Unit 2 Lesson 3 Study Notes
advertisement

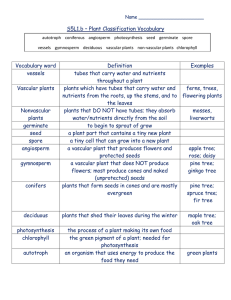
Unit 2, Lesson 3 All Plants: Introduction to Plants (Study Review) BIG IDEAS: are Multicellular (Eukaryotic) can Reproduce either Sexually or Asexually depending on what type of plant they are. All Plant Cells: 1. have a nucleus control center for the cell contains a chemical called DNA 2. have a cell wall hard and rigid completely surrounds the plant cell offers protection from the weather gives the plant support making it able to grow tall 3. have Chloroplasts these contain a chemical called Chlorophyll this is where Photosynthesis takes place Chlorophyll turns sunlight into sugar that is used for Energy Chlorophyll makes the plant green. 4. have a Vacuole vacuoles are storage tanks the Large Central Vacuole stores an emergency water supply Plants can be placed into 2 categories: Vascular / Nonvascular Vascular plants have veins that allow them to have the source of water (the ground) far from where it is needed. (leaves, branches/ stem) Examples of Nonvascular plants are: Moss, Liverworts, Hornworts. Examples of Vascular plants are Ferns and Horsetails. Other Vascular plant examples are trees, celery, and other tall plants. Almost all plants you see are Vascular plants. All Nonvascular plants and some Vascular plants do not grow from seeds. They grow from spores. Spores are the single-celled reproductive unit of nonflowering plants, bacteria, fungi, and algae. Most vascular plants form seeds. If the plant has a flower and a seed is formed and fruit forms around the seed, then the plant is called an Angiosperm. Most plants fall into this category. If NO fruit forms around the seed, it is called a Gymnosperm. Pine trees are typical examples of a Gymnosperm. The seed is usually found in a pine cone. Plants Nonvascular Vascular Seeds Angiosperm (Fruit) Spores Gymnosperm (NO fruit) Spores