Seed Plant Reproduction: Gymnosperms & Angiosperms Life Cycles
advertisement

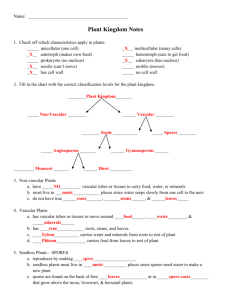
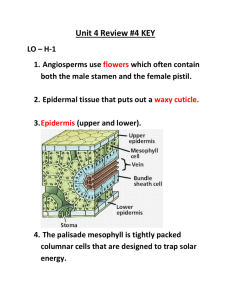
Ch 24- Reproduction of Seed Plants • Life Cycle of Gymnosperms – Reproduction takes place in cones- produced by mature sporophyte plant • 2 types of cones- pollen cones and seed cones – Pollen- male – Seed- female – Ovules- base of seed cone where female gametophytes develop • Pollen tube- structure that contains 2 haploid sperm nuclei, one sperm disintegrates and other fertilizes egg Structure of Flowers • Flowers are reproductive organs- composed of sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels • Sepals- outermost circle of flower parts, encloses bud, protects the flower while it is developing • Petals- brightly colored structure just inside the sepals, attracts insects and other pollinators • Stamen- male part of flower, made up of anther and filament • Filament-long, thin structure that supports an anther • Anther- flower structure where haploid male gametophytes are produced • Carpels- innermost part of flower that produces female gametophyte • Ovary- contains ovules from which female gametophytes are produced • Style- narrow stalk of the carpel in flower • Stigma- sticky portion at top of style where pollen grains land Life Cycle of Angiosperms • Reproduction takes place within flower- the seeds develop inside protective structures following pollination and fertilization • Most gymnosperms and some gymnosperms are wind pollinated • Most angiosperms are pollinated by animals • Fertilization in angiosperms – One sperm fuses with egg to form zygote – Second sperm fuses with two polar nuclei to form endosperm- food rich tissue that nourishes the seed – Double fertilization Sec 2- Seed Development/Germination • What is a fruit? – Ripened ovary that contains angiosperm seeds, any seed that is enclosed within its embryo wall – As angiosperm seeds mature, ovary walls thicken to form fruit – Apples, grapes, strawberries – Peas, corn, rice • How are seeds dispersed? – By animals, wind, water • What type of seeds are dispersed by animals? By wind and water? • What factors influence dormancy and germination? – Temperature and moisture • Dormancy- period where plant is alive but not growing – Varies between plants • Germination- early growth stage of plant embryo – Seed absorbs water causing it to swell and crack open