KAENAT NASIR-mcqs+answer key
advertisement

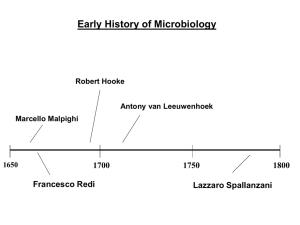
MCQS PAGE# 1-19: 1. Microorganism played a major role in history : (a) a. Decline of roman empire b. Evolution c. Independence of Pakistan d. Destroying books 2. Microorganisms are: (c) a. Agents that can be seen with naked eye b. Agents too large to be seen with naked eye c. Agents too small to be seen with naked eye d. All of the above 3. “microbiology” is the study of : (d) a. Plants b. Animals c. Only fungi d. All microorganisms 4. The bacteria that are visible even without microscope are: (c) a. Thiomargarita b. Epulopiscium c. Both a and b d. None of the above 5. who suggested that “disease was caused by invisible living organisms”? (c) a. Lucretius b. Fracastoro c. both a and b d. newton 6. the earliest microscopic observation was made in: (a) a. 1625-1630 b. 1500 c. 1990-2000 d. 2012 7. the first microscopic examination was made on: (b) a. viruses b. bees c. elephants d. dinosaurs 8. Leeuwenhoek’s microscope could magnify the object upto: (d) a. 3000-50000 times b. 2-4 times c. 100 times d. 50-300 times 9. in earlier times, people believed in which concept of generation? (b) a. biogenesis b. abiogenesis c. decomposition d. mutation 10. abiogenesis was first challenged by: a. Francesco Redi b. Isaac Newton c. Galileo d. Einstien 11. Needham was a supporter of: (a) a. spontaneous generation b. aspontaneous generation c. both a and b d. none of the above 12. Needham’s experiment was improved by: (b) a. newton b. Spallanzani c. Einstein d. Needham 13. the controversy of abiogenesis was finally resolved by? (d) a. Needham b. Redi c. Spallanzani d. Pasteur 14. The great potato blight of Ireland was caused by: (a) a. fungus b. bacteria c. virus d. none of the above 15. which of the following is NOT among the four humors? (b) a. blood b. brain c. phlegm d. yellow bile 16. according to Agostino Bassi, the silkworm disease was due to a: a. fungal infection b. protozoan infection c. bacterial infection d. viral infection 17. Lister used which chemical agent for sterilization? (c) a. water b. acid c. phenol d. Mercury 18. Indirect evidence that microorganisms were agents of human disease came from the work of: (b) a. Einstein b. Lister c. Newton d. Galileo 19. Joseph Lister worked on: (d) a. brain cells b. muscle cells c. PCR d. wound infection 20. The first direct demonstration of the role of bacteria in causing disease came from the study of: (b) a. HIV b. anthrax c. HPV d. HBV 21. Who proposed that bacteria have a role in causing disease? (a) a. Koch b. Newton c. Redi d. Aristotle 22. Robert Koch published his findings in: (b) a. 1857 b. 1876 c. 2012 d. 1980 23. the animal model used by Koch was: (d) a. horse b. sheep c. goat d. mouse 24. Koch’s criteria for proving the relationship between a microorganism and a specific disease is known as: (c) a. Liser’s points b. Einstein’s theory c. Koch’s postulates d. Newton’s laws 25. on the basis of observations, a _________ is developed. (a) a. hypothesis b. conclusion c. observation d. none of the above 26. A ____________ is a set of propositions and concepts that provides a reliable, systematic, and rigorous account of an aspect of nature: (d) a. observation b. hypothesis c. idea d. theory 27. whilw conducting an experiment, it is essential to set up a ____________ group along with an experimental group: (d) a. typicsl b. classical c. compact d. control 28. Koch’s proof that ___________ caused anthrax was independently confirmed by Pasteur and his coworkers: (a) a. Bacillus anthracis b. E.coli c. HIV d. Salmonella 29. it was discovered that after the burial of dead animals, anthraxspores survived and were brought to the surface by ___________: (b) a. butterflies b. earthworms c. silkworms d. cobras 30. healthy animal ingesting the anthrax spores became _________: (b) a. healthy b. ill c. vampires d. all of the above 31. gelatin was not an ideal solidifying agent because: (a) a. it was digested by many bacteria b. it was sticky c. it was hazardous d. none of the above 32. Koch used ________ as a solidifying agent: (c) a. glue b. water c. gelatin d. soft drinks 33. Eilshemius Hesse suggested the use of _____________ as a solidifying agent: (a) a. agar b. gelatin c. glue d. water 34. Agar did not melt until reaching a temperature of ____________ : (b) a. 10 C b. 1000 C c. 100 C d. 1 C 35. one of the Koch’s assistant, __________ developed the petri dish: (c) a. Walther Hesse b. Albert Einstein c. Richard