Regulating the cell cycle
advertisement
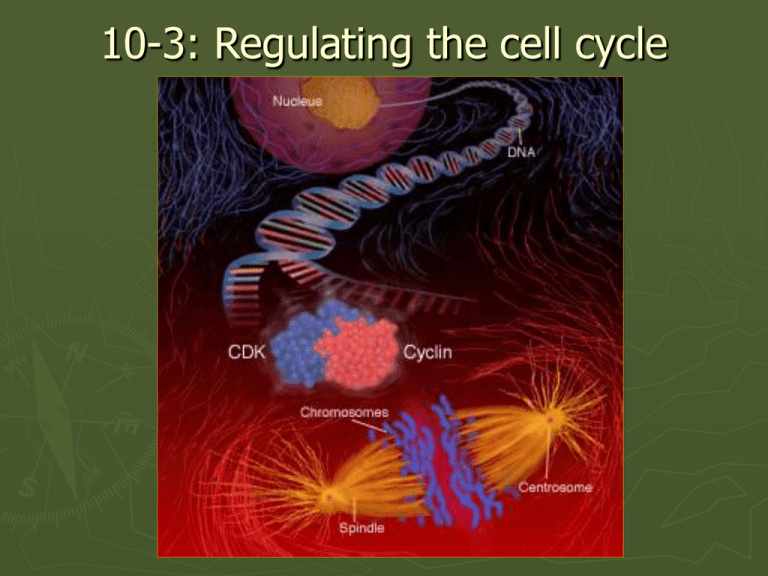
10-3: Regulating the cell cycle Specialized cells divide at different rates Some cells never divide Cardiac: cannot divide Smooth muscle: can divide Intestine: 1-2 days, can divide Nerve cell: cannot divide RBC: 120 days, cannot divide Nerve cell: brain Red blood cell Cardiac cells Smooth muscle Small intestine Controls on cell division ► ► ► ► Not all cells in the body divide at the same rate Cells in a petri dish will divide until they fill the dish, then they stop. If cells are removed, they’ll grow until the space is filled again. Controls on cell division can be turned on and off. Cell cycle regulators ► The protein cyclin regulates the timing of the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells. When present, cyclin triggers cell division. Internal regulators ► Proteins Different cyclins active at phases of the cell cycle that respond to internal events in the cell. ► Some make sure that the cell doesn’t enter mitosis until the DNA is replicated ► Another makes sure that chromosomes are attached to the spindle before anaphase. External regulators ► Proteins that respond to events outside the cell. ► Direct the cell to speed up or slow down the cell cycle. ► Growth regulators: important in embryos, for healing wounds Cat embryo Rubber bullet wound Inhibitors on cell surfaces cause cells to slow or stop division Uncontrolled cell growth ► ► ► ► ► Cancer is a disease of the cell cycle Cancer cells don’t respond to the signals that regulate growth. Leads to uncontrolled cell growth. Causes: viruses, tobacco, radiation exposure Form masses of cells: tumors Melanoma: skin cancer Oral cancer Stem cells ► Unspecialized cells that have the ability to turn into any kind of cell. ► Could replace damaged cells of brain, nervous system. Human stem cell stem cell controversy ► ► Stem cells are produced from human embryos, and are destroyed when used for research Raises moral and ethical questions as to their use: Is a fertilized egg a human being? Stem cells in umbilical cord blood Human blastocyte: 100 cells Adult stem cells ► Adult stem cells are found in bone marrow ► Future possibility: a person’s own stem cells could be used to heal previously untreatable conditions: spinal cord injury, grow new liver tissue, replace heart valves, reverse the effects of diabetes.