Sem 1 Course Review
Physical Science Semester 1 Course Review Name__________________________ Date___________ Per___
Unit 1 & 2: Nature of Science (Throughout course) & Intro to Physical Science
Essential questions:
What are the different types of scientific investigations?
What are the components of a good scientific experiment?
What steps are involved in conducting scientific investigations?
What are the requirements for a valid hypothesis?
Has scientific knowledge changed over time?
What can change scientific knowledge?
Do changes in scientific knowledge occur often?
Key vocabulary:
Hypothesis
Independent variable
Dependent variable
Experimental group
Control group
Constants
Experiment
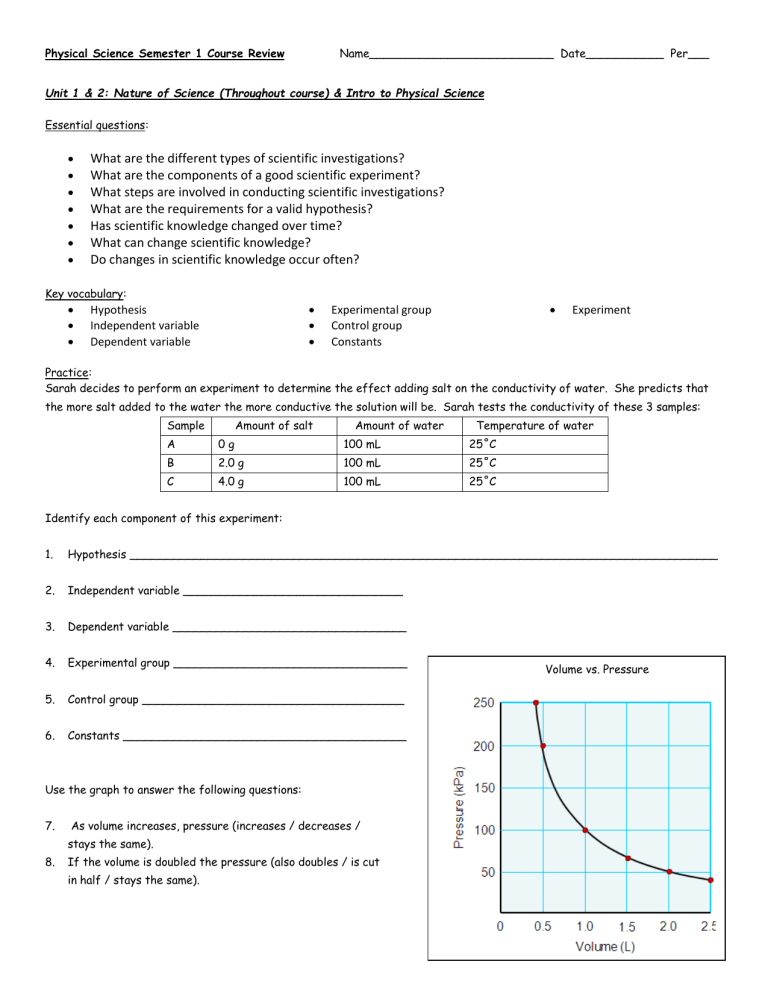
Practice:
Sarah decides to perform an experiment to determine the effect adding salt on the conductivity of water. She predicts that the more salt added to the water the more conductive the solution will be. Sarah tests the conductivity of these 3 samples:
Sample Amount of salt Amount of water Temperature of water
A
B
C
0 g
2.0 g
4.0 g
100 mL
100 mL
100 mL
25˚C
25˚C
25˚C
Identify each component of this experiment:
1.
Hypothesis ___________________________________________________________________________________
2.
Independent variable _______________________________
3.
Dependent variable _________________________________
4.
Experimental group _________________________________
5.
Control group _____________________________________
6.
Constants ________________________________________
Volume vs. Pressure
Use the graph to answer the following questions:
7.
As volume increases, pressure (increases / decreases / stays the same).
8.
If the volume is doubled the pressure (also doubles / is cut in half / stays the same).
1
Physical Science Semester 1 Course Review
Unit 3: Matter
Essential questions:
Name__________________________ Date___________ Per___
What are the four states of matter?
