Properties of Water Homework
advertisement

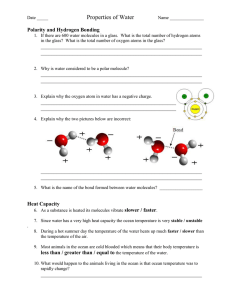
Textbook Section: 2-2 Properties of Water Outline: A. The Water Molecule a. Polarity i. Water molecules are polar because there is an uneven distribution of electrons between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms. ii. The negative pole is near the ______________________ atom and the ______________ pole is near the hydrogen atoms. b. Hydrogen Bonds i. Because of their partial positive and negative charges, polar molecules can attract each other. Example of a polar molecule: ____________________ ii. Hydrogen bonds form between the Hydrogen atom on one molecule with an oxygen atom on another molecule. Hydrogen bonds are ___________ bonds. iii. Cohesion- an attraction between water molecules of the same substance. Water is extremely cohesive because of _____________________________. Example of cohesion: _____________________________________________ iv. Adhesion- is an attraction between molecules of different substances. Example of adhesion: _____________________________________________________ c. Reflection of Reading: i. Points of Confusion: ii. Summary of Section: B. Solutions and Suspensions a. Mixture________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ i. Example of a mixture: ______________________________________________ ii. Two types of mixtures made with water are _____________________________ and __________________________. b. Solution- mixture of two or more substances in which the molecules of the substances are evenly distributed. i. Solute- _________________________________________________________ ii. Solvent- ________________________________________________________ c. Suspensions- mixture of water and nondissolved material. i. Example of suspension: ____________________________________________ d. Reflection of Reading: i. Points of Confusion: ii. Summary of Section: C. Acids, Bases, and pH a. Write the equation for the ionization of water b. The pH Scale i. Definition: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ ii. Range: ___________________________________________________________ 1. 0-6 = _________________ ex: __________________________________ 2. 7= ___________________ ex: __________________________________ 3. 8-14= ________________ ex: __________________________________ iii. The lower the pH, the greater the ___________________________. iv. The higher the pH, the more _______________________ the solution. c. Acids: i. Definition: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ ii. 2 examples: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ d. Bases: i. Definition: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ ii. 2 examples: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ e. Buffer i. Definition: _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ ii. What pH do the fluids of most cells in our bodies like to maintain? ___________ f. Reflection of Reading: i. Points of Confusion: ii. Summary of Section: