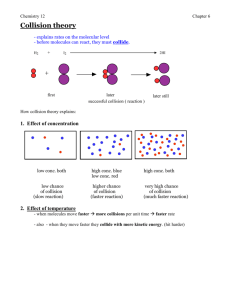
Ch. 5 Review
advertisement
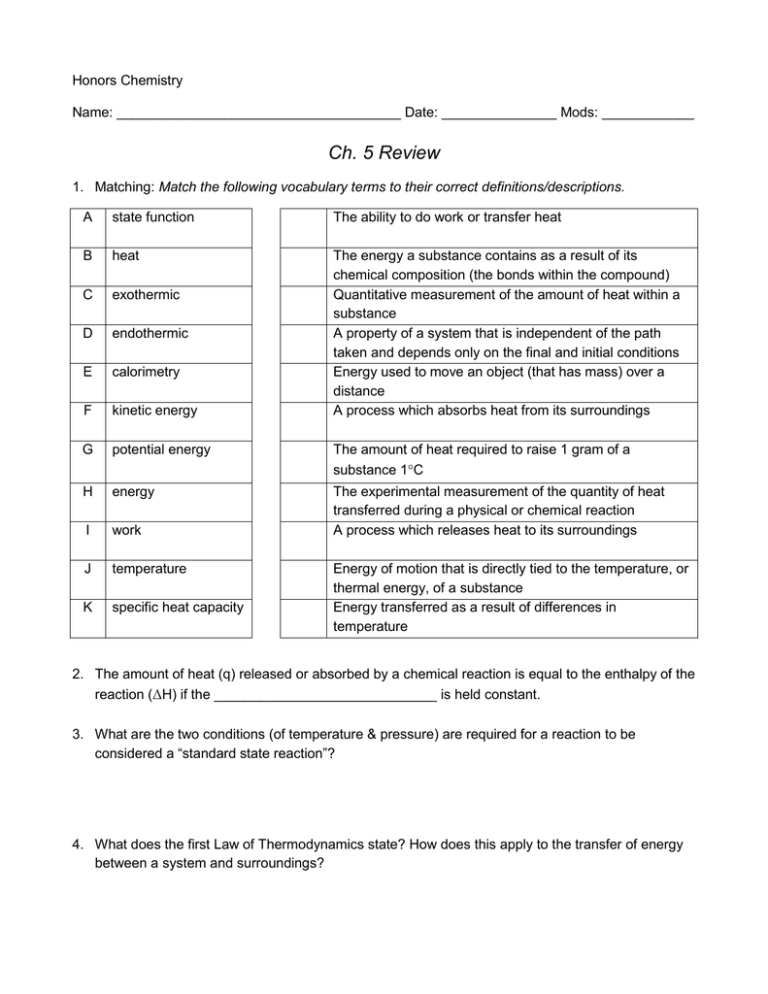
Honors Chemistry Name: _____________________________________ Date: _______________ Mods: ____________ Ch. 5 Review 1. Matching: Match the following vocabulary terms to their correct definitions/descriptions. A state function The ability to do work or transfer heat B heat C exothermic D endothermic E calorimetry F kinetic energy The energy a substance contains as a result of its chemical composition (the bonds within the compound) Quantitative measurement of the amount of heat within a substance A property of a system that is independent of the path taken and depends only on the final and initial conditions Energy used to move an object (that has mass) over a distance A process which absorbs heat from its surroundings G potential energy The amount of heat required to raise 1 gram of a substance 1°C H energy I work The experimental measurement of the quantity of heat transferred during a physical or chemical reaction A process which releases heat to its surroundings J temperature K specific heat capacity Energy of motion that is directly tied to the temperature, or thermal energy, of a substance Energy transferred as a result of differences in temperature 2. The amount of heat (q) released or absorbed by a chemical reaction is equal to the enthalpy of the reaction (ΔH) if the _____________________________ is held constant. 3. What are the two conditions (of temperature & pressure) are required for a reaction to be considered a “standard state reaction”? 4. What does the first Law of Thermodynamics state? How does this apply to the transfer of energy between a system and surroundings? 5. Classify each of the following as either EXOthermic or ENDOthermic: a) ___________ surroundings get hot f) ___________ ΔH is negative b) ___________ enthalpy diagram is “uphill” g) ___________ enthalpy diagram is “downhill” c) ___________ heat is a product h) ___________ surroundings get cold d) ___________ ΔH is positive i) ___________ products have higher enthalpy e) ___________ reactants have higher enthalpy j) ___________ heat is a reactant 6. Determine the change in internal energy, ΔE, in kilojoules for each system below: a) A windmill emits 1290.6 calories of heat while doing 129 kJ of work done on its surroundings. What is the internal energy change of the windmill? b) A snow plow has 41 kJ of work done on while it releases 3.8 kcal of heat to its surroundings. What is the internal energy change of the snow plow? 7. Write the enthalpy of formation equation, including the ΔHf°, for the formation of solid rubidium chlorate. 8. A layer of copper welded to the bottom of a skillet weighs 125 g. How much heat is needed to raise the temperature of the copper layer from 25˚C to 300˚C if the specific heat capacity of Cu is 0.387 J/g°C? 9. Water is cooled from an initial temperature of 74.5°C down to 3.9°C. This decrease in temperature releases 162.8 kJ of heat. What was the mass, in grams, of water cooled? 10. In a purity check for industrial diamonds, a 10.25-carat (1 carat = 0.20 g) diamond is heated to 73.0°C and immersed in 26.05 g of water inside a calorimeter. The initial temperature of the water is 27.0°C. Calculate the final temperature of water and diamond (Cp(diamond) = 0.519 J/g°C). 11. Given the following information, calculate the enthalpy of the reaction between gaseous hydrochloric acid and solid sodium nitrite: HCl (g) + NaNO2 (s) HNO2(l) + NaCl (s) Reaction A: 2 NaCl (s) + H2O (l) 2 HCl (g) + Na2O (s) ΔHA = +507.0 kJ Reaction B: Reaction C: NO (g) + NO2 (g) + Na2O (s) 2 NaNO2 (s) NO (g) + NO2 (g) N2O (g) + O2 (g) ΔHB = - 427.0 kJ ΔHC = - 43.0 kJ Reaction D: 2 HNO2 (l) N2O (g) + O2 (g) + H2O (l) ΔHD = +34.0 kJ 12. Ammonia gas (NH3) and oxygen gas react to produce nitrogen gas and water vapor. a) Write the balanced chemical equation to express this reaction b) Calculate the standard enthalpy change, H°rxn, for this reaction. c) Re-write the reaction above as a thermochemical equation where the enthalpy of reaction is expressed as either a reactant or product. 13. The standard heat of formation, ΔHf°, for gaseous sulfur dioxide (SO2) is -297 kJ/mol. How many kJ of energy are given off when 25.0 g of SO2 (g) is produced from its elements? 14. The combustion of one mole of liquid pentane, C5H12, releases 3003.5 kJ of heat. Determine the heat of formation, ΔHf°, of liquid pentane. 15. Questions a-e are based on the following reaction: 2 N2O5(g) + 64.5 kJ 4 NO2(g) + O2(g) a) Is the above reaction exothermic or endothermic? _____________________________ b) Which has a higher enthalpy, the reactants or products? ________________________ c) If 220 grams of dinitrogen pentoxide are decomposed, what would be the associated enthalpy change (in kJ)? d) If the enthalpy change associated with this reaction is 52.8 kJ, what mass of nitrogen dioxide will be produced? e) Draw an enthalpy diagram below to describe this reaction.