Why are the characteristics of each state of matter?
What is the difference between physical and chemical properties?
What is the difference between physical and chemical changes?
Identify examples of physical and chemical changes.
What is the difference between heat and temperature?
What are the types of phase changes and where would you find them on a heating / cooling curve?
What is the relationship between temperature and kinetic energy?
How is a heating curve used to relate phase changes, temperature, and kinetic energy?
What is the kinetic molecular theory of gases?
On a molecular level, why do substances change phases when energy is added or removed?
Key vocabulary:
Density
Physical change
Chemical change
Practice:
Temperature
Kinetic Molecular Theory
Heat
Kinetic energy
Phase change
1.
Identify the four states of matter on the following table and describe each of their volume and shape as definite or indefinite.
State of Matter
1.
2.
3.
4.
Volume (definite or indefinite) Shape (definite or indefinite)
2.
Identify which state of matter would be most commonly associated with each of the following properties: a.
High boiling and melting points b.
Low boiling and melting points c.
High density d.
Low density
3.
Identify each of the following properties as either chemical or physical. a.
Melting point b.
Density c.
Color d.
Reactivity e.
Flammability f.
Texture
4.
Identify each of the following changes as either chemical or physical. a.
Filtering water b.
Silver tarnishing c.
Food cooking on a stove d.
Water boils e.
Paper catches fire
2
Physical Science Semester 1 Course Review Name__________________________ Date___________ Per___
5.
What does temperature measure? _________________________________________________________________
6.
Convert 50˚C to Kelvin.
7.
Identify the four major phase changes and fill in the state change:
Phase Change
1.
State Conversion (From what state to what state)
__________________ _____________________
2.
__________________ _____________________
3.
4.
__________________ _____________________
__________________ _____________________
8.
State the Kinetic Molecular Theory. ________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________
9.
Sketch a heating curve and label the following parts: a.
Boiling phase change b.
Melting phase change c.
Freezing phase change d.
Only liquid is present e.
Gas and liquid are present f.
Period of time in which kinetic energy is constant
3
Physical Science Semester 1 Course Review Name__________________________ Date___________ Per___
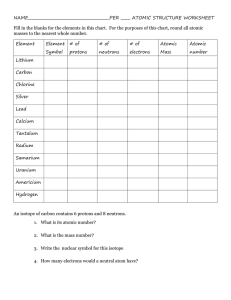
Unit 4: Atomic Structure
Essential questions:
What is an atom?
What are the three smaller subatomic particles that make up an atom?
Where are protons, neutrons, and electrons located in an atom?
What are the charges of protons, neutrons, and electrons?
Which subatomic particles are heaviest and which are lightest?
What overall charge does an atom have?
What is the relationship between numbers of electrons and protons in a neutral atom?
What subatomic particle is related to the atomic number of an element?
How can the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons be calculated when given atomic number and atomic mass?
Key vocabulary:
Neutral atom
Subatomic particles
Protons
Practice:
1.
What is an atom?
Neutrons
Electrons
Atomic number
Mass number
2.
Identify the three basic particles in the atom. Give their location, charge, and mass. (Fill in the table)
Particle Location Charge Mass (amu)
3.
Describe in words the modern model of an atom. ________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.
What information does the atomic number of an element give us? __________________________________________________
If an element has an atomic number of 15, how many protons and electrons would a neutral atom of that element have? _____
5.
What information does the mass number of an element give us? ___________________________________________________
If an element has a mass number of 35 and an atomic number of 17, how many protons, electrons, and neutrons would a
neutral atom of that element have? Protons = _______, Electrons = _______, Neutrons = _______
6.
Be able to determine the atomic number , atomic mass, number of protons, neutrons , and electrons for the following:
Element Atomic no. Mass number
No. of protons
No. of neutrons
No. of electrons
Mg 12 12 12 12
Cu
Br
Hg
Ba
29 64
80
137
35
80
56
120
56
4
Physical Science Semester 1 Course Review Name__________________________ Date___________ Per___
Unit 5: Periodic Table
Essential questions:
What information about an element is usually provided within each square on the periodic table?
What property is used to arrange elements on the periodic table?
