Ovarian Cancer

By Deborah Wilson-Brosseau
What is Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is any cancerous growth that develops in any part of the ovaries.
Demographics of Ovarian Cancer
Eighth most common cancer among women in the
United States
Accounts for 3.3% of all new cancer in American women
Fifth most common cause of cancer death among women due to poor early detection
One in 71 women will develop ovarian cancer
One in 95 will die from it
21,550 new cases each year
14,600 deaths per year (6)
Demographic of Ovarian Cancer
Most likely to occur over the age of 50
After menopause
Caucasian Women have a higher risk especially
Ashkenazi Jewish descent women
African-American and Asian women have a lower risk of ovarian cancer
Half of the ovarian cancer cases will develop in women over the age of 63
Highest incidence of ovarian cancer occurs in industrialized countries (6)
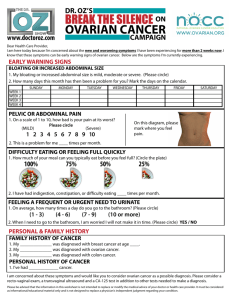
Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
It is often called the silent killer because it produces few symptoms in its early stages
Most women are unaware they have the disease until it has progressed to advanced stages.
Most early symptoms are vague and either abdominal or gastrointestinal in nature’
If you have any of the following symptoms that persist for two weeks or more contact your doctor (4,6)
Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
Digestive symptoms
Gas, indigestion, constipation
Bloating, distention or cramping
Abdominal or low back discomfort
Pelvic pressure
Vaginal bleeding in post menopausal woman
Frequent urination
Unexplained changes in bowel habits
Nausea or vomiting
Pain or swelling in abdomen
Loss of appetite
Fatigue
Pain during intercourse
(4,6)
Risk Factors for Ovarian Cancer
Age is the greatest risk factor
Risk increases after menopause
Family or personal history of cancers of the female reproductive tract or breast that is caused by an inherited the genetic mutation
Early menstruation-before age 12
Late menopause
Use of talcum powder in the genital area
Female workers exposed to asbestos
Genital deodorant sprays
Eating a diet high in saturated fats
Treatment with androgens (male hormones)
Never having been pregnant
Obesity increases risk
If you have been pregnant, breastfed and took oral contraceptives your risk of developing ovarian cancer is lowered. (1,6)
How is Ovarian Cancer Diagnosed
A complete medical history to assess all the risk factors
A thorough bi-manual pelvic examination
CA-125 assay
Blood test to determine the level of CA-125
One or more various imaging procedure
Ultrasound, CT, MRI
A lower GI series or barium enema
Diagnostic laparoscopy for definitive diagnose
Uses a thin instrument inserted in the abdomen to visualize the organs inside the abdominal cavity(4,6)
Variations in Ovarian Tumors
Three main types
Epithelial Cells
90% of all ovarian cancers develop from epithelial cells lining the surface of the ovaries
Stromal Cells
5% of ovarian cancers begin in the stromal cells that produce estrogen and progesterone
Germ Cells
2% of ovarian tumors develop in the cells that would become eggs.
Many are benign (noncancerous)
(2,4)
Stages in Diagnosis
Stage 1- Tumor limited to ovary or ovaries
Stage 2- Ovarian tumor with pelvic extension, involves the uterus or fallopian tubes and/or other pelvic organs
Stage 3- Tumor involving the upper abdomen or lymph nodes
Stage 4- Tumor involving distant organs including pleural space or hepatic/splenic parenchyma (6)
Current Treatment
Three treatments for ovarian cancer
Surgery
It is done to remove as much of the tumor as possible and it is usually followed by chemotherapy and/or radiation
Chemotherapy
It is used to target cells that have traveled to other organs and throughout the body via the lymphatic system or the blood stream
Radiation
It uses high energy, highly focused x-rays to target very specific areas of cancer. A machine with external energy beam and radioactive liquids are used for radiation treatments. (4,6)
Chemotherapy and Ovarian Cancer
Chemotherapy is most often a systemic treatment
It is used to kill cancer cells
It is administered several ways
Intravenous, IV
Travels throughout the body
Orally
Travels throughout the body
Intraperitoneal
Is localized in the abdominal cavity (4,6)
Chemotherapy
A combination of two or more drugs should be given to help to kill cancer cells
Platinum compounds is the single most active drug in the treatment of Ovarian cancer
The combination of intravenous platinum compound such as cisplatin and a taxane such as paclitaxel is the first line for many patients
3 to 6 cycles of chemotherapy should reduce the size of the tumor (4,6)
Cisplatin Platinol-AQ
A chemotherapy treatment used for testicular, ovarian, bladder or lung cancer
Intravenous- Parenteral Only
It is sometimes combined with other cancer drugs
Some Side Effects
Altered taste, stomatitis, severe prolong vomiting and nausea, diarrhea, renal toxicity, weakness, infections, hair loss and peripheral neuropathy
Anorexia and weight loss (3)
Cure or Remission Rate
5 Year Survival Rates
Stage 1------92.8%
Stage 2------78.6%
Stage 3------50%
Stage 4------17.5%
(6)
The Impact of Cancer and
Treatment on Nutrition
Cancer can cause chronic nausea and early satiety
Fatigue
Pain
Mental Stress
Vomiting
Metabolic changes
Muscle wasting
Altered taste perception intestinal cramping
Diarrhea
Constipation (5)
Nutrition Therapy
Treatment for Bowel Issues
Drink lots of fluid
Eat small meals
Have salty soup and broths
Don’t eat or drink foods that will increase gas
No caffeine
No foods that contain high fat
Talk to your doctor about using digestive enzyme replacements for prolong diarrhea (5)
Prevention Theories
Decrease Ovulation
Pregnancy stops ovulation
Multiple pregnancies
Breastfeeding children
Taking oral contraceptives
Genetic Testing
To detect if you are carrying certain genes that increase your risk
Test positive for BRCA1 OR
BRCA2
Surgery
Having a tubal ligation lowers your risk
Hysterectomy also lowers your risk
Screening
Women at high risk should talk to their doctor
Regular Screening
Blood test and ultrasound
Annual pelvic exam (6)
Gynecological Cancer Support
Group
a support group for women diagnosed with gynecological cancer, their families and friends to share experiences.
When: Meetings are held the second Tuesday of every month from 5 to 6:15 p.m.
Where : Banner Desert Cancer Center
Phone Number: (480) 412-HOPE (4673).
Address: 1400 S. Dobson Road
Mesa, AZ 85202
Citation
Cancer.org. Cancer. 23 January 2012.
<http://www.cancer.org/cancer/ovariancancer/overviewguide/ovarian-cancer-overview-what-isovarian-cancer>.
Cherry, James Michael. Comparative study of molecular changes in ovarian tumor progression and the identification of biomarkers. 2009. <http://www.grin.com/en/doc/275123/comparativestudy-of-molecular-changes-in-ovarian-tumor-progression-and>.
Crowe, Zaneta M. Pronsky and Sr Jeanne P. "Food Medication Interaction." 2010: 84.
Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins. "Cancer-Principles and Practice of Oncology 9th Edition." 2011:
1368-1377.
Sharon Rady Rolfes, Kathryn Pinna and Ellie Whitney. "Understanding Normal and Clinical
Nutrition." Sharon Rady Rolfes, Kathryn Pinna and Ellie Whitney. Belmont, Ca: Wadworth, 2009.
907-910.
Thompson. "The Gale Encyclopedia of Cancer Third Edition Volume 2." 2010: 1090-1097.