Lewis Dot part 4
advertisement

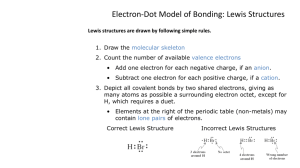
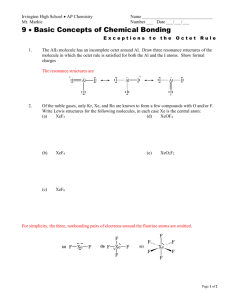
Lewis Dot Chapter 8 Another model The localized electron model assumes compounds are held together by sharing electron pairs. Pairs of electrons may be • localized pairs or • bonding pairs. There are 3 parts to this. The LE Model Description of the electrons in a molecule using Lewis model. Prediction of the geometry of the molecule using valence shell electronpair repulsion (VSEPR). Description of atomic orbitals used by atoms to share electrons or hold lone pairs (Molecular Orbital model in chapter 9). Lewis Dot Structure Duet Rule H does not need 8 electron to reach a stable noble gas configuration. It needs only 2 electrons to reach He. Note lone pair electrons and bonding electrons in HCl Steps for writing Lewis dot structures 1. Sum the valence e-’s from all the atoms. The total # of e-’s is what is important. 2. Use e- pairs to form bond between each pair of bound atoms. 3. Arrange e-’s to satisfy duet & octet rules. Example: Water Sum up valence e’s 8 Draw e- pairs, may use a line to designate e- pair. H-O-H Distribute remaining e-’s to fill octet or duet. How about CO2? How many Valence electrons? 16 Bond the three atoms. O-C-O How to arrange the remaining e-’s? More examples What is the Lewis structure for: HF N2 NH4+ CH4 CF4 NO+ Find the errors in these N has only 5 valence electrons Si does not have an octet. H does not have a duet. N does not have an octet. More errors H does not follow duet. Cl does not follow octet. (10) C doest not follow octet. (6) H does not follow duet and Br does not follow octet. Exceptions to the octet rule. Like most models the Lewis dot is flawed. Boron for example may have only three bonds. We know this due to its reactivity with ammonia Exceptions continued Boron acts in chemical reactions as though it needs an electron pair. It is highly reactive with ammonia forming H3NBF3. This supports Boron as an exception to the octet rule. Other exceptions Beryllium and nitrogen are also exceptions. Exception are not reserved for less than octet. Exceptions of greater than 8 in the Octet. Atoms from P and larger have access to the d orbitals. This gives these atom the ability to have more than 4 bonding sites and access to more than 8 electrons and still be stable. Summary Second row elements C, N, O & F always follow the octet rule. Second row B, & Be may have less than 8. These electron deficient molecules are highly reactive. 2nd row elements may never exceed the octet since they do not have access to d orbitals in the second energy level. Summary continued Third row and higher elements often satisfy the octet rule but may exceed the rule as they have access to the d orbital. When writing the Lewis structure, follow the octet rule. If electrons remain, only then may you add extra electron pairs to the element having available d orbitals.