What does the group number on the periodic table represent?
How is the position on the periodic table related to the chemical properties of an element?
How are the elements in a given group related?
Where are metals, nonmetals, transition metals, and metalloids located on the periodic table?
Key vocabulary:
Period
Group
Chemical symbol
Metal
Practice:
Nonmetal
Metalloid
Transition metal
Alkali metal
Alkaline earth metal
Halogen
Noble gas
1.
Be able to determine name of element, atomic number and atomic mass of an element by reading the periodic table.
11
Na
22.98977
2. The order of the elements on the periodic table is based upon which subatomic particle? _______________________________
3. What is the chemical symbol for each of the following elements?
Potassium _______
Cadmium _______
Gallium ________
Gold _________
Beryllium _______
Iron ________
Sodium _______
Nitrogen ________
4. Where are the following located on the periodic table? a) alkali metals b) alkaline earth metals c) nonmetals d) metalloids e) transition metals f) halogens g) noble gases
5
Physical Science Semester 1 Course Review Name__________________________ Date___________ Per___
5. Define period (series) of elements. What do they have in common? __________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6. Define group(family) of elements. What do they have in common? __________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
7. Why do the elements in a group all behave similarly? ______________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
8. Why are the alkali metals and the halogens very reactive? Why are the noble gases unreactive? ___________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
9. Look at the location of chlorine on the periodic table. Name 2 elements that would behave in a very similar manner to chlorine.
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Unit 6: Molecules & Compounds
Essential questions:
What is a chemical bond?
How is an ionic bond different from a covalent bond?
Identify elements in a compound from its formula.
What information do you need to consider in order to write the correct formula for a compound?
Identify a correct formula given elements from the periodic table.
What is the rule used for naming a binary compound composed of a metal bonded to a nonmetal?
What is the rule used for naming binary compounds composed of transition metals bonded to nonmetals?
What is the rule used for naming binary compounds composed of nonmetals bonded to other nonmetals?
Correctly match simple binary compound names to their formulas.
Key vocabulary:
Ionic bond
Covalent compound
Valence
Chemical formula
Molecule
Ionic compound
Outer shell
Ions
Compound
Binary compound
Covalent bond
Inner shell
Charge
Molecular formula
Practice:
1. Which electrons are involved in bonding? ___________________________________________
2. How many valence (outer shell) electrons does each of the following elements have?
Sodium ______ Nitrogen _______ Sulfur _______ Silicon ________
3. Why does sodium form an ion with a +1 charge? __________________________________________________________________
Why does oxygen form an ion with a -2 charge? __________________________________________________________________
4. Write formulas for the following compounds: a. magnesium chloride________________ e. calcium bromide________________
6
Physical Science Semester 1 Course Review b. aluminum fluoride _____________ c. nitrogen dioxide _____________________
Name__________________________ Date___________ Per___ f. iron (II) sulfide ___________ g. sodium chloride ______________ d. copper (II) oxide _________________ h. dinitrogen tetroxide ___________
5. In the formulas you wrote above, what do the subscripts indicate? ___________________________________________________
6. Name the following compounds: a. NBr
3
___________________________ h. Mg
3
N
2
____________________________ b. Fe
2
O
3
___________________________ c. LiF ___________________________ i. S
2
O ____________________________ j. KCl ____________________________ k. FeO ___________________________ e. NiCl
2
____________________________
7. What does the name diphosphorus pentoxide tell us? _____________________________________________________________
8. When Ca +2 and O -2 form a compound, what is the overall charge of the compound formed? _______________________________
9. When we are naming elements with a transition metal, why do we need to write a Roman numeral in the middle? ____________
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Unit 7: Chemical Reactions
Essential questions:
What are the main types of chemical reactions?
How can you identify in the laboratory that a chemical change has occurred?
Why and how is a chemical equation balanced?
What factors impact the rate of a chemical reaction?
What is an endothermic process?
What is an exothermic process?
Key vocabulary terms:
Chemical reaction
Reactant
Product
Precipitate
Synthesis
Decomposition
Single replacement
Double replacement
Law of Conservation of Mass
Concentration
Catalyst
Endothermic
Exothermic
Practice:
1.
