Plant Classification
advertisement
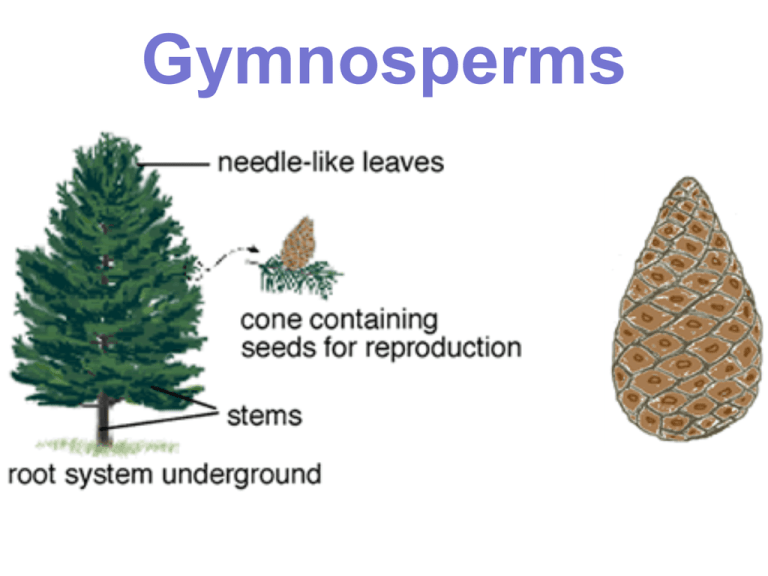
Gymnosperms Group 3: Seed producing, Vascular Plants • Gymnosperms – Cycads – Ginko – Conifers • Angiosperms Seeds and their advantages • 1) Seed plants don’t depend on water to reproduce – Pollen (contains sperm) carried by wind/animals – Zygote hardens into a seed • 2) Embryo has… – Nourishment: Nutrients inside feed embryo – Protection: Hard shell • 3) Allow dispersal – Carried by wind, water, animals Some seeds are “dispersed” by “wings” animals Some seeds have Seeds and their advantages • 1) Seed plants don’t depend on water to reproduce – Pollen (contains sperm) carried by wind/animals – Zygote hardens into a seed • 2) Embryo has… – Nourishishment: Nutrients inside feed embryo – Protection: Hard shell • 3) Allow dispersal – Carried by wind, water, animals Seeds and their advantages • 1) Seed plants don’t depend on water to reproduce – Pollen (contains sperm) carried by wind/animals – Zygote hardens into a seed • 2) Embryo has… – Nourishishment: Nutrients inside feed embryo – Protection: Hard shell • 3) Allow dispersal – Carried by wind, water, animals Group 3: Seed producing, Vascular Plants • Type 1: Gymnosperms • Needle-like leaves (reduces water loss) • Common to lumber industry • Seeds enclosed in cones – Male cones: produce pollen (pollen cone) – Female cones: produce eggs (seed cone) • Zygote hardens into seed (protected inside cones) • Ex: Evergreen, Pine, Redwood, Cedar Conifer Life Cycle . Z e • Sporophyte phase (dominant) – Cones grow on tree – Male cones • Spores created by meiosis & released • Spores develop into pollen – Female cones • Spores created by meiosis • Male pollen lands on female cone • Pollen tube grows towards egg • Sperm travels down pollen tube • Spore hardens into seed • Seed released & grows into new sporophyte Conifer Life Cycle • Sporophyte phase (dominant) – Cones grow on tree – Male cones • Spores created by meiosis & released • Spores develop into pollen – Female cones • Spores created by meiosis – Egg forms inside spore • Male pollen lands on female cone • Pollen tube grows towards egg • Sperm travels down pollen tube • Spore hardens into seed • Seed released & grows into new sporophyte 1) Male and female seed cones grow on adult sporophytes 2) Pollen grains released from the male seed cones -- Pollen is the male gametophyte Let’s zoom into the female seed cone… 3) Pollen grain sticks to the female ovule 4) Pollen tube grows from the male spore 5) Two sperm travel into female spore - one fertilizes the egg 6) Diploid embryo develops inside female cone (sporophyte stage restarts) 7) After seeds harden, the cone reopens and the seeds are released 8) Seed will land Ground 9) Seedling grows into (sporophyte)…the cycle repeats Ground female male Plant Life Cycle Comparisons ` Sporophyte Gametophyte Dominant? Moss Stalk with cup at tip, which is where spores are produced. More familiar, carpetlike plant that produces specialized gametes XX - Archegonium XY - Antheridium GAMETOPHYTE Fern More familiar, leafy plant with clusters of spore producing sacs (sori) Haploid plant body (prothallus) is size of a finger nail, produces both male and female parts SPOROPHYTE Conifer (Gymnosperm) More familiar- like pine trees, produces male and female cones that produce spores Male gametophytes are pollen grains sperm Female gametophytes are microscopic eggs SPOROPHYTE Review 1) Name three advantages of seeds. 2) Which structure will protect gymnosperm seeds? 3) What do male cones produce? 4) What do female cones produce? 5) What is created when the sperm and egg fuse: sporophyte or gametophyte?