Chp 18: Physical Geography of Africa
advertisement

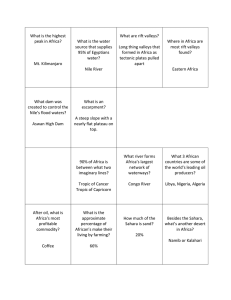
Chp 18: Physical Geography of Africa Take Five… Complete the Skill Builder questions on pg 415 Landforms of The African Continent Plateau over most of the continent 1,000 feet above sea level “plateau continent” Water Basins (depressions) 625 miles wide 5,000 feet deep Ex: Chad, Sudan, Congo, & Djouf Basins Rivers Nile=Longest river in the world 4,000 miles Provides Irrigation waters 95% of water resource for Egypt Nile River Valleys, Mountains, & Lakes (Oh My…) Rift Valleys—caused by continental separation Lake Tanganyika—longest freshwater lake in the world Lake Victoria—world’s 2nd largest freshwater lake Volcanic mountains Mount Kenya Mount Kilimanjaro--Africa’s Highest Mtn. Escarpment—steep slope with plateau on top The Great Escarpment in Southern Africa Wally Points… What is the problem associated with rift valleys in Africa? Africa’s Natural Resources Rich mineral resources Gold (30% of world’s resources); Platinum (80%) Cobalt; Copper; Diamonds; Chromium (used in production of stainless steel) Oil—Libya, Nigeria, Algeria (world’s leading petroleum countries); Angola & Gabon also rich in oil resources Is not rich in economic development Exploited by European imperialist countries Africa slow to develop infrastructure and industries Gold Production Take Five… What do African countries, such as Angola spend the oil money on? In class assignment…pg 419 Complete the Economic Map Activity on pg 419 In class assignment Read Chp 18 Section 3 and make a list of pros and cons for the building of the Aswan Dam Then, write a paragraph either defending or supporting the Dam African Climate and Vegetation Deserts Kalahari Namib Sahara=largest desert in the world 3,000 miles Temperatures over 100 during the day and freezing at night Only 2 million Africans live here Aquifers=underground water resources Oasis Tropics of Africa? 90% of continent lies between the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn Kalahari Sahara Native Peoples of the Sahara Take Five… From the youtube video—how did the Bushmen survive without a lot of rainfall? Where did they live? The Gods Must Be Crazy… Oasis in Kenya Rainfall in Africa Mediterranean climates in Northern and Southern Africa Rainfall N =(Dec & Jan) & S = (June & July) East Africa Periodic droughts Central Africa Rainforest=throughout the year ½ of Africa is the tropical savannah w/ 2 rainy seasons each year Western Africa Adequate rainfall Vegetation Tropical grasslands cover the majority of African landscapes Serengeti Plain Rainforest in the Central regions of Africa Congo Basin Variety of plant and animal life Canopy Problems with slash/burn techniques ½ of original rainforest destroyed Serengeti Plain Congo Basin Interesting and Unusual Plant and Animal Life in Africa Human-Environment Interaction Desertification of the Sahel Causes Overgrazing of livestock Farming and increased soil erosion Wind erosion Drilling for water leads to increased levels of salt which prevents growth Increased population Effects Destroying forests and rainforests Human-Environment Interaction Oil Resources in Nigeria World’s 6th largest oil exporter Nigeria borrowed money against oil profits for internal improvements Oil prices dropped leaving Nigeria in debt to foreign countries Effects of Nigerian Oil Industry Mismanagement of money, corruption of government officials and decline of oil prices has injured the Nigerian economy 400+ oil spills Bandits sabotaging oil pipelines with consent of the government New leadership-President Olusegun Obasanjo (1999) pledged to fire corrupt government employees and clean up corruption and mismanagement Controlling the Nile River Periods of drought/flooding Flooding provided silt for fertile soils along the banks of the Nile—but also destroyed homes/farms etc Egyptians tried canals and dams to stop the environmental problem Aswan High Dam (1970) Created Lake Nasser—300 mile lake Regulates water flow to farming regions Aswan Dam Aswan High Dam Aswan High Dam Lake Nasser Problems associated with the Aswan Dam Relocation of Nubian population Relocation of artifacts from the Temple Abu Simbel Destruction of some Egyptian artifacts Decreased fertility without seasonal floods Drains installed to flush out the salt deposits which would have naturally been removed with seasonal flooding Increased in mosquito born diseases (malaria) Evaporation of Lake Nasser Temple of Abu Simbel In Class Assignment… Make a chart of the 5 different regions of Africa include: primary climate of the region, countries in the region, imperialistic nations taking over the region, government of the region and major natural resources of the region. Take Five… Complete the Skill Builder Questions on pg 431 Chp 19: From Human Beginnings to New Nations East Africa North Africa West Africa Central Africa Southern Africa East Africa “cradle of humanity” Evidence of humanoids from 2 mill years ago Burundi, Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Rwanda, Seychelles, Somalia, Tanzania, and Uganda Northern Africa East African Trade 100s AD-Trade along the Red Sea & Indian Ocean-Aksum (Ethiopia) Center for Christianity Taking advantage of Monsoon winds 600s AD-Kilwa (Tanzania) emerges as a new trading center with middle east East Africa= cultural crossroads Aksum Colonization and Imperialism Europe interested in rich natural resources Berlin Conference 1884-1885 Dividing Africa among European rulers African chiefs were not invited European country must illustrate and maintain control in a region Division without regard to cultural, ethnical or any other African considerations Colonization… By 1914 only Liberia & Ethiopia was free from European control U.S. in Liberia Ethiopia defeated the Italians in 1896 Take Five… What happens to African countries, after receiving their independence from European countries? Ex? Problems associated with ending colonization Political instability Economic hardship Ethnical disputes Ex: Rwanda’s Civil War in 1990 East African Economies Farming 