Supplementary-sub
advertisement

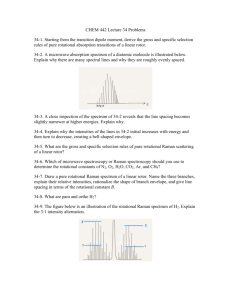
Supplementary Material Infrared absorption of gaseous CH2BrOO detected with a step-scan Fourier-transform absorption spectrometer Yu-Hsuan Huanga) and Yuan-Pern Leea), b) * a) Department of Applied Chemistry and Institute of Molecular Science, National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu 30010, Taiwan b) Institute of Atomic and Molecular Sciences, Academia Sinica, Taipei 10617, Taiwan (Received xx August 2014 accepted xx xxxx 2014) Running title: IR absorption of CH2BrOO Key words: IR spectroscopy, CH2BrOO, bromomethylperoxy, CH2Br, free radical a) Author to whom correspondence should be addressed. Electronic mail: yplee@mail.nctu.edu.tw; FAX: 886-3-5713491. Comparison of rotational parameters of syn-CH281BrOO and anti-CH281BrOO in their ground and vibrationally excited states predicted with the B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ method is shown in Table SI. Comparison of rotational parameters and type ratios of CH2BrO and CH2BrOOBr in their ground and vibrationally excited states predicted with the B3LYP/augcc-pVTZ method is presented in Table SII. Figure S1 shows the displacement vectors and directions of dipole derivatives for all vibrational modes of syn-CH2BrOO predicted with the B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ method. Figure S2 shows the simulated rotational contours for 4 and 8 modes of syn-CH2BrOO; individual bands types as well as resultant rotational contours are presented. TABLE SI. Comparison of rotational parameters of syn-CH281BrOO and anti-CH281BrOO in their ground and vibrationally excited states predicted with the B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ method. syn-CH281BrOOa a anti-CH281BrOOb i A'/A" B'/B" C'/C" A'/A" B'/B" C'/C" 1 0.9979 1.0017 1.0012 0.9991 1.0008 1.0008 2 0.9985 1.0005 1.0004 0.9974 1.0004 1.0005 3 1.0015 0.9985 0.9992 0.9970 0.9994 1.0002 4 0.9976 0.9990 0.9987 0.9966 0.9996 0.9983 5 0.9961 1.0010 1.0006 0.9927 1.0005 1.0006 6 0.9946 0.9992 0.9987 0.9992 0.9978 0.9982 7 0.9949 1.0006 0.9996 1.0076 0.9968 0.9963 8 1.0001 0.9946 0.9958 0.9865 0.9975 0.9975 9 1.0017 0.9936 0.9945 0.9944 0.9968 0.9960 10 0.9976 0.9998 0.9984 1.0096 0.9984 0.9983 11 0.9991 0.9986 0.9986 1.0171 0.9998 0.9992 12 1.0223 0.9957 0.9965 0.9493 1.0029 1.0053 For syn-CH281BrOO, A" = 0.5670 cm1, B" = 0.0726 cm1, C" = 0.0678 cm1 for = 0 and Ae" = 0.5664 cm1, Be" = 0.0732 cm1, Ce" = 0.0684 cm1 for the equilibrium geometry. b For anti-CH281BrOO, A" = 1.2048 cm1, B" = 0.0604 cm1, C" = 0.0582 cm1 for = 0 and Ae" = 1.2370 cm1, Be" = 0.0607 cm1, Ce" = 0.0585 cm1 for the equilibrium geometry. TABLE SII. Comparison of rotational parameters and type ratios of CH2BrO and CH2BrOOBr in their ground and vibrationally excited states predicted with the B3LYP/augcc-pVTZ method. CH2BrOa CH2BrOOBrb a i harmonic anharmic. 2 1300 (65) 1246 1.0001 0.9997 1.0014 a:b = 44:56 4 1115 (53) 1088 0.9984 0.9942 0.9930 a:b = 96:4 4 1288 (36) 1261 0.9989 0.9994 0.9989 a:b:c = 55:40:5 5 1258 (21) 1229 0.9987 1.0004 1.0004 a:b:c = 73:20:7 6 1041 (156) 1009 0.9956 1.0016 1.0003 a:b:c = 88:10:2 7 922 (8) 904 0.9992 0.9979 0.9982 a:b:c = 82:2:16 A'/A" B'/B" C'/C" type ratio For CH2BrO, A" = 1.6133 cm1, B" = 0.1227 cm1, C" = 0.1165 cm1 for = 0 and Ae" = 1.6107 cm1, Be" = 0.1237 cm1, Ce" = 0.1175 cm1 for the equilibrium geometry. b For CH2BrOOBr, A" = 0.1323 cm1, B" = 0.0262 cm1, C" = 0.0224 cm1 for = 0 and Ae" = 0.1312 cm1, Be" = 0.0267 cm1, Ce" = 0.0227 cm1 for the equilibrium geometry. 1, a:b:c = 0.33:0.35:0.31 2, a:b:c = 0.08:0.88:0.04 , a:b:c = 0.02:0.29:0.69 4, a:b:c = 0.78:0.2:0.02 5, a:b:c = 0.2:0.18:0.63 6, a:b:c = 0.75:0.11:0.14 7, a:b = 0.98:0.02 8, a:b:c = 0.92:0.02:0.06 9, a:b:c = 0.83:0.16:0.01 10, a:b = 0.78:0.22 11, a:b:c = 0.3:0.1:0.6 12, a:b:c = 0.18:0.63:0.19 Fig. S1. Displacement vectors (thin arrows) and directions of dipole derivatives (thick arrows) for all vibrational modes of syn-CH2BrOO predicted with the B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ method. Molecular rotational axes are represented as arrows with labels. v4 3 v6 2 4 a-type 2 6 a-type 1 1 0 0 b-type b-type 1 Intensity / arb. unit Intensity / arb. unit 2 1 0 c-type 5 0 3 3 c-type 0 a:b:c = 0.78:0.2:0.02 2 a:b:c = 0.75:0.11:0.14 2 1 0 0 1300 1290 1280 1270 wavenumber / cm 1 1260 1250 1110 1100 1090 v7 2 1080 wavenumber / cm 1070 1 v8 7 a-type 4 8 a-type 2 0 0 b-type b-type 1 Intensity / arb. unit Intensity / arb. unit 1 c-type 3 0 2 2 c-type 0 4 a:b= 0.98:0.02 a:b:c = 0.92:0.02:0.06 2 0 980 0 970 960 wavenumber / cm 950 1 940 910 900 890 880 wavenumber / cm 870 860 1 Fig. S2. Simulated rotational contours for 4 and 8 modes of syn-CH2BrOO. (a) type a; (b) type b; (c) type c; (d) resultant rotational contours according to the weighting factors determined according to the projections of the predicted dipole derivatives onto axes a, b and c.