Petri d. John Salker 36. isolation of pure culture stimulated developments in all the areas of ____________: (d) a. physics b. chemistry c. philosophy d. bacteriology 37. meat axtracts and ________ digests were used as nutrient sources for growing bacteria: a. protein b. grass c. leaf d. insect 38. By 1882 Koch had used these techniques to isolate the bacillus that caused __________: (a ) a. tuberculsosis b. cancer c. illness d. malaise 39. most of the bacterial pathogens were isolated in : (c) a. silver age b. diamond age c. golden age d. black age 40. the first viral pathogen to be studied was? (a) a. Tobacco Mosaic Virus b. Influenza virus c. Polio virus d. HIV 41. porcelain bacterial filters were constructd by? (b) a. Walther Hesse b. Charles Chamberland c. Robert Koch d. Redi 42. the construction of ____________________ by Charles Chamberland made possible the discovery of virus: (a) a. porcelain bacterial filters b. candle wax c. gelatin d. none of the above 43. Pastuer named the attenuated cultures as? (a) a. vaccine b. waste c. tablet d. threat 44. Pasteur and _________ discovered that incubating their cultures for long intervals between transfers would attenuate the bacteria. (c) a. Redi b. Stanley c. Roux d. Chamberland 45.The name “ vaccine” is derived from a latin word “vacca” which means ___________: (a) a. cow b. horse c. hen d. birds 46. the attenuated material was named as vaccine by Pasteur, in honor of __________; (b) a. Robert Brown b. Edward Jenner c. William Shakespeare d. Albert Einstein 47. Jenner had used vaccination with material from ___________ lesions: (d) a. bacterial b. fungal c. B. anthracis d. cowpox 48. _____________ and Chamberland developed an attenuated anthrax vaccine: (a) a. Pasteur b. Jenner c. Newton d. Darwin 49. Pasteur and Chamberland developed an attenuated anthrax vaccine by treating the culture with ______________: (b) a. Sodium Chloride b. Potassium bichromate c. Magnessium chloride d. Sodium bicarbonate 50. Pasteur and Chamberland developed an attenuated anthrax vaccine by incubating the bacteria at ______________; (c) a. 10-15 C b. 2-3 C c. 42-43 C d. 63-72 C 51. After the anthrax vaccine, Pasteur prepared ________ vaccine: (a) a. rabies b. influenza c. tetanus d. rotavirus 52. In the process of preparing rabies vaccine, the virus was first grown in the abnormal host ____________: (a) a. rabbit b. monkey c. chimpanzee d. frog 53. the _____________ and spinal cord of rabbits were used during the course of rabbies vaccine preparation: (b) a.liver b. brain c. heart d. lungs 54. Pasteur injected the first rabbies vaccine to a: (a) a. 9 year old boy b. 20 year old boy c. 50 year old man d. dead man 55. Pasteur injected the first rabbies vaccine to: (c) a. John Francis b.Robert Brown c. Joseph Meister d. Lister 56. Joseph was injected ____________ times by Pasteur with the rabbies vaccine: (d) a. 3 b. 23 c. 33 d. 13 57. “Pasteur Institute in Paris” is situated in: (b) a. Rome b. France c. Italy d. America 58. the initial task of “Pasteur Institute in Paris” was : (a) a. vaccine production b. PCR development c. antibiotic production d. none of the above 59. antibodies are a component of : (b) a. cell mediated immunity b. humoral immunity c. both of the above d. none of the above 60. blood cells are a component of: a. cell mediated immunity b. humoral immunity c. both of the above d. none of the above 61. Elie Metchnikoff discovered _______________: (d) a. blood b. antibodies c. RBCs d. phagocytes 62. phagocytes were discovered by ______________: (a) a. Elie Metchnikoff b. Edward Jenner c. Vont Hoff d. Elbert Einstein 63. the process of engulfing the disease causing bacteria by phagocytes is called as: (c) a. dialysis b. hemolysis c. phagocytosis d. digestion 64. the process of phagocytosis is performed by: (a) a. phagocytes b. antibodies c. alveoli d. RBCs 65. the term phagocytosis comes from the greek word “phagein”, it means: (a) a. eating b. playing c. cooling d. sweet 66. the process of conversion of sugar to alcohol is called as: (b) a. streaking b. alcoholic fermentation c. pasteurization d. sterilization 67. in alcoholic fermentation, there is an interconversion of: (a) a. sugar to alcohol b. milk to tea c. tea to coffee d. sugar to honey 68. Pasteur’s study on fermentation continued for almost ___ years: (d) a. 50 b. 46 c. 2 d. 20 69. The Russian microbiologist Sergei N. Winogradsky made many contributions to _________________________: (c) a. pasteurization b. immunology