No Slide Title
advertisement
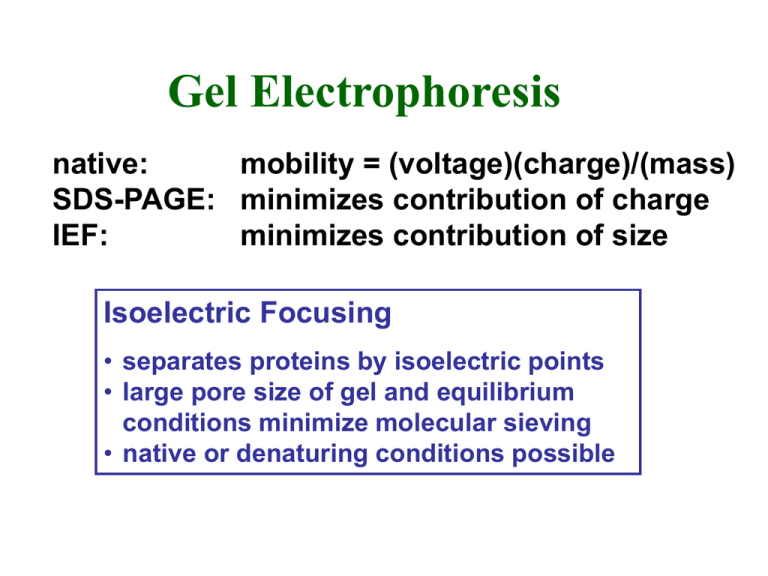
Gel Electrophoresis native: mobility = (voltage)(charge)/(mass) SDS-PAGE: minimizes contribution of charge IEF: minimizes contribution of size Isoelectric Focusing • separates proteins by isoelectric points • large pore size of gel and equilibrium conditions minimize molecular sieving • native or denaturing conditions possible Carrier Ampholytes • mixture of aliphatic amines + either carboxylic or sulfonic acid groups • generates pH gradient in electric field • gradient range depends on ampholyte pKa values • proteins migrate to position = isoelectric point Preparative IEF (Rotofor) • polyester screens separate chamber into 20 compartments • fractions rapidly harvested following electrofocusing IEF Practical Considerations • gradient range • low ionic strength for maximum resolution • gels: acetone ppt. • precipitation problems • include urea, non-ionic detergents • heating • gradient breakdown Two-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis Protein Detection Following Electrophoresis General Proteins • organic dyes (eg., Coomassie blue) • R-250 (slow) • G-250 (fast) Silver Staining Methods • diamine (ammonical) • non-diamine • photodevelopment • silver stain • 10-100X more sensitive than CB • fluorescence • radioactivity Specific Proteins • enzyme activity • antibody/immunoblot Radiolabeling Proteins • metabolic • amino acids • post-translational • chemical • iodination • alkylating agents Autoradiography/Fluorography • electrophoresis of radioactive proteins • dry gel and expose to X-ray film • use intensifying screens for high energy isotopes • use fluors impregnated in gel for low and medium energy isotopes Enhancement of Autoradiographic Methods for Detection of Radioisotopes Detection Sensitivity 2 Isotope Energy Method (dpm/mm ) direct 2-5 32 125 High ( P, I) screen 0.5 direct 15-25 35 14 Medium ( S, C) fluor 2 3 Low ( H) fluor 10-20 Enhancement shortens exposure times by 7-10 fold Phosphor Imaging • filmless autoradiography • screens contain 'storage-phosphors' • traps the energy of radioactive emissions • sensitive to both b-particles and g-rays • efficiency ~100% for particle striking screen • scanning the screen with a laser beam releases the stored energy as light • ‘fluorescence’ converted into an image file for display and quantification • high sensitivity short exposure times • range of 5 orders of magnitude • screens are 'erased' and reused Quantifying Proteins • subjective estimates • scanning densitometry • excise bands and count radioactivity Protein Detection General Proteins • Coomassie blue • silver stains • fluorescence • radioactivity Activity Gels • carry out electrophoresis under native conditions • or remove SDS following SDS-PAGE • some proteins refold • lower SDS and no heat • replace with non-ionic detergent Specific Proteins • antibody/immunoblot Protease Activity • enzyme activity • protease activity • co-polymerize PAG with • redox reactions protein substrate • clear zones following incubation and staining Redox Reactions and Tetrazolium Salts • reduced tetrazolium salts form insoluble formazan dyes • eg, nitro-blue tetrazolium (NBT) • measure dehydrogenases and other redox reactions • coupled reactions • non-redox reactions also possible • eg, phosphatase (BCIP)