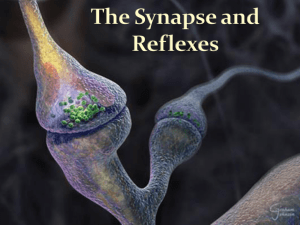
Reflexes
advertisement
November 2015 Objectives: To describe the pathway nervous impulses travel through a reflex To observe reflexes and reaction times Journal: List the layers of protection around the central nervous system from the vertebrae to the spinal cord. Reflexes • Involuntary reactions that protect you • Response is proportionate to the stimulus • Only the spinal cord is necessary Reflex Arc Nerve impulses, or action potential, travel routes made up of neurons Paths are called neuron pathways Reflex arc is specialized type of neuron pathway Allow impulse conduction in only one direction Receptors - beginning of dendrites of sensory neurons, where impulse conduction starts Located far from spinal cord (tendons, skin, etc) Causes muscle contraction or gland secretion Two-Neuron Arc Simplest type of reflex arc – only involves sensory and motor neuron with one synapse Most common is the “knee jerk” Sensory neuron sends message (chemicals) across synapse to motor neuron Motor neuron forms synapse with an Effector – organ that puts nerve signals “into effect” Usually muscles or glands Response is called a Reflex Three-Neuron Arc Involves a sensory, motor, AND interneuron More complex response Two synapses – between sensory and interneuron and between interneuron and motor All interneurons are in the brain or spinal cord Example: withdrawal reflex Since in contact with CNS, may feel pain