c. soil microbiology d. sterilization techniques 70. The Russian microbiologist ______________ made many contributions to soil microbiology: a. S.N Winogradsky b. W.M Stanley c. Lister d. Newton 71. Winogradsky studied the: (a) a. decomposition of cellulose b. wound healing c. pasteurization d. disinfection 72.Winogradsky isolated anaerobic ________________________ soil bacteria: (b) a. parasitic b. nitrogen fixing c. both of the above d. none of the above 73. Winogradsky discovered that soil bacteria could oxidize _________________________ to obtain energy: (d) a. iron b. sulfur c. ammonium d. all of the above 74. Winogradsky discovered that soil bacteria could oxidize iron, sulfur and ammonium to obtain ______________: (c) a. water b. light c. energy d. soil 75. Martinus W.Beijernick made fundamental contributions to ____________________: (b) a. microbial parasitology b. microbial ecology c. microbial pathology d. none of the above 76. _____________________ made fundamental contributions to microbial ecology: (a) a. M.W Beijernick b. Newton c. Einstein d. Galileo 77. M.W Beijernick discovered aerobic nitrogen fixing bacteria _____________: (a) a. Azotobacter b. E.coli c. Salmonella d. none of the above 78. _____________ is a root nodule bacterium; (a) a. Azotobacter b. E.coli c. Salmonella d. none of the above 79. Azotobacter is a _______________________: (d) a. sulfate reducing bacterium b. nitrogen fixing bacterium c. root nodule bacterium d. all of the above 80. Winogradsky and Beijernick developed the ____________________: (a) a. enrichment culture technique b. streaking technique c. autoclaving d. PCR 81. Winogradsky and Beijernick developed the use of : (b) a. PCR b. selective media c. autoclaving d. energy 82. ________________ and Beijernick developed the use of selective media: (c) a. Stanley b. Lister c. Winogridsky d. Newton 83. Winogridsky and _________________ developed the enrichment culture technique: (a) a. Beijernick b. Lister c. Darwin d. Brown 84. prokaryotic cells are ________________ than eukaryotic cells: (b) a. complex b. simpler c. complicated d. all of the above 85. eukaryotic cells are ___________________ than prokaryotic cells: (b) a. simpler b. complex c. both of the above d. none of the above 86. prokaryotic cells lack a membrane bound ______________; (a) a. nucleus b. cytoplasm c. cell wall d. none of the above 87. the word “prokaryote” has a greek origin, “pro” stands for: (b) a. after b. before c. both of the above d. none of the above 88. the word “eukaryote” has a greek origin, “eu” stands for: (a) a. true b. false c. both of the above d. none of the above 89. the words prokaryote and eukaryote has a greek origin, “karyon” stands for: (c) a. cell wall b. cell membrane c. nucleus d. cytoplasm 90. eukaryotic cells are usually ________________ than prokaryotic cells: (b) a. smaller b. larger c. both of the above d. none of the above 91. prokaryotic cells are usually ______________ than eukaryotic cells: (a) a. smaller b. larger c. both of the above d. none of the above 92. algae and fungi are ____________: (b) a. prokaryotic b. eukaryotic c. both of the above d. none of the above 93. higher plants and animals are ___________________: (b) a. prokaryotic b. eukaryotic c. both of the above d. none of the above 94. protozoa are _________________: (b) a. prokaryotic b. eukaryotic c. both of the above d. none of the above 95 which of the following are eukaryotes? (d) a. algae b. fungi c. animals d. all of the above 96. which of the following are prokaryotes? (d) a. algae b. fungi c. animals d. none of the above 97. The early description of organisms as either plants or animals is too _______________: (a) a. simplified b. complicated c. complex d. none of the above 98. Monera, Protista, Fungi, Animalia, and Plantae all are a part of __________ kingdom system: (d) a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 5 99. Monera, Protista, Fungi, Animalia, and _______________ , all are a part of 5 kingdom system: (a) a. Plantae b. viruses c. both of the above d. none of the above 100. Monera, Protista, Fungi, ____________,and Plantae all are a part of 5 kingdom system: (b) a. viruses b. Animalia c. both of the above d. none of the above 101: Monera, Protista, ______________, Animalia, and Plantae all are a part of 5 kingdom system: (a) a. fungi b.viruses c. both of the above d. none of the above 102: Monera, __________,Fungi, Animalia, and Plantae all are a part of 5 kingdom system: (b) a.. viruses