File
advertisement

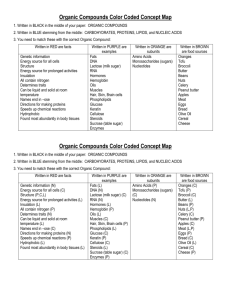
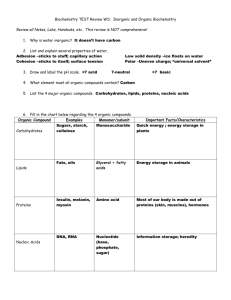
Chemistry of Living Things Chemistry Chemistry- the study of the structure of matter and composition of substances, their properties, and their chemical reactions Many chemical reactions occur in the human body Reactions can range from digestion of meat in the stomach and formation of urine in the kidneys The study of the chemical reactions of living things is called biochemistry Matter and Energy Matter- anything that has weight and takes up space Matter exists in the forms of solid, liquid, and gas Example in our bodies Solid: bone Liquid: blood Gas: oxygen Physical changes occur when we chew a piece of food and break it into smaller pieces Chemical changes occur when food is acted upon by chemicals in the body that change its composition Energy- the ability to do work or put matter into motion Potential energy- energy stored in cells waiting to be released (lying in bed) Kinetic energy- work resulting in motion (getting out of bed) Atoms Atom- smallest piece of an element Invisible to the human eye but are part of our human structure Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons Protons- positive Electrons- negative Neutrons- neutral Number of protons=number of electrons Isotopes- atoms of a specific element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons Radioactive isotopes- unstable and may decay As they decay they may give off radiation Used to study structure and function of particular tissue Strong radiation is useful in the treatment of cancer and other diseases Chemical terms Ion: A positively or negatively charged particle Organic compounds: compounds found in living things that contain carbon Element: combined atoms that are alike Compound: various elements that combine in a definite proportion Types of compounds Inorganic compounds Made of molecules that do not contain carbon Water is an inorganic compound Makes up between 55 to 65% of human body weight Most important inorganic compound to living organisms Small Organic compounds Always contain carbon More than a million known organic compounds Large and complex 4 main organic compounds Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids Carbohydrates Compounds that contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen Divided into 3 groups Monosaccharides Disaccharides Polysaccharides Monosaccharides Means one sugar and cannot be broken down any farther Known as single or simple sugars Types Glucose- main source of energy in cells Fructose- sweetest monosaccharide found in fruit and honey Galactose Ribose- found in RNA Deoxyribose – found in DNA Disaccharides Known as a double sugar Formed from two monosaccharides Types Sucrose- table sugar Maltose- found in grains Lactose- found in milk Must be broken down by digestion to be absorbed and used by the body Polysaccharides Large complex molecules of hundreds to thousands of glucose molecules bonded together in a long chain Types Starch- found in grain products and potatoes Cellulose- main structural component in plant tissue Glycogen- stored in the liver Lipids Molecules containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen Fats- consist of glycerol and fatty acids Also known as triglycerides Most abundant in the body Phospholipids- contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and phosphorous Found in cell membranes, the brain, and nervous tissue Steroids- lipids that contain cholesterol Cholesterol is needed to make cortisol Proteins Contain C, H, O, N, phosphorous and sulfur Found in every part of the living cell Also found in the outer protein coat of a virus Serve as binding and structural components of all living things Example: large amounts of protein are found in fingernails, hair, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, and muscle Building blocks of proteins are amino acids 22 different amino acids that can combine to form different proteins Essential amino acids must be ingested because the body does not naturally make them Histidine Isoleucine Leucine Lysine Methionine Phenylalanine Threonine Tryptophan Valine Enzymes Special proteins found in all cells Help control chemical reactions Help provide energy for the cell Assist in making new cell parts Control almost every process in the cell Known as organic catalysts Nucleic Acids Contains carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and phosphorus 2 major nucleic acids DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) RNA (ribonucleic acid) Largest known organic molecule Made of repeating subunits called nucleotides DNA structure and function Involved in the process of heredity DNA molecule passes on genetic information from one generation to the next Double stranded referred to as a double helix Sides of ladder are made of sugars and phosphates Rungs of the ladder are nitrogenous bases A with T G with C DNA is unique for every person and is used as a means of identification Because all cells contain DNA a very small amount can identify anyone RNA structure and function A with U G with C Single stranded 3 types of RNA Messenger RNA- carries instructions for protein synthesis Transfer RNA- picks up amino acids and transfers them to the ribosome to form proteins Ribosomal RNA- helps in the attachment of mRNA to the ribosome