Chapter 4: Integumentary System
advertisement

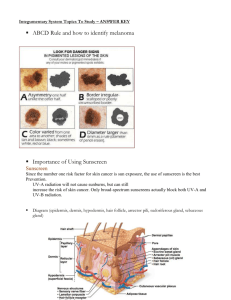
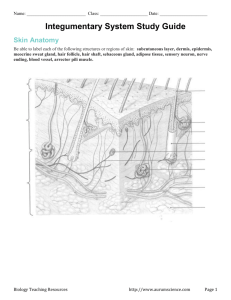
Chapter 4: Integumentary System Entry Task 1/7 Brainstorm AND record 3 possible functions of the integumentary (skin) system… Wednesday 1/7 Mini-Quiz: Body Tissues Begin CH 4: Skin & Body Membranes – Worksheet: Skin Structure Take notes from PowerPoint – Integumentary System Function p.108-114 Melanin Skin & Body Membranes Epithelial tissue membrane (3 types) – – – Cutaneous Stratified squamous on a layer of dense fibrous connective tissue Mucous Stratified squamous on simple columnar Serous Simple squamous on areolar tissue A Closer Look at the Serosa… Parietal layer – lines ventral cavity, folds on itself to form visceral layer Visceral layer – – covers outside of organs in cavity Serous fluid fills the pocket The Serosa Skin & Body Membranes, cont… Connective tissue membranes – Synovial Soft areolar connective tissue NO epithelial cells Functions of I.S. Protects from: – Mechanical, chemical, bacterial, UV, thermal, & dessication Heat loss/retention Excretion of urea/uric acid Makes Vitamin D Tells us about external environment Structure Epidermis – Dermis – Stratified squamous Dense fibrous conn. tissue Hypodermis – Adipose tissue Firmly connected together! Skin Structure Epidermis 5 layers called “strata” (deep to superficial) – – – – – stratum basale stratum spinosum stratum granulosum stratum lucidum stratum corneum Avascular—no blood supply Keratinocytes—produce keratin Epidermis of Thick Skin A Closer Look at the Strata… Stratum basale – – – Stratum spinosum Stratum granulosum – Cells become flatter, full of keratin Stratum lucidum – deepest layer receives nutrients constantly dividing Cells beginning to die, extra thick, hairless skin Stratum corneum – – DEAD!!! 20-30 cell layers thick Fun Facts Every 25-45 days, you have a completely NEW epidermis! Everything you see when you look at someone else is DEAD! Gross! Melanin Melanin is a pigment – – yellow to brown to black Melanocytes make the pigment Freckles/moles – Melanin is concentrated in 1 area Dermis Your dermis is your “hide” – – Strong, stretchy envelope Dense fibrous conn. tissue – Collagen Elastic fibers 2 Regions: Papillary layer—upper dermis – House pain receptors/free nerve endings & touch receptors (Meissner’s corpuscles) Reticular layer—deepest skin layer – Pressure receptors (Pacinian corpuscles) Dermis, continued… Blood Vessels—maintain homeostasis Rich nerve supply Entry Task 1. 2. 3. 1/8 Explain the function of the stratum basale of the epidermal layer. Why do we get wrinkled, saggy skin as we age? Be sure to identify the layer of skin involved in your answer. What part of skin do you think pain receptors are found in? Touch receptors? Skin Color 3 Pigments – – – Melanin Carotene Oxygen-rich hemoglobin Alterations in skin color – – – – redness/erythema pallor/blanching jaundice bruises Appendages of the Skin Includes: – cutaneous glands, hair, hair follicles, and nails Exocrine glands—release secretions through ducts – 2 Types Sebaceous glands (oil) Sudoriferous glands (sweat) Sebaceous Glands (Oil) All over skin (not on palms/feet) Empties into hair follicles Secretes sebum—oil & fragmented cells – – – Keeps skin soft Has chemicals that kill bacteria Clogged duct = whitehead Sudoriferous Glands (sweat) 2.5 million/person 2 Types: Eccrine & Apocrine Eccrine – – – More common, produces sweat Heat regulation 7L sweat on a hot day! Sudoriferous Glands, cont… Apocrine – – – – Mainly in axillary & genital area Larger than eccrine glands Secretes fatty acid/protein along with other components Bacteria have a hay day!!! Hair & Hair Follicles Components: – – – – – – – – – Follicle: produces hair Shaft: part of hair exposed to environment Root: part of hair enclosed in the follicle Medulla: central core Cortex: area between medulla & cuticle Cuticle: heavily keratinized; shingles Arrector pili: smooth muscle, connects follicle to tissue Matrix: growth zone Hair bulb: contain melanocytes Nails Components: – – – – – – – – Free edge Body Root: embedded in skin Nail folds: sides of nails, connected to skin Cuticle: thick proximal nail fold Lunula: crescent Nail bed: extends beneath the nail Nail matrix: thick part of nail bed; growth Homeostatic Imbalances Over 1000 ailments of the skin! – Mostly allergies, fungus, burns, & cancer Athlete’s foot—fungus Boils/carbuncles—inflamed oil glands Cold sores—herpes virus Contact dermatitis—chemical contact Impetigo—bacterial infection Psoriasis—autoimmune disorder Burns Def: Tissue damage/cell death caused by intense heat Skin = thick as a paper towel Almost all body systems suffer when skin is burned 2 life threatening problems: fluid loss & kidney shutdown/circulatory shock Burns, cont… Rule of Nines: – – Body divided into 11 areas, each covering 9% surface area Helps determine volume of fluid lost Infection is leading cause of death Burns are sterile 24 hours after – Then pathogens invade Burn Classification 1° Burn – – – – Epidermis damaged Red, swollen Lasts 2-3 days EX: sunburn Burn Classification 2° Burn – – – – Epidermis & Upper Dermis damaged Red, painful blisters Regrowth can occur No permanent scarring if taken care of Burn Classification 3° Burn – – – – – Entire thickness of skin destroyed Blanched/Black No pain—nerves destroyed Regeneration not possible Skin grafting Burn Classification CRITICAL burns meet this criteria: – – – 25+% of the body has 2° burns 10% has 3° burns 3° burns on the face, hands, and/or feet Skin Cancer Most common of all cancers 1 in 5 people will have skin cancer in their lifetime 3 Types – – – Basal cell carcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma Malignant melanoma Basal Cell Carcinoma Least malignant, most common No keratin/boundary formed by stratum basale Invades dermis/hypodermis On face, shiny, slowgrowing Full cure @ 99% in most cases Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stratum spinosum Scaly, reddened papule Shallow ulcer, raised border Scalp, ears, hands, lips Fast growing If caught early full recovery can be made Malignant Melanoma Cancer of melanocytes 5+% cases are melanoma Appears spontaneously, develops from pigmented moles brown to black patches 50% survival rate ABCD Rule Asymmetry – Border irregularity – Borders not smooth, have indents Color – 2 sides of mole/spot don’t match Different colors, range from black/brown/tan, blues/reds Diameter – 6+ mm Thursday 3/27 Identify different types of burns and skin cancers Finish PowerPoint Notes Begin Review assignment – P.127 MC: #1-2, 4, 6-7; SA: #1-4, 6-11, 13; At the Clinic: #1-4 Friday Correct Review Play Flyswatter Review game Test over all of CH 4 on Monday after break! 3/28 Have a Great Spring Break!