b. protista c. both of the above d. none of the above 103: __________, Protista, Fungi, Animalia, and Plantae all are a part of 5 kingdom system: (a) a. monera b. viruses c. both of the above d. none of the above 104. which of the following kingdoms are of interest for the microbiologists? (d) a. monera b. protista c. fungi d. all of the above 105. kingdom protista was considered to be divided into _______ or more kingdoms: a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. none of the above 106. ____________ and Archae are two quite different groups of prokaryotic organisms: (b) a. viruses b.bacteria c. plants d. animals 107. bacteria and ____________ are two quite different groups of prokaryotic organism: (d) a. viruses b. plants c. animals d. archae 108. according to the scientist-writer Steven Jay Gould emphasized, we live in the age of _____________: (c) a. dinosaurs b. mountains c. bacteria d. cells 109. ____________________ are more numerous than any other kind of living organism on our planet: (c) a. mosquitoes b. plants c.bacteria d. nematodes 110. _______________ probably constitute the largest component of earth’s biomass: (c) a. mosquitoes b. plants c.bacteria d. nematodes 111. modern microbiology has an impact on the fields of: (d) a. medicine b. ecology c. genetics d. all of the above 112. In the 1970s new discoveries in microbiology led to the development of recombinant DNA technology and _________________: (a) a. genetic engineering b. Autoclave c. peptide synthesizer d. lyophilization 113. In the 1970s new discoveries in microbiology led to the development of __________________ and genetic engineering: (a) a. recombinant DNA technology b. Autoclave c. peptide synthesizer d. lyophilization 114. about one third of the nobel prizes given for work in physiology or medicine in the twentieth century have been awarded to the scientists working on _______________ problems: (c) a. social b. environment c. microbiological d. pollution 115. microbiologists focusing on viruses are called: (a) a. virologist b. bacteriologist c. phycologist d. algologist 116. microbiologists focusing on bacteria are called : (b) a. virologist b. bacteriologist c. phycologist d. algologist 117. microbiologists working on fungi are called : (c) a. virologist b. bacteriologist c. phycologist d. algologist 118. microbiologists working on protozoa are called : (d) a. virologist b. bacteriologist c. phycologist d. protozoologist 119. microbiologists working on algae are called: (d) a. virologist b. bacteriologist c. phycologist d. algologist 120 _________ microbiology deals with diseases of humans and animals: (a) a. medical b. taxonomic c. ecological d. physiological 121. Medical microbiologists identify the agent causing an ______________ and plan measures to eliminate it: (b) a. benefit b. infectious disease c. advantage d. none of the above 122. ______________________ is closely related to medical microbiology: (a) a. public health microbiology b. botany c. zoology d. astronomy 123. public health microbiology is closely related to ____________________: (a) a. medical microbiology b. botany c. zoology d. astronomy 124. _______________________ try to control the spread of communicable diseases: (d) a. psychologists b. teachers c. engineers d. public health microbiologists 125. _______________________ often monitor community food establishments and water supplies in an attempt to keep them safe and free from infectious disease agents: (d) a. psychologists b. teachers c. engineers d. public health microbiologists 126. Immunology is concerned with how the immune system protects the body from pathogens and the response of infectious agents: (c) a. cardiology b. microbiology c. immunology d. parasitology 127. Immunology is concerned with how the ___________ system protects the body from pathogens and the response of infectious agents: (c) a. cardiac b. nervous c. immune d. respiratory 128. immunology also deals with allergies and _________________ diseases: (a) a. auto-immune diseases b. cardiac diseases c. respiratory diseases d. liver diseases 129. immunology also deals with ________________ and auto-immune diseases: (a) a. allergies b. skin burns c. color blindness d. autism 130. rheumatoid arthiritis is an ___________________ disease: (c) a. cardiac b. respiratory c. auto-immune d. none of the above 131. about ____________ of the nobel prizes given for work in physiology or medicine in the twentieth century have been awarded to the