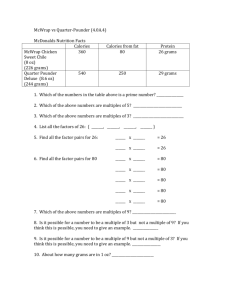
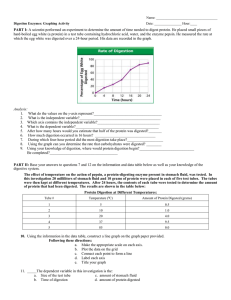
Review for Test
advertisement
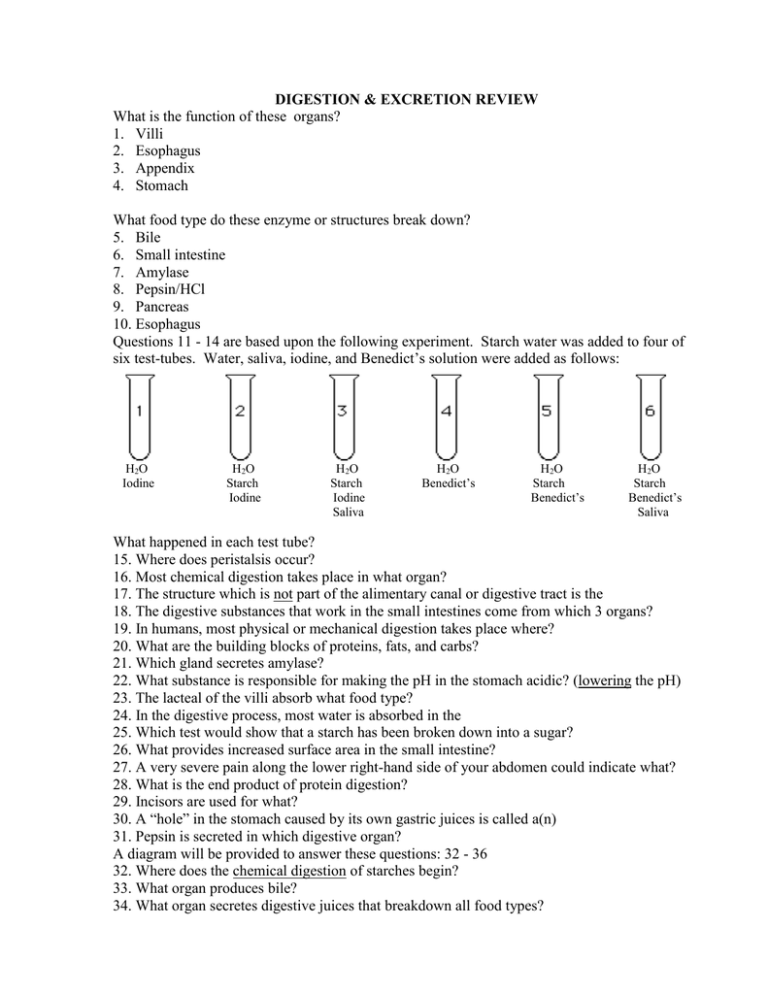
DIGESTION & EXCRETION REVIEW What is the function of these organs? 1. Villi 2. Esophagus 3. Appendix 4. Stomach What food type do these enzyme or structures break down? 5. Bile 6. Small intestine 7. Amylase 8. Pepsin/HCl 9. Pancreas 10. Esophagus Questions 11 - 14 are based upon the following experiment. Starch water was added to four of six test-tubes. Water, saliva, iodine, and Benedict’s solution were added as follows: H 2O Iodine H 2O Starch Iodine H2O Starch Iodine Saliva H2O Benedict’s H2O Starch Benedict’s H 2O Starch Benedict’s Saliva What happened in each test tube? 15. Where does peristalsis occur? 16. Most chemical digestion takes place in what organ? 17. The structure which is not part of the alimentary canal or digestive tract is the 18. The digestive substances that work in the small intestines come from which 3 organs? 19. In humans, most physical or mechanical digestion takes place where? 20. What are the building blocks of proteins, fats, and carbs? 21. Which gland secretes amylase? 22. What substance is responsible for making the pH in the stomach acidic? (lowering the pH) 23. The lacteal of the villi absorb what food type? 24. In the digestive process, most water is absorbed in the 25. Which test would show that a starch has been broken down into a sugar? 26. What provides increased surface area in the small intestine? 27. A very severe pain along the lower right-hand side of your abdomen could indicate what? 28. What is the end product of protein digestion? 29. Incisors are used for what? 30. A “hole” in the stomach caused by its own gastric juices is called a(n) 31. Pepsin is secreted in which digestive organ? A diagram will be provided to answer these questions: 32 - 36 32. Where does the chemical digestion of starches begin? 33. What organ produces bile? 34. What organ secretes digestive juices that breakdown all food types? 35. Which organ receives the secretions of the pancreas and the liver? 36. Where are the gastric juices located? 37. The amount of energy stored in food is referred to as a(n) Use the following choices for questions 39 – 42: Carbohydrates Fats Proteins 38. Supply the raw materials for growth and repair of structures 39. Main source of energy for the body 40. Helps produce cell membranes and nerve cell covering, stored energy 41. Includes starches, fruits, vegetables, and whole-grains. 42. When you go to the doctor for an exam, she will usually require you to give a urine sample. What should not be found? 43. The kidney’s chief function is to? 44. What are the individual filtering units within each kidney? 45. Before it is released from the body, urine is stored in the Question 47 - 48 will be based on the table below. The data was obtained from the kidneys of rats. SUBSTANCE water BLOOD ENTERING KIDNEY BLOOD LEAVING KIDNEY (re-absorbed) 100 liters URINE 99 liters 1 liter glucose 70 grams 70 grams 0 grams urea 30 grams 4 grams 26 grams salts 370 grams 364 grams 6 grams Understand what’s happening in the chart Use the diagram on the right to answer questions 48 – 51, which will be about the Nephron and what happens at the various locations: C D E AB