aof constitutional convention heldthe in Philadelphia to fix possible the Articles Constitution & of is Confederation referred to butthe a new gov’tof was instead as “father thecreated Constitution” Key Ideas of the Constitution The bicameral Congress created by the Great Compromise Federalism—state gov’ts & the national gov’t both have power The supremacy clause establishes the Constitution (not the states) as the "the supreme law of the land" Anti-Federalists Federalists ■Against ratification ■Supported ratification of the ■Feared a strong national gov’t Constitution ■Wanted a Bill of ■Used Federalist Rights Papers to argue for ratification Bill of Rights: Amendments 1-10 1. George st president, ■As the 1 Washington Washington established 2. John important precedents: Adams 3. Thomas –Created the 1st cabinet Jefferson –Two terms 4. James –American neutrality Madison 5. James ■Hamilton’s Financial Plan Monroe ■Whiskey Rebellion 6. John Q. ■Farewell Address: Adams 7. Andrew –Neutrality & Parties Jackson 1. George Washingto n 2. John Adams 3. Thomas Jefferson 4. James Madison 5. James Monroe 6. John Q. Adams 7. Andrew ■War between England & France & Impressment ■XYZ Affair ■Alien & Sedition Acts ■VA & KY Resolves Unit 4: The Early Antebellum Era (1800-1840) 1. George Washingto n 2. John Adams 3. Thomas Jefferson 4. James Madison 5. James Monroe 6. John Q. Adams 7. Andrew ■ Marbury v Madison (1803) & judicial review ■ Louisiana Purchase ■ Lewis & Clark 1. George ■ War of 1812—England vs. Washingto USA over trade rights n ■ Battle of New Orleans 2. John ■ Treaty of Ghent Adams 3. Thomas Jefferson 4. James Madison 5. James Monroe 6. John Q. Adams 7. Andrew 1. George Washingto n 2. John Adams 3. Thomas Jefferson 4. James Madison 5. James Monroe 6. John Q. Adams 7. Andrew ■ Nationalism: –Clay’s American System –John Marshall & the Supreme Court –Monroe Doctrine (1823) ■ Sectionalism: –Growth of slavery –Missouri Compromise (1820) –Debate over tariffs The Market Revolution Transportation Revolution 1820-1860 Rivers, Roads, Canals, & Railroads Propaganda from the Know-Nothing Party attacking German & Irish immigrants 1. George Washingto n 2. John Adams 3. Thomas Jefferson 4. James Madison 5. James Monroe 6. John Q. Adams 7. Andrew ■ Common Man & Universal White Male Suffrage ■ Democratic Party (vs the Whigs) ■ Nullification Crisis ■ Indian Removal Act (1830) ■ Bank War (2nd BUS) Social Reforms of the 1830s