The Synapse
advertisement
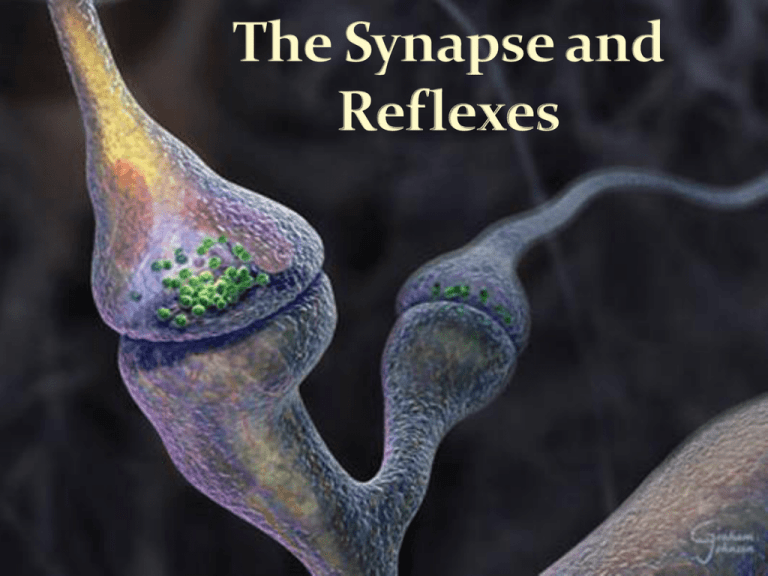
Structure of a Synapses Synapse: Is a junction where a axon interacts with another neuron Presynaptic Terminal: End of the axon Postsynaptic Membrane: Membrane of the dendrite Synaptic Cleft: Space between the presynaptic membrane and postsynaptic membrane Synaptic vesicles: Stores chemical neurotransmitters Excitatory - increase membrane permeability, increases chance for threshold to be achieved to trigger an action potential Inhibitory - decrease membrane permeability, decrease chance for threshold to be achieved to trigger an action potential Acetylcholine ACh - stimulates muscle contraction Norepinephrine & Dopamine (sense of feeling good, low levels = probable cause to depression) Serotonin (sleepiness) Endorphins (reduce pain, inhibit receptors) Reflex: An involuntary reaction in response to a stimulus Reflex Arch: Pathway in which a reflex occurs. Sensory Nerves - conduct impulses into the brain or spinal cord Motor Nerves - carry impulses to muscles of glands from the brain and spinal cord Mixed Nerves - contain both sensory and motor nerves 5 steps of Reflex Arch 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Sensory Receptor Afferent neuron interneuron Motor neuron Effector organ Reflex arc - only includes a few neurons Reflex Behavior – automatic and subconscious responses Stretch or Knee-jerk reflex – Muscles contract when applied force it put on them (patellar reflex) Withdrawal reflex - avoidance of painful stimuli Converging Pathways: More than one neuron synapses converge on the same neuron. (more than one neuronal pathway) Diverging Pathways: The axon from one neuron divides or diverges with one or more neurons. (one neuronal pathways can diverge into multiple pathways)