Balance the chemical equation and identify the type of chemical reaction:
S = Synthesis D = Decomposition SR = Single replacement
______a. _____ N
2
+ _____ H
2
_____ NH
3
______ b. _____ Al + _____ HCl
_____ AlCl
DR = Double replacement
3
+ _____ H
2
______c. _____ FeS + _____ HCl
_____ FeCl
2
+ _____ H
2
S
______d. _____ N
2
+ _____ O
2
_____ N
2
O
______e. _____ HgO
_____ Hg + _____ O
2
7
Physical Science Semester 1 Course Review Name__________________________ Date___________ Per___
2.
In reaction (c) in the question above, which substances are products? _____________________
Which substances are reactants? _____________________
3.
Use the following equation to answer the questions: 2H
2
+ O
2
2H
2
O a.
If 4.0 g of H
2
reacts with 32 g of O
2
, how much water would be produced? _______________ b.
If 8.0 g of H
2
reacts and 72 g of H
2
O is produced, how much O
2
is consumed in the reaction? _______________
4.
List 3 ways to speed up the rate of a chemical reaction: a.
_____________________________________________________________________________________ b.
_____________________________________________________________________________________ c.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Unit 8: Acids & Bases
Essential questions:
What is the definition of an acid? Base?
What are the properties of acids? Bases?
How can you test if a substance is an acid, base, or neutral?
What are some common acids and bases?
What is pH? What is the pH range of an acid? Of a base? Of a neutral?
What happens when an acid and base react?
Key vocabulary:
Acid
Base
Neutral
Hydronium ion
Hydroxide ion
Concentration
Indicator pH
Practice:
1.
Classify each of the following chemicals as an acid or base:
Acid-base neutralization reaction
Salt
NaOH ______________ HCl ______________ H
2
SO
4
______________ NH
3
______________
2.
Label the following on the pH scale below: a.
range of the scale that represents acids b.
range of the scale that represents bases c.
range of the scale that represents neutral substances d.
range of the scale where the hydronium ion concentration is greater than the hydroxide concentration ([H
3
O + ] > [OH ]) e.
range of the scale where the hydroxide ion concentration is greater than the hydronium concentration ([OH ] > [H
3
O + ])
0________________________________________7________________________________________14
3.
Give an example of an acid-base neutralization reaction. What are the products of this type of reaction?
8
Physical Science Semester 1 Course Review Name__________________________ Date___________ Per___
Unit 9: Nuclear Chemistry
Essential questions:
What is nuclear fission? What is nuclear fusion?
What is alpha, beta and gamma radiation?
What happens in a radioactive decay?
How are nuclear reactions balanced?
What is the difference between a chemical reaction and a nuclear reaction?
How can radioactive half-life be used to date fossils?
What is a molecular clock? How are molecular clocks used to show evolutionary relationships?
Key vocabulary:
Fission
Fusion
Alpha radiation
Practice:
Beta radiation
Gamma radiation
Radioactive decay
1.
Compare and contrast nuclear fission and nuclear fusion:
Radioisotope
Half-life
Molecular clock
Nuclear fission Nuclear fusion
2.
Compare and contrast alpha, beta and gamma radiation:
Alpha radiation Beta radiation Gamma radiation
3.
Yucca Mountain is the proposed site for a national repository for high level nuclear waste. Identify 3 characteristics of this site that make it suitable for this purpose: a.
______________________________________________________________________________________________ b.
______________________________________________________________________________________________ c.
______________________________________________________________________________________________
4.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using nuclear power plants to generate electricity?
Advantages Disadvantages
9
Physical Science Semester 1 Course Review Name__________________________ Date___________ Per___
5.
Compare and contrast nuclear reactions and chemical reactions:
Nuclear reactions
6.
Balance the following nuclear reactions:
Chemical reactions a.
99
43
Tc _____ + 0
-1 e d.
239
93
Np
239
94
Pu + _____ b.
239
94
Pu 4
2
He + _____ c.
_____
4
2
He + 208
81
Tl e.
42
19
K 0
-1 e + _____ f.
1
1
H + 3
1
H _____
10