Train the Trainer - County of Santa Cruz Health Services Agency
advertisement

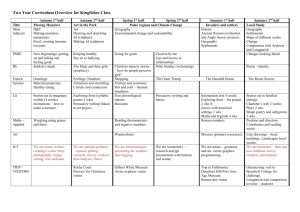
Learning Plan Workshop Learning Plan Workshop Agenda • Workshop Objectives • Roles and Responsibilities • Types of Training – Training Objectives – Train the Trainer (Netsmart Led) – End User Training (Client Trainer Led) • Adult Learning Principles • Training Requirements – Audience – Method/Suggested Outline Learning Plan Workshop Agenda - Continued • Training Timeline – Schedule – Resource Requirements • Sample Training Scripts – Avatar PM Training Examples – Avatar CWS Training Examples • Evaluations • Post Implementation Training Strategy Workshop Objectives Workshop Objectives • Understand the Learning Plan and begin its creation. • Understand Adult Learning Principles and best practices for training. • Understand the roles and responsibilities for training. • Begin to review the training scripts and how they can be used to create solution training. • Begin to formulate a plan for end user training, including identifying resources, method of training and schedule. • Understand the training timeline. • Identify personnel for training, including solution training demo to the project team during the Go-Live Preparation event. Roles & Responsibilities Client Roles & Responsibilities • Learning Coordinator • Complete the Learning Plan, including the Learning/Training Timeline. • Identify and Coordinate Training Resources. • Assign and Coordinate Training Development, including Training Scripts. • Schedule Training Resources. • Secure Facilities, Location and Equipment for all Training. • Track and Communicate Progress Against the Learning Plan. • Trainers • • • • Train end users. Create (or co-create) training. Provide Feedback for training refinement. Qualities – Patient, Knowledgeable, Respected Netsmart Role & Responsibilities • Netsmart Associates • • • • Lead the Learning Workshop. Deliver Train the Trainer training. Provide and review the Training Script Templates. Collaborate with the Learning Coordinator to develop a feasible timeline and Learning Plan. • Offer feedback to the trainers providing the solution training demo during the Go-Live Preparation event. • Assist in order to successfully execute the learning plan objectives. Types of Training Training Objectives • Train the Trainer • Ensure all trainers are adequately prepared to deliver solutions training. • Demo to Project Team during Go-Live Preparation to confirm readiness for end user training. • Solutions Training • All users have the necessary knowledge and skills to be effective, efficient and proficient users of the solutions used in daily work activities. Train the Trainer • What: • Training delivered to client to review solution training and training objectives • When: • Final Review & Validation • Who: • Netsmart: Provides training • Client: Learning Coordinator and client trainers who will be providing solutions training (end user training) Solutions Training (End User Training) • What: • Training delivered to staff members in preparation for Go-Live • When: • Between the completion of Go-Live Preparation and prior to Go-Live • Who: • Netsmart: Support Role • Client: Client trainers to demo training during GoLive Preparation and deliver solutions training to end users Adult Learning Principles Adult Learning Principles • Malcolm Knowles – Theory of Adult Learning (Andragogy) • Emphasizes that adults are self-directed and expect to take responsibility for decisions. • Adults need to know why they need to learn something. • Adults need to learn experientially. • Adults approach learning as problem-solving. • Adults learn best when the topic is of immediate value. Adult Learning Principles • Software Training Example by Knowles • Need to explain why specific things are being taught (e.g., certain commands, functions, operations, etc.) • Instruction should be task-oriented instead of memorization - learning activities should be in the context of common tasks to be performed. • Instruction should take into account the wide range of different backgrounds of learners; learning materials and activities should allow for different levels/types of previous experience with computers. • Since adults are self-directed, instruction should allow learners to discover things for themselves, providing guidance and help when mistakes are made. References • • • Knowles, M. (1975). Self-Directed Learning. Chicago: Follet. Knowles, M. (1984). The Adult Learner: A Neglected Species (3rd Ed.). Houston: Gulf Publishing. Knowles, M. (1984). Andragogy in Action. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass. Adult Learning Principles I hear and I forget. I see and I remember. I do and I understand. ~Confucius c.450 BC Adult Learning Principles • Types of Learning Styles • Auditory – Learn through listening (lectures, discussions) – Written information has little meaning • Visual – Learning through seeing (demonstrations, diagrams, handouts) – Instructor’s body language/facial expressions help in learning process • Tactile or Kinesthetic – Learn by doing, touching (hands-on activities) – Want to explore • Combination – Good instruction should combine auditory, visual and tactile – Retention increases when learning involves more senses and activities Reference • FEMA/CERT (Community Emergency Response Team) Basic Train-the-Trainer Training Training Requirements Training Audience • Training Category Breakdown • Ensures all staff is adequately trained for their role in the organization. • Ensures correct personnel are chosen to train those end users. • Table provided in Learning Plan to list the Training Category, End User Roles in that category and any Comments. Training Category Ex: Clinical Staff End User Roles Ex: Nursing, SW, Psychiatrists Comments CWS, Order Entry Training Method/Suggested Outline • Traditional Face-to-Face Training in Classroom Setting – Minimizes distractions – Allows for more users to be training at one time – Users can learn from each other’s questions • Suggested Outline – – – – – – – – – – Introduction Learning Objectives Solutions Training demo Hands-on Exercises Assessment for Learning Confirmation Exceptions/Misc. Items in Solution Workflow Hands-on Exercises if applicable Question/Answer Session Summary Training Evaluation Training Timeline Santa Cruz County Proposed Project Timeline 4 wks Nov 20 2014 12 wks Dec 18 2014 12 wks March 11 2015 12 wks July 20 2015 4 wks Sept 28 2015 4 wks Oct 26 2015 6 wks Nov 23 2015 16 wks Jan 1 2015 May 1 2016 Project Management Office Oversight Data Collection Design Build Unit Test End-User Training System Test Int. Testing Identify Improvement and Optimization Opportunities Test Script Dev 10 Wks Client Train 6 Wks DC1 4 Wks Train Mat. Dev 10 Wks DC2 8 Wks Syst Test 6 Wks INT 2 Wk Legend Client Site DC3 16 Wks Netsmart Netsmart Quality Control Rev 1 Wk Bld/Test1 4 Wks Client Owned Bld/Test2 4 Wks Bld/Test3 4 Wk Netsmart Owned Training Timeline Considerations • A detailed timeline needs to be developed to ensure all steps in the Learning Plan are met. Items include: – – – – – Train the Trainer Training Script Development Demo to Project Team Finalization of Training Materials Training schedule timeline • Other Resource Items to Consider – – – – – Number of People to Train, including Multiple Shifts (If Applicable) Number of Training Scripts Needed Facilities and/or Equipment Constraints Trainer Availability Staff Availability Training Timeline Considerations • Utilize the Training Activity Table in the Learning Plan map out deliverables and completion dates Training Activity Completion Date Learning Workshop MM/DD/YYYY Train the Trainer MM/DD/YYYY Training Script Development MM/DD/YYYY Demo to Project Team (Go-Live Preparation) MM/DD/YYYY Finalization of Training Materials MM/DD/YYYY End User Training MM/DD/YYYY Other Activities MM/DD/YYYY Sample Training Scripts Sample Training Scripts • Library of Sample Training Scripts Available – Use to piece together workflow for your site – Steps are in place but may need modified based on specific workflow needs – Placeholders in place for screenshots – Can be used for training as well as job aids or other training materials deemed necessary Other Training Considerations • Evaluations – Critical to Ensure Training is Effective – Types of Evaluations: » Assessments during training » Surveys after training » Observations post go-live • Post Implementation Training Strategy – Need strategy for future hires – New Workflow Implementations, Software Changes – Analysis of evaluations may find potential need for supplemental training or job aids