scientists working on microbiological problems: (a) a. 0ne third b. one fourth c. half d. none of the above 132. _____________________________ is concerned with the impact of microorganisms on agriculture: (c) a.public health microbiology b. ecological microbiology c. agricultural microbiology d. medicinal microbiology 133. agricultural microbiology is concerned with the impact of microorganisms on ______________: (c) a. public health b. environment c. agriculture d. medicine 134. _________________ microbiologists try to combat plant diseases that attack important food crops: (b) a. public health b. agricultural c. taxonomical d. none of the above 135. agricultural microbiologists try to: (d) a. combat plant diseases that attack important food crops b. work on methods to increase soil fertility c. work on methods to increase crop yield d. all of the above 136. The field of microbial _______________ is concerned with the relationships between microorganisms and their living and nonliving habitats: (a) a. ecology b. parasitology c. pathology d. none of the above 137. The field of microbial ecology is concerned with the relationships between ______________ and their living and nonliving habitats: (b) a. cactus b. microorganisms c. insects d. dinosaurs 138. The field of microbial ecology is concerned with the relationships between microorganisms and their living and nonliving ____________: (c) a. water b. habits c. habitats d. food 139. Microbial ____________ study the contributions of microorganisms to the carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur cycles in soil: (a) a. ecologist b. physiologist c. psychologist d. parasitologist 140. Microbial ecologists study the contributions of ______________ to the carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur cycles in soil: (b) a. cactus b. microorganisms c. insects d. dinosaurs 141. Microbial ecologists study the contributions of microorganisms to the ____________, nitrogen, and sulfur cycles in soil: (d) a. leaf b. energy c. fermentation d. carbon 142. Microbial ecologists study the contributions of microorganisms to the carbon, __________, and sulfur cycles in soil: (d) a. leaf b. energy c. fermentation d. nitrogen 143. Microbial ecologists study the contributions of microorganisms to the carbon, nitrogen and ___________ cycles in soil: (d) a. leaf b. energy c. fermentation d. sulfur 144. Microbial ecologists are employing microorganisms in ____________ to reduce pollution effects: (b) a. bioterrorism b. bioremediation c. biomass d. none of the above 145. Microbial ecologists are employing microorganisms in bioremediation to reduce ___________ effects: (c) a. beneficial b. colorful c. pollution d. bright 146. Scientists working in ___________________________ microbiology try to prevent microbial spoilage of food: (a) a. food and dairy b. plant and animals c. bleck and white d. leaf and shoot 147. Scientists working in food and dairy microbiology try to prevent microbial spoilage of ________: (b) a. rain water b. food c. leaves d. none of the above 148. In ________________________ microorganisms are used to make products such as antibiotics, vaccines, steroids, alcohols and other solvents, vitamins, amino acids, and enzymes: (c) a. environmental microbiology b. agricultural microbiology c. industrial microbiology d. none of the above 149. In industrial microbiology microorganisms are used to make products such as : (d) a. antibiotics b. vaccines c. vitamins d. all of the above 150. microbiologists working in microbial _______________________________ study the synthesis of antibiotics and toxins and microbial energy production: (a) a. physiology and biochemistry b. biomass c. environment d. none of the above 151. Microbial ____________ and molecular biology focus on the nature of genetic information: (c) a. physiology b. psychology c. genetics d. cytology 152. Microbial genetics and ____________________________ focus on the nature of genetic information: (d) a. zoology b. botany c. bacteriology d. molecular biology 153. microbial genetics focus on: (d) a. nature of genetic information b. how the genetic material regulates the development and function of cells c. understanding gene function d. all of the above 154. new ___________ can be inserted into plants and animals by the use of genetic techniques: (a) a. genes b. cytoplasm c. colors d. none of the above 155. _____________________ are finding ways to control the spread of already established infectious