5784-C5 INTERVENTION ACTIVITIES - 230.25 KB
advertisement
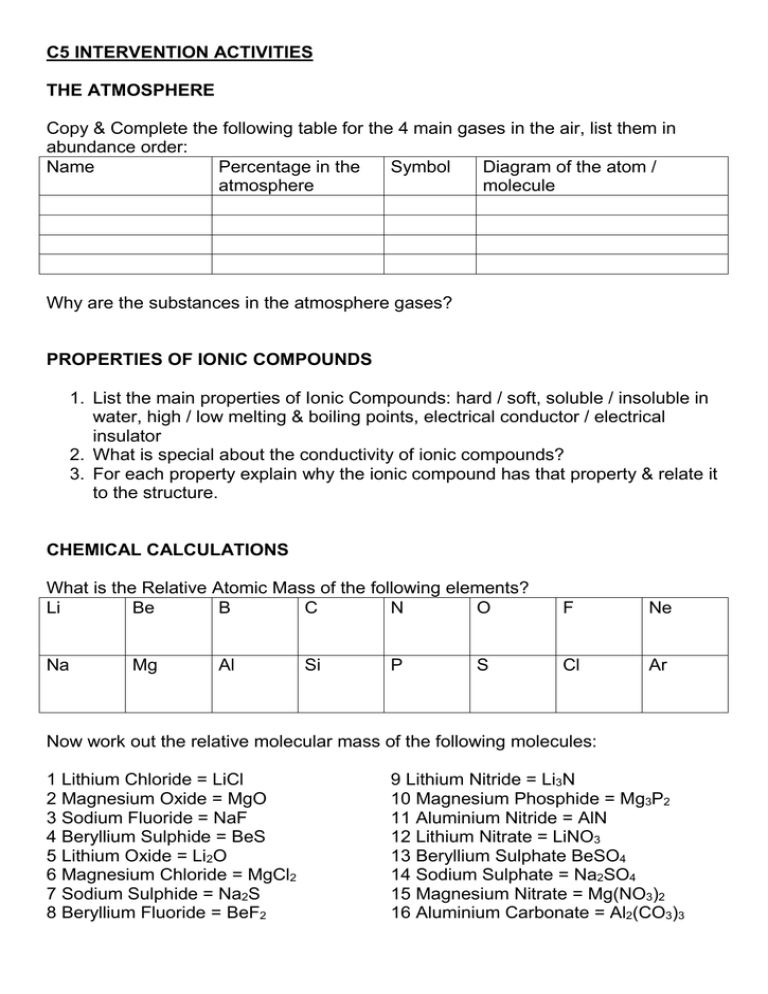
C5 INTERVENTION ACTIVITIES THE ATMOSPHERE Copy & Complete the following table for the 4 main gases in the air, list them in abundance order: Name Percentage in the Symbol Diagram of the atom / atmosphere molecule Why are the substances in the atmosphere gases? PROPERTIES OF IONIC COMPOUNDS 1. List the main properties of Ionic Compounds: hard / soft, soluble / insoluble in water, high / low melting & boiling points, electrical conductor / electrical insulator 2. What is special about the conductivity of ionic compounds? 3. For each property explain why the ionic compound has that property & relate it to the structure. CHEMICAL CALCULATIONS What is the Relative Atomic Mass of the following elements? Li Be B C N O F Ne Na Cl Ar Mg Al Si P S Now work out the relative molecular mass of the following molecules: 1 Lithium Chloride = LiCl 2 Magnesium Oxide = MgO 3 Sodium Fluoride = NaF 4 Beryllium Sulphide = BeS 5 Lithium Oxide = Li2O 6 Magnesium Chloride = MgCl2 7 Sodium Sulphide = Na2S 8 Beryllium Fluoride = BeF2 9 Lithium Nitride = Li3N 10 Magnesium Phosphide = Mg3P2 11 Aluminium Nitride = AlN 12 Lithium Nitrate = LiNO3 13 Beryllium Sulphate BeSO4 14 Sodium Sulphate = Na2SO4 15 Magnesium Nitrate = Mg(NO3)2 16 Aluminium Carbonate = Al2(CO3)3 TESTING FOR IONIC COMPOUNDS This is an extract from the June 2012 C4 C5 C6 exam paper: Use this information to explain how you would test unknown solutions that were suspected to contain: 1 Copper (II) Sulphate 2 Iron (III) Chloride 3 Calcium Carbonate For each test explain what you would do & what you would see if these substances were present. MATERIALS FROM THE EARTHS CRUST 3 Giant covalent structures we study are: 1 Diamond 2 Silicon Dioxide & 3 Graphite Here are diagrams of their structures: A B C Here are some properties of these substances: Electrical conductor / electrical insulator Hard / Soft High / Low Melting & Boiling Points Soluble / Insoluble in water Link the names with the diagrams of the structure of these substances. State whether they are an element or a compound & explain how you know. Describe the structure of each & link it to the properties of the substance. Give some uses of these substances. What is the difference between a rock & an ore? Give some examples of ores & the metals we can get from them. We mine & quarry rock to extract the ores we need to produce metals. How do these activities affect the environment? ELECTROLYSIS Copy the diagram into the middle of a page use these keywords to label it: Keywords: Electrodes Anion Cation Cathode Anode Electrolyte → or ← Current flow Anions move to the anode/cathode Cations move to the anode/cathode Metal deposits on the anode/cathode In your own words explain what’s happening. COVALENT BONDING Explain (using text & diagrams) how the following diatomic gas molecules are formed: 1 Hydrogen 2 Oxygen 3 Nitrogen 4 Carbon dioxide 1. What is a diatomic molecule? 2. Which of these 4 gases in NOT present in the air? Which property of this gas helps you to answer this question? 3. Why do atoms react? 4. Which gas, also present in the air, does NOT react? Why does this gas NOT react? METALLIC BONDING With reference to the following diagrams explain metallic bonding: Explain how the structure you describe accounts for the general properties of metals: 1 They all conduct an electric current 2 They are all bendy (malleable) REDOX 1. What happens in an oxidation reaction? (Give 2 definitions) 2. What happens in a reduction reaction? (Give 2 definitions) 3. Why are these reactions called REDOX reactions? In this reaction: Fe2O3 + CO → Fe + 4. What is being oxidised? 5. What is being reduced? 6. Balance the equation. CO2