70% rural Cash crops: coffee, tea, sugar Dependent on world market Tourism Wildlife parks Game reserves Kenyan Wildlife Reserve Maintaining East African Traditions 160 different ethnic groups 2 largest ethnic groups Masai Mainly traditional farmers Kikuyu Farmers as well as urban workers The Mau Mau How East Africans Cope with the AIDS Pandemic HIV infections Spread of the disease Tradition vs modern medicine Economy Population decline Orphans North Africa Countries of North Africa: Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, Sudan & Tunisia Life along the Nile river The “gift of the Nile” Seasonal floods Prosperous agriculture Egyptian Pharaohs 3300 BC earliest Egyptian civilizations 3100 BC unification of Egypt Artifacts and gains from Egyptians Pyramids Papyrus Advances in Medicine Pyramids The Sphinx Papyrus Take Five… Complete the Skill Builder questions on pg 439 Islam in North Africa Fall of the Egyptians to the Romans/ Byzantine Empire Northern African invaded numerous times By 632 AD Muslims spread Islam to Northern Africa 750 AD Muslims controlled most of N. Africa Economies of Northern Africa Agriculture Cash crops Mining Oil Algeria= major export Libya 99% of exports Labor shortages African Souks Culture… Souks Protest music Rai—Algerian resentment toward French colonization Banning and criticizing rai Women in Northern Africa Slow to have reforms for women Polygamy Tunisia 7% parliament 9 % business owners Take Five… Complete the Skill Builder questions on pg 442 West Africa Countries of Western Africa: Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, Chad, Cote d’Ivorie, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierre Leone, and Togo West Africa Wally Points… Why would people want to trade gold for salt? The importance of trade Location, location, location 200 AD trade between West Africa and the Sahara Gold for salt trade Good ports, open to European traders by 1300’s Stateless societies Many African states lived as extended family clan groups without official leadership other than the patriarch of the family Blood money Polygamy Polytheistic Take Five… Complete the Skill Builder questions on pg 443 Economies of West Africa Exports Gold, diamonds, magnesium & bauxite Dependent upon world market Sierra Leone One of the worst economic countries in West Africa Civil war, instable governments and uneducated population Culture of West Africa Asasia-cloth historically created for royalty by the Ashanti people of Ghana Benin bronzes Music Elements of jazz, blues, reggae Kora=cross between the a lute and a harp Wally Points… What is significant about a father giving his son a stool as a present in Ashanti culture? Asasia Benin Bronze Works Central Africa Countries of Central Africa: Cameroon, Central African Republic, Dem. Rep. of Congo, Rep. of Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon and Sao Tome and Principe European colonization Begin in Central Africa Importance of the slave trade Willingness of African leaders to trade Portuguese island of Sao Tome The “Gold Coast” The slave trade Competing tribes selling prisoners of war to Europeans Portuguese and Dutch The middle passage Tight and loose packing Fear of depopulation Triangle Trade Routes Middle Passage Tight Packing European Colonization Role of King Leopold II of Belgium Rubber workers and beginning of European colonization within the interior Central Africa colonized primarily by Belgium and France Independence in the 1960’s Central African Culture Reflections against colonization and retaining African culture Ex: Congolese—culture above the West Picasso—Fang sculpture Central African Education Focusing on education to improve workforce Less than ½ 16-20 year olds in SubSaharan Africa attend school Language barriers (700+ languages spoken) Shortage of teachers Hopeful for the future Southern Africa Countries of Southern Africa: Angola, Botswana, Comoros, Lesotho, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, S. Africa, Swaziland, Zambia and Zimbabwe Southern Africa Take Five… Complete the Skill Builder questions on pg 454 Mutapa Empire Mwene Mutapa Economy based on Gold trade Portuguese colonization Imperialism and Colonization South Africa The Zulu Dutch colonization (1600’s) Boer’s-Dutch farmers British imperialism Defeat the Zulu Defeat the Boers Zulu Boers KhoiKhoi and San People of South Africa Apartheid White minority controlled government, economy, everything 75% black majority controlled nothing Separation of the races Nelson Mandela Jailed from 1964-1982 House arrest from 1982-1990 Elected President in democratic election of 1994 Nelson Mandela Economies of Southern Africa Sanctions during Apartheid Gaps between the rich and poor—based on race and ethnicity Ex: Botswana resources (3rd largest diamond producer) Mismanagement of money Lack of agricultural goods Unequal distribution of wealth Valuable Affects of AIDS in Southern Africa 25% of all adults infected in Zimbabwe and Botswana Reduction of labor Orphans Chp 20 Today’s Issues Africa after colonization Political instability Economic uncertainty Lack of education in some areas Tribal warfare (Civil war) Mismanagement of resources Lacking infrastructure & technology Indebtedness Take Five… Do you think that African countries should have their debt forgiven or reduced? Why or why not? Reducing debt and raising standard of living Debt forgiveness Regional cooperation to promote trade Ex: Economic Community of West African States Cash crops to diversification Education Diseases Cholera Malaria Sleeping Sickness Smallpox AIDS Tuberculosis Ebola virus Why so proliferate? Lack of clean drinking water Mosquitoes—no netting Lack of education Lack of medicine Lack of doctors Assistance… World financial assistance World government agencies Global Fund for Children’s Vaccines Peace Corps Education Public health Private charity Mental maps Look at your own maps then put them away and find the following locations— are you right? Nigeria Nile River Johannesburg Sahara Algeria Kalihari Lake Victoria Congo R Sudan Egypt Somalia Botswana