diseases: (b) a. engineers b. microbiologists c. architects d. teachers 156. _________________________________________ render a pathogen impervious to current medical treatment: (c) a. PCR b. injections c. multiple drug resistence d. none of the above 157. ____________________ helps us to understand that how pathogen interacts with the host cells: (a) a. microbiology b. botany c. zoology d. phtsiology 158. microorganisms can serve as a source of high quality __________: (a) a. food b. animals c. plants d. none of the above 159. it is estimated that less than _______ of microorganisms have been cultured: (d) a. 50% b. 30% c. 6% d. 1% 160. __________________________ was the first person to describe microorganism; (c) a. Einstein b. Newton c. Leeuwenhoek d. Galileo 161. Leeuwenhoek was the first person to describe ________________; (b) a. humans b. microorganisms c. dinosaurs d. elephants 162. the spontaneous generation of microorganisms was disapproved by: (c) a. spallanzani b. Pasteur c. both of the above d. none of the above 163. support for the germ theory of disease came from the experiment of : (d) a. Bassi b. Pasteur c. Koch d. all of the above 164. Lister provided indirect evidence for the germ theory with his development of: (a) a. antiseptic surgery b. septic surgery c. fermentation d. none of the above 165. _____________________ and molecular Koch’s postulates are used to prove a direct relationship between a suspected pathogen and a disease: (a) a. Koch’s postulates b. Newton’s postulates c. Einstein’s postulates d. none of the above 166. . Koch’s postulates and ________________________________ are used to prove a direct relationship between a suspected pathogen and a disease: (a0 a. molecular Koch’s postulates b. molecular Newton’s postulates c. molecular Einstein’s postulates d. none of the above 167. Koch’s postulates and molecular Koch’s postulates are used to prove a direct relationship between a suspected ___________ and a disease: (b) a. disease b. pathogen c. insects d. all of the above 168. Koch developed the techniques required to grow bacteria on ___________ media: (a) a. solid b. liquid c. both of the above d. none of the above 169. vaccines against ________________ and rabies were made by Pasteur; (b) a. polio b. anthrax c. HIV d. influenza 170. vaccines against anthrax and _____________ were made by Pasteur: (b) a. polio b. rabies c. HIV d. influenza 171. vaccines against anthrax and rabies were made by ______________: (a) a. Pasteur b. Galileo c. Newton d. Einstein 172. Pasteur showed that fermentations were caused by ________________; (c) a. plants b. animals c. microorganisms d. none of the above 173. _____________________ microorganisms can live in the absence of oxygen: (b) a. aerobic b. anaerobic c. both of the above d. none of the above 174. The Archaea are so different that many microbiologists divide organisms into __________ domains: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eucarya; (d) a. one b. four c. five d. three 175. The Archaea are so different that many microbiologists divide organisms into three domains: __________, Archaea, and Eucarya. (b) a. viruses b. bacteria c. protists d. none of the above 176. The Archaea are so different that many microbiologists divide organisms into three domains: Bacteria, ___________, and Eucarya. (a) a. Archaea b. animalia c. plantae d. none of the above 177. The Archaea are so different that many microbiologists divide organisms into three domains: Bacteria, Archaea, and ____________ (c) a.viruses b. animalia c. Eucarya d. none of the above 178. light microscopes use glass lenses to bend and focus light rays to produce enlarged images of __________ objects: (b) a. enlarged b. small c. both of the above d. none of the above 179. light microscopes use glass lenses to bend and focus light rays to produce ___________ images of small objects: (a) a. enlarged b. small c. both of the above d. none of the above 180. _________ microscopes use glass lenses to bend and focus light rays to produce enlarged images of small objects: (d) a. infrared b. U.V c. electron d. light 181. The maximum resolution of light microscope is ________: (b) a. 0.1 micrometer b. 0.2 micrometer c. 0.1 nanometer d. 0.2 nanometer 182. The most common types of __________ microscopes are the bright-field, darkfield, phase-contrast, and fluorescence microscopes: (a) a. light b. electron c.both of the above d. none of the above 183. The most common types of light microscopes are the ____________, darkfield, phase-contrast, and fluorescence microscopes: (b) a. glass b. brightfield c. star d. tree 184. The most common types of light microscopes are the bright-field, _____________, phase-contrast, and fluorescence microscopes: (b) a. glass b. darkfield c. star d. tree 185. The most common types of light microscopes are the bright-field, darkfield, ______________, and fluorescence microscopes: (b) a. glass b. phase-contrast c. star d. tree 186. The most common types of light microscopes are the bright-field, darkfield, phase-contrast, and ________________ microscopes: (b) a. glass b. fluorescence c. star d. tree 187. most microorganisms are colorless and therefore not easily seen in the bright-field microscope, they are usually fixed and ________ before observation: (a) a. stained b. burnt c. sterilized d. none of the above 188. either simple or ______________ staining can be used to enhance the contrast between the microorganisms: (c) a. colorful b.shining c. differential d. none of the above 189. either _____________ or differential staining can be used to enhnce the contrast between the miocroorganisms: (b) a. colorful b. simple c. shining d. none of the above 190. the electron microscope has a resolution of about: (d) a. 0.2 micrometer b. 0.5 micrometer c. 0.2 nanometer d. 0.5 nanometer 191. electron microscopes use ______________ of very short wavelengths rather than visible light: (b) a. light rays b. electron beams c. infrared rays d. U.V rays 192. _____________________ use electron beams of very short wavelengths rather than visible light: (a) a. electron microscope b. light microscope c. both of the above d. none of the above 193. electron microscopes use electron beams of very __________ wavelengths rather than visible light: (a) a. short b. long c. both of the above d. none of the above 194. which of the following is an example of new form of microscopy? (c) a. light microscope b. compound microscope c. scanning probe microscope d. all of the above 195. There are _________ animals living in the scum on the teeth in a man’s mouth than there are men in a whole kingdom: (a) a. more b. less c. equal d. none of the above 196. _____________________ is concerned with organisms so small that can not be seen with an un-aided eye: (c) a. zoology b. botany c. microbiology d. all of the above 197. when a ray of light passes from one medium to another and the ray is bent at the interface, this phenomenon is known as: (c) a. transmission b. reflection c. refraction d. all of the above 198. when a ray of light passes from one medium to another and the ray of light is _______ at the interface, the phenomenon is known as refraction: (c) a. transmitted b. reflected c. bent d. all of the above 199. _________________________ is a measure of how greatly a substance slows the velocity of light: (d) a. reflective index b. transmission index c. flow index d. refractive index 200. the direction and magnitude of bending of light is determined by the __________________: (d) a. reflective index b. transmission index c. flow index d. refractive index 201. glass has _____________ refractive index than air: (a) a. greater b. lesser c. equal d. none of the above 202. air has ______________ refractive index than glass: (b) a. greater b. lesser c. equal d. none of the above 203. when light passes from air into glass, it is _______________ (a) a. slows down b. speeds up c. no effect d. all of the above 204. when light passes from air into glass, it, (d) a. slows down b. bent towards the normal c. no efeect d. both a and b 205. normal is a line ______________ to the surface. (b) a. parallel b. perpendicular c. horizontal d. none of the above 206. when light passes from glass into air, it _____________: (b) a. slows down b. speeds up c. no effect d. all of the above 207. when light passes from glass into air, it: (d) a. speeds up b. bent away from the normal c. no effect d. both a and b 208. a prism ___________________: (a) a. bends light b. has no effect on light c. both of the above d. none of the above 209. a prism bends light because the refractive index of glass is ____________ from air: (b) a. same b. different c. both of the above d. none of the above 210. a prism bends light because the _________________ of glass is different from air: (d) a. reflective index b. transmission index c. flow index d. refractive index 211. our eyes can not focus on objects nearer than _______________; a. 16cm b. 10 inches c. 25cm d. both b and c 212. lenses act like a collection of _______________ acting as a unit: (c) a. stars b. beads c. prisms d. plates 213. lenses act like a collection of prisms acting as a ___________: (d) a. actor b. actress c. galaxy d. unit 214. When the light source is distant so that parallel rays of light strike the lens, a convex lens will focus these rays at a specific point called as: (b) a. local point b. focal point c. line point d. all of the above 215. the distance between the center of the lens and the focal point is called as _______________: (b) a. local length b. focal length c. road length d. all of the above 216. the distance between the _________________________ and the focal point is called as focal length: (c) a. top of the lens b. back of the lens c. center of the lens d. bottom of the lens 217. the distance between the center of the lens and ______________ is called as focal length: (b) a. local point b. focal point c. line point d. all of the above 218. convex lens can act as ______________ : (c) a. microscope b. magnifier c. both of the above d. none of the above 219. __________ lens can act as a magnifier: a. convex b. concave c. both of the above d. none of the above 220. a magnifying glass provides a clear image at much ___________ range: (b) a. distant b. closer c. both of the above d. none of the above 221. a magnifying glass makes the object appear ____________: (b) a. smaller b. larger c. same size d. none of the above 222. lens strength is related to _____________: (d) a. plates b. water c. eyes d. focal length 223. lens having a longer focal length are _________ lens: (b) a. stronger b. weaker c. both of the above d. none of the above 224. lens having a shorter focal length are ________ lens: (a) a. stronger b. weaker c. both of the above d. none of the above 225. ___________ used the criteria proposed by his former teacher, Jacob Henle, to establish the relationship between Bacillus anthracis and anthrax: (c) a. Newton b. Einstein c. Koch d. Galileo 226. Koch used the criteria proposed by his former teacher _____________, to establish the relationship between Bacillus anthracis and anthrax: (d) a. Robert Brown b. John Salker c. Albert Einstein d. Jacob Henle 227. Koch used the criteria proposed by his former teacher, Jacob Henle, to establish the relationship between _________________ and anthrax: (c) a. Streptococcus pnemoniae b. Staphylococcus aureus c. Bacillus anthracis d. none of the above 228. Koch used the criteria proposed by his former teacher, Jacob Henle, to establish the relationship between Bacillus anthracis and _____________: (d) a. AIDS b. influenza c. polio d. anthrax 229. _______________ thought that some of the simpler invertebrates could arise by spontaneous generation: (a) a. Aristotle b. newton c. Darwin d. Einstein 230. microorganisms are not generated spontaneously but arise from other _______________; (c) a. animals b. plants c. microorganisms d. none of the above 231. microorganisms are not generated _______________ but arise from other microorganisms: (a) a. spontaneously b. non-spontaneously c. both of the above d. none of the above 232. Louis Pasteur is one of the greatest scientist of _________ century: (c) a. 16th b. 17th c. 19th d. 21st 233. Lucretius and Fracastoro suggested that disease was caused due to invisible _____________ creatures: a. living b. non-living c. both of the above d. none of the above 234. ___________ and Fracastoro suggested that disease was caused due to invisible living creatures: (a) a. Lucretius b. Redi c.Brown d. Darwin 235: Lucretius and ____________ suggested that disease was caused due to invisible living creatures: (c) a. Redi b. Brown c. Fracastoro d. Darwin 236. Leeuwenhoek earned his living as: (c) a. barber b. harberdasher c. both of the above d. none of the above 237. _________________’s discovery of microorganisms renewed the controversy of abiogenesis: (a) a. Leeuwenhoek b. Lister c. Brown d. Darwin 238. Leeuwenhoek’s discovery of _________________ renewed the controversy of abiogenesis: (c) a. plants b. animals c. microorganisms d. all of the above 239. during Pasteur’s experiment, no growth occurred in the flasks because the dust and germs got trapped on the walls of _______________: (b) a. straight tube b. curved necks c. linear tube d. none of the above 240. during _________’s experiment, no growth occurred in the flasks because the dust and germs got trapped on the walls of curved necks: (a) a. Pasteur b. Lister c. Darwin d. Einstein