Properties of Water
advertisement

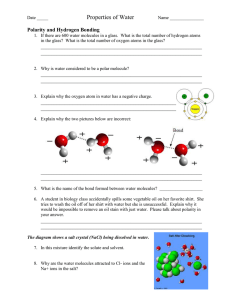
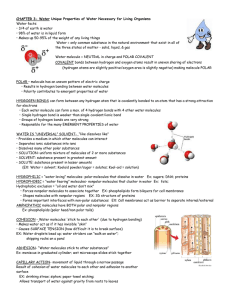
Properties of Water Copy notes into note guide. Choose a different color for each property of water to color code your notes. 1. POLARITY • The Oxygen end of the water molecule has a partial negative charge (due to pulling Hydrogen’s electrons towards its nucleus) while the Hydrogen end has a partial positive charge. • Overall charge on molecule is neutral however the charge is unevenly distributed thus making water a Polar Compound. • Polar nature of water causes molecules to be attracted to one another. 2. SOLUBILITY OR SOLVENT • From Latin solvere meaning “to loosen.” • Water dissolves other polar substances (ionic compounds, sugar, some proteins) • Water does not dissolve nonpolar substances (oil) due to a weaker attraction between polar and non-polar molecules. 3. HYDROGEN BONDING I’m stuck on you !!!! http://www.northland.cc.mn.us/biology /Biology1111/animations/hydrogenbond s.html • Hydrogen bonds are weak bonds that form between the partial positive hydrogen atom and the partial or negative oxygen atom. • Hydrogen bonds form, break, and reform frequently. • Hydrogen bonds cause water to form a liquid at room temperature. 4. COHESION Ex.) Basilisk Lizard • Attractive force that holds molecules of water together. • Creates surface tension where water “sticks” to water and forms a “skin” http://animals.nationalgeographic.com/ animals/reptiles/green-basilisk-lizard/ by pulling the molecules at the surface of the water downward into the liquid. 5. ADHESION • The attractive force of water molecules to “stick” to another material or surface. • Water “sticks” to other substances that also have a charge. • Holds two different substances together. 6. CAPILLARITY or CAPILLARY ACTION • Attraction between molecules that results in the rise of the surface of a liquid when in contact with a solid. • Water molecules are attracted to another surface (adhesion). Water “sticks” to water (cohesion) and moves up the straw. • Forces of adhesion, cohesion, and capillarity help water rise through narrow tubes against gravity (ex. Stem of flower) 7. DENSITY • Water has a density of 1.00g/mL • Any substance that has a density less than 1.00g/mL will float while any substance that has a density greater than 1.00g/mL will ______. • Density = Mass (g) / Volume (mL) 8. Temperature Moderation • Water has a high heat capacity- can absorb or release large amounts of energy with only a slight temp. change. • Energy is absorbed to break hydrogen bonds and is released